Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the prostate gland?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the prostate gland?
- Produces alkaline fluid that aids sperm motility (correct)
- Secretes enzymes that digest pathogens
- Absorbs nutrients from seminal fluid
- Stores sperm until ejaculation
Which change in prostate tissue leads to the development of BPH?
Which change in prostate tissue leads to the development of BPH?
- Atrophy of stromal tissue
- Dysplasia of prostate cells
- Metaplasia of epithelial cells
- Hyperplasia of stromal and epithelial cells (correct)
Which of the following are clinical manifestations of BPH? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following are clinical manifestations of BPH? (Select all that apply)
- Urinary retention (correct)
- Weak urinary stream (correct)
- Urinary urgency (correct)
- Nocturia (correct)
- Polyuria
An older male patient reports difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and nocturia. What would the nurse suspect based on these symptoms?
An older male patient reports difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and nocturia. What would the nurse suspect based on these symptoms?
Which mechanism leads to urinary retention in patients with BPH?
Which mechanism leads to urinary retention in patients with BPH?
A nurse is assessing a patient suspected of having BPH. Which findings would support this diagnosis? (Select all that apply)
A nurse is assessing a patient suspected of having BPH. Which findings would support this diagnosis? (Select all that apply)
The nurse notes bladder distention and reports of dribbling urine. Which pathophysiological change is most likely occurring?
The nurse notes bladder distention and reports of dribbling urine. Which pathophysiological change is most likely occurring?
Why might a patient with BPH develop a urinary tract infection?
Why might a patient with BPH develop a urinary tract infection?
A patient presents with lower abdominal pain and a sense of incomplete bladder emptying. Which diagnostic test would the nurse expect the provider to order first?
A patient presents with lower abdominal pain and a sense of incomplete bladder emptying. Which diagnostic test would the nurse expect the provider to order first?
A patient with BPH has a distended bladder and reports hesitancy. Post-void residual urine is >200 mL. What does this most likely indicate?
A patient with BPH has a distended bladder and reports hesitancy. Post-void residual urine is >200 mL. What does this most likely indicate?
Which lab test is ordered to help rule out prostate cancer when evaluating a patient with BPH symptoms?
Which lab test is ordered to help rule out prostate cancer when evaluating a patient with BPH symptoms?
Why is a urinalysis ordered for a patient with suspected BPH?
Why is a urinalysis ordered for a patient with suspected BPH?
Which of the following medications are used to manage symptoms of BPH? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following medications are used to manage symptoms of BPH? (Select all that apply)
A patient newly prescribed tamsulosin (Flomax) reports feeling dizzy when standing. What is the most appropriate nursing action?
A patient newly prescribed tamsulosin (Flomax) reports feeling dizzy when standing. What is the most appropriate nursing action?
A nurse is teaching a patient about finasteride. Which statement indicates understanding?
A nurse is teaching a patient about finasteride. Which statement indicates understanding?
A patient on both finasteride and tamsulosin reports improvement in urinary stream. What does this indicate?
A patient on both finasteride and tamsulosin reports improvement in urinary stream. What does this indicate?
The nurse is assessing a patient's risk for medication side effects. Which findings would increase the risk for complications with alpha-blockers? (Select all that apply)
The nurse is assessing a patient's risk for medication side effects. Which findings would increase the risk for complications with alpha-blockers? (Select all that apply)
A patient taking finasteride is concerned about sexual side effects. What is the nurse's best response?
A patient taking finasteride is concerned about sexual side effects. What is the nurse's best response?
How do 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help treat BPH?
How do 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help treat BPH?
Which finding would indicate that BPH medications are effective?
Which finding would indicate that BPH medications are effective?
What is the most common surgical procedure performed to relieve symptoms of BPH?
What is the most common surgical procedure performed to relieve symptoms of BPH?
What is the purpose of continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) following a TURP?
What is the purpose of continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) following a TURP?
Which of the following are complications that can occur following a TURP procedure? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following are complications that can occur following a TURP procedure? (Select all that apply)
A post-TURP patient complains of a burning sensation in the hands and face, restlessness, and headache. What condition should the nurse suspect?
A post-TURP patient complains of a burning sensation in the hands and face, restlessness, and headache. What condition should the nurse suspect?
During CBI, the nurse notes the outflow is significantly less than the inflow. What is the priority nursing action?
During CBI, the nurse notes the outflow is significantly less than the inflow. What is the priority nursing action?
A patient's sodium drops to 125 mEq/L post-TURP. Which symptom would you expect?
A patient's sodium drops to 125 mEq/L post-TURP. Which symptom would you expect?
Which nursing interventions are appropriate to monitor or prevent complications related to TURP surgery? (Select all that apply)
Which nursing interventions are appropriate to monitor or prevent complications related to TURP surgery? (Select all that apply)
The nurse is educating a patient post-TURP. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
The nurse is educating a patient post-TURP. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
A patient has reddish-pink urine in the catheter bag 24 hours post-TURP. What is the appropriate nursing action?
