Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of a loop in programming?
What is the primary purpose of a loop in programming?
- To skip over a section of code
- To repeat a task until a certain condition is met (correct)
- To execute a series of actions in a specific order
- To make decisions based on conditional statements
What is the main difference between a sequence and a selection?
What is the main difference between a sequence and a selection?
- The type of data being processed
- The presence of conditional statements (correct)
- The order in which actions are performed
- The number of actions in the sequence
What is an example of a real-life sequence?
What is an example of a real-life sequence?
- Checking if you have toothpaste before brushing your teeth
- Hammering a nail until it's all the way in
- Deciding what to wear based on the weather
- Following a recipe to bake a cake (correct)
What is the purpose of a selection in programming?
What is the purpose of a selection in programming?
Which of the following is NOT a type of programming structure?
Which of the following is NOT a type of programming structure?
What is an example of a loop in real life?
What is an example of a loop in real life?
What is the primary benefit of using loops in programming?
What is the primary benefit of using loops in programming?
What is the primary mechanism by which selections determine the path to take next?
What is the primary mechanism by which selections determine the path to take next?
What is a key benefit of using sequences in programming?
What is a key benefit of using sequences in programming?
What is the main difference between a loop and a sequence?
What is the main difference between a loop and a sequence?
What is a common use case for selections in programming?
What is a common use case for selections in programming?
What is a key characteristic of loops in programming?
What is a key characteristic of loops in programming?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Programming Structures
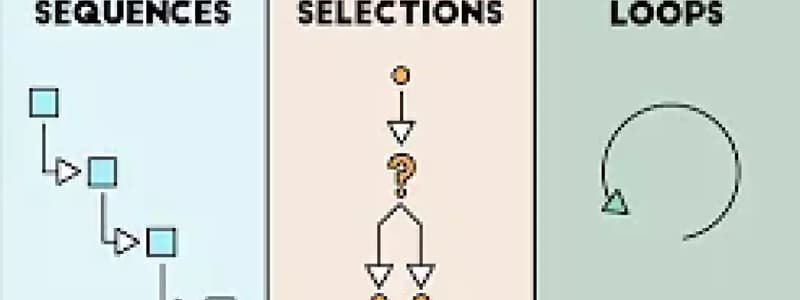
- Behind every software, there are codes being run with different terms and symbols that can be broken down into three simple programming structures: sequences, selections, and loops.
Sequences
- A sequence is a series of actions that are completed in a specific order.
- Each action is performed in order, one after the other, until all actions in the sequence have been carried out.
- Example: Morning routine - waking up, drinking water, taking a shower, eating breakfast, etc.
Selections
- A selection is a programming structure that asks a question to figure out which path to take next.
- It answers a question based on what it finds, and then takes action accordingly.
- Example: Checking if you have toothpaste - if no, add it to the shopping list; if yes, use it.
Loops
- A loop is a programming structure that asks a question repeatedly until a certain task is complete.
- It continues to ask the same question over and over again until the desired outcome is achieved.
- Example: Hammering a nail - asking "Is the nail all the way in?" and repeating the action until the answer is yes.
- Loops allow programmers to efficiently code repetitive tasks without having to write the same actions over and over again.
Programming Structures
- Programming structures are the building blocks of software, consisting of sequences, selections, and loops.
Sequences
- A sequence is a series of actions performed in a specific order.
- Each action is carried out one after the other until all actions are completed.
- Examples of sequences include morning routines, such as waking up, drinking water, taking a shower, and eating breakfast.
Selections
- A selection is a programming structure that makes a decision based on a question.
- It answers a question and takes action accordingly.
- Examples of selections include checking if you have toothpaste, and if not, adding it to the shopping list, or if you do, using it.
Loops
- A loop is a programming structure that repeatedly asks a question until a task is complete.
- It continues to ask the same question until the desired outcome is achieved.
- Examples of loops include hammering a nail, where you repeatedly ask "Is the nail all the way in?" and repeat the action until the answer is yes.
- Loops allow programmers to efficiently code repetitive tasks without writing the same actions multiple times.
Programming Structures
- Programming structures are the building blocks of software, consisting of sequences, selections, and loops.
Sequences
- A sequence is a series of actions performed in a specific order.
- Each action is carried out one after the other until all actions are completed.
- Examples of sequences include morning routines, such as waking up, drinking water, taking a shower, and eating breakfast.
Selections
- A selection is a programming structure that makes a decision based on a question.
- It answers a question and takes action accordingly.
- Examples of selections include checking if you have toothpaste, and if not, adding it to the shopping list, or if you do, using it.
Loops
- A loop is a programming structure that repeatedly asks a question until a task is complete.
- It continues to ask the same question until the desired outcome is achieved.
- Examples of loops include hammering a nail, where you repeatedly ask "Is the nail all the way in?" and repeat the action until the answer is yes.
- Loops allow programmers to efficiently code repetitive tasks without writing the same actions multiple times.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.