A patient has reddish-pink urine in the catheter bag 24 hours post-TURP. What is the appropriate nursing action?
After TURP, a patient reports an urgent need to void despite having a catheter in place. What should the nurse assess first?
After TURP, a patient reports an urgent need to void despite having a catheter in place. What should the nurse assess first?
Which complication is considered the most common and most serious immediately after a TURP?
Which complication is considered the most common and most serious immediately after a TURP?
Why is it important to encourage coughing and deep breathing exercises post-TURP?
Why is it important to encourage coughing and deep breathing exercises post-TURP?
Which post-op instructions should be included in patient teaching after a TURP procedure? (Select all that apply)
Which post-op instructions should be included in patient teaching after a TURP procedure? (Select all that apply)
A post-op TURP patient asks why he's experiencing cloudy urine with small clots. What is the nurse's best response?
A post-op TURP patient asks why he's experiencing cloudy urine with small clots. What is the nurse's best response?
A nurse is preparing to remove a 3-way Foley catheter from a post-TURP patient. What is the priority action before removal?
A nurse is preparing to remove a 3-way Foley catheter from a post-TURP patient. What is the priority action before removal?
A nurse is evaluating a patient post-TURP. Which finding indicates a potential complication?
A nurse is evaluating a patient post-TURP. Which finding indicates a potential complication?
Which nursing actions help evaluate the effectiveness of BPH or TURP treatment? (Select all that apply)
Which nursing actions help evaluate the effectiveness of BPH or TURP treatment? (Select all that apply)
What is the primary reason a post-op TURP patient is instructed to avoid NSAIDs?
What is the primary reason a post-op TURP patient is instructed to avoid NSAIDs?
A patient post-TURP has stable vital signs, mild bladder discomfort, and clear urine. What should the nurse include in discharge instructions?
A patient post-TURP has stable vital signs, mild bladder discomfort, and clear urine. What should the nurse include in discharge instructions?
A patient is discharged home with instructions to report any signs of infection. Which symptom should they be taught to recognize and report?
A patient is discharged home with instructions to report any signs of infection. Which symptom should they be taught to recognize and report?
Flashcards
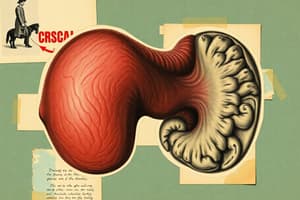
Primary function of the prostate gland?
Primary function of the prostate gland?
The prostate secretes a milky, alkaline solution into the urethra that aids sperm motility and neutralizes the acidic vaginal environment.
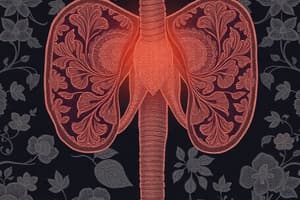
Tissue change leads to BPH development?
Tissue change leads to BPH development?
BPH is characterized by hyperplasia (increase in number) of both stromal and epithelial cells, forming nodules that compress the urethra.
Clinical manifestations of BPH?
Clinical manifestations of BPH?
BPH leads to urinary outflow obstruction causing weak stream, urgency, nocturia, and urinary retention.
Symptoms: difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and nocturia?
Symptoms: difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and nocturia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanism leads to urinary retention in patients with BPH?
Mechanism leads to urinary retention in patients with BPH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Findings support BPH?
Findings support BPH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathophysiological change is most likely occurring when bladder distention and reports of dribbling urine are noted?
Pathophysiological change is most likely occurring when bladder distention and reports of dribbling urine are noted?
Signup and view all the flashcards
BPH lead to a urinary tract infection?
BPH lead to a urinary tract infection?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnostic test would the nurse expect the provider to order first?
Diagnostic test would the nurse expect the provider to order first?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indication when a patient with BPH: distended bladder and reports hesitancy. Post-void residual urine is >200 mL?
Indication when a patient with BPH: distended bladder and reports hesitancy. Post-void residual urine is >200 mL?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lab test is ordered to help rule out prostate cancer when evaluating a patient with BPH symptoms?
Lab test is ordered to help rule out prostate cancer when evaluating a patient with BPH symptoms?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is a urinalysis ordered for a patient with suspected BPH?
Why is a urinalysis ordered for a patient with suspected BPH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which of the following medications are used to manage symptoms of BPH?
Which of the following medications are used to manage symptoms of BPH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Action when tamsulosin (Flomax) reports feeling dizzy when standing?
Action when tamsulosin (Flomax) reports feeling dizzy when standing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Statement indicates understanding of finasteride?
Statement indicates understanding of finasteride?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indication of finasteride and tamsulosin improvement in urinary stream?
Indication of finasteride and tamsulosin improvement in urinary stream?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Findings increase the risk for complications with alpha-blockers?
Findings increase the risk for complications with alpha-blockers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response to a patient taking finasteride who is concerned about sexual side-effects?
Response to a patient taking finasteride who is concerned about sexual side-effects?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help treat BPH?
How do 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help treat BPH?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indication of effective BPH medications?
Indication of effective BPH medications?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Prostate Basics & Pathophysiology
- The prostate gland primarily produces alkaline fluid to aid sperm motility and neutralize the acidic vaginal environment.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) development involves hyperplasia (increase in number) of both stromal and epithelial cells, forming nodules that compress the urethra.
- Clinical manifestations of BPH include weak urinary stream, urinary urgency, nocturia, and urinary retention. Polyuria is not a typical symptom.
- Difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and nocturia are hallmark symptoms, suggesting BPH due to urethral compression from prostate enlargement.
- Urinary retention in BPH patients is caused by compression of the urethra by hyperplastic prostate tissue.
- Hematuria and overflow incontinence can result from BPH. Fever and CVA tenderness suggest infection, not BPH specifically.
- Incomplete bladder emptying from BPH, leads to dribbling and distention.
- BPH can cause urinary retention, creating an environment for bacterial growth and increasing the risk for UTIs.
Diagnostics & Medications
- A digital rectal exam (DRE) is a common and immediate method to evaluate prostate enlargement.
- In BPH, the prostate can block the urethra, leading to retention of significant urine volumes even after voiding, which can be confirmed with post-void residual measurements >200mL.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels help distinguish BPH from prostate cancer, elevated PSA can indicate cancer, but useful for screening.
- Urinalysis in suspected BPH cases will detect hematuria or signs of infection due to urinary retention.
- Medications for managing BPH symptoms include tamsulosin and terazosin (alpha-blockers to relax the prostate and bladder neck), and finasteride (a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor to shrink the prostate).
- Tamsulosin can cause orthostatic hypotension; patients should be taught to change positions slowly.
- Finasteride can take 3–6 months to have a full effect by shrinking the prostate over time.
- Improved urinary stream after taking finasteride and tamsulosin indicates the medications are effectively reducing prostate size or relaxing the prostate/bladder neck.
- The risk for complications with alpha-blockers increases with a history of orthostatic hypotension, concurrent antihypertensive use, or use of erectile dysfunction medication.
- Finasteride may cause decreased libido or erectile dysfunction, which are often reversible after discontinuation.
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors treat BPH by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT and reducing prostate size.
- Effective BPH treatment should result in reduced symptoms like nocturia and improved urine flow.
Surgery, TURP, and Post-Op Complications
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is the gold-standard surgical intervention for relieving BPH symptoms by removing obstructive prostate tissue.
- Continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) following a TURP helps flush blood clots from the bladder and keeps the urinary catheter from becoming blocked.
- Complications following a TURP procedure include hemorrhage, urinary tract infection, retrograde ejaculation, and clot retention. Testicular torsion is unrelated to TURP.
- Burning sensation in the hands and face, restlessness, and headache in a post-TURP patient indicate TURP syndrome caused by hyponatremia due to absorption of irrigating fluid.
- A discrepancy in I&Os during CBI may indicate catheter blockage; gentle irrigation can dislodge clots and restore flow.
- If a patient's sodium drops to 125 mEq/L post-TURP, expect confusion and muscle twitching, as hyponatremia affects neuro function.
- Appropriate nursing interventions to monitor or prevent complications related to TURP surgery include monitoring H&H for signs of bleeding, monitoring sodium levels for dilutional hyponatremia, keeping irrigation bag <100 cm above patient, and encouraging early ambulation.
- To be avoided post TURP is NSAIDs, due to their increased bleeding risk.
- Avoid NSAIDs to minimize bleeding risk.
- Pinkish urine is expected after TURP. Bright red blood or large clots would be concerning.
- Assess for bladder distention if a post-TURP patient reports an urgent need to void despite having a catheter in place, as it could indicate clot retention or catheter blockage.
Nursing Care, Patient Education & Evaluation
- Post-op hemorrhage is the most common and most serious complication immediately after a TURP and requires vigilant monitoring.
- Encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises post-TURP is important to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia.
- Post-op instructions after a TURP procedure should include avoiding constipation and straining, drinking 2000–3000 mL of fluids per day, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and reporting bright red bleeding.
- Cloudy urine with small clots is an expected finding in the early recovery period post-TURP, persistent heavy bleeding is not.
- CBI must be stopped before removing the catheter to prevent uncontrolled irrigation fluid drainage and discomfort.
- A drop in H&H is a red flag requiring immediate intervention and may indicate internal bleeding.
- Nursing actions that help evaluate the effectiveness of BPH or TURP treatment include monitoring urine output and color, assessing for bladder distention, tracking sodium and H&H values, and assessing the patient's report of pain.
- NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and increase the risk of post-op bleeding. Avoid after TURP.
- Discharge instructions for post-TURP patients should include avoiding activities that cause strain to promote healing and prevent complications.
- Signs of infection (fever, chills, and foul-smelling or cloudy urine) must be reported by patients discharged after TURP.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.