Podcast
Questions and Answers
What can be specified for a subprogram parameter?
What can be specified for a subprogram parameter?
- An identifier
- A mode (correct)
- A data type
- A constant
All subprogram parameters must have a mode specified.
All subprogram parameters must have a mode specified.
False (B)
What are the two main categories of subprograms?
What are the two main categories of subprograms?
Functions and Procedures
A subprogram's behavior is defined based on its ______ and ______.
A subprogram's behavior is defined based on its ______ and ______.
Match the following terms related to subprograms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms related to subprograms with their descriptions:
Flashcards
Subprogram parameter mode
Subprogram parameter mode
A subprogram parameter can have a mode, which determines how data is passed to and from the subprogram.
Subprogram parameter mode 'in'
Subprogram parameter mode 'in'
The mode 'in' indicates that the subprogram parameter is used only for input. The value is passed into the subprogram but cannot be modified within it.
Subprogram parameter mode 'out'
Subprogram parameter mode 'out'
The mode 'out' indicates that the subprogram parameter is used only for output. The subprogram modifies the parameter's value, which is then returned to the calling program.
Subprogram parameter mode 'in out'
Subprogram parameter mode 'in out'
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subprogram parameter modes: importance
Subprogram parameter modes: importance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chapter 6: Subprograms
- Subprograms are self-contained blocks of code
- Subprograms have a single entry point
- Execution of the calling program is suspended whilst the subprogram runs
- Control returns to the caller when the subprogram's execution finishes
Subprogram General Form
subprogram_type subprogram_name(parameter_list){ body of the subprogram }subprogram_type: specifies the subprogram typesubprogram_name: a valid identifierparameter_list: variables receiving values upon calling
Parameters
- Formal parameters are dummy variables within the subprogram header
- Parameters in a call statement are 'actual' parameters, which are bound to formal parameters
- Subprogram call statements need the subprogram name and a list of actual parameters matching formal parameters
Parameter Modes
in: parameter can only be read, not writtenout: parameter is written to and then read, potentially changed after the subprogramin out: parameter can be both read and written to, potentially changing
Models of Parameter Passing
- Diagrams illustrate 'in', 'out', and 'inout' modes as different data flow between calling and called programs
- Diagrams visually represent parameter passing within subprograms
Pass-by-Value (In Mode)
- The actual parameter's value initializes the formal parameter
- Usually implemented by copying the value
- Can be implemented by transmitting an access path instead of copying but is less efficient
- Disadvantages involve extra storage if the physical move approach is used, particularly for large parameters
Pass-by-Result (Out Mode)
- Requires extra storage space
- A copy operation is necessary to update the value of the caller's parameter after the subprogram step
Pass-by-Value-Result (Inout Mode)
- A hybrid of pass-by-value and pass-by-result methods
- Sometimes called pass-by-copy
- Formal parameters often have local storage for this method
Types of Subprograms
- Two main categories: Procedures and Functions
Procedures: sets of statements that create parameterized computationsFunctions: semantically similar to procedures, but modeled on mathematical functions
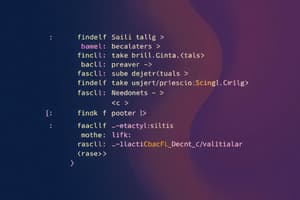
Sample Procedure
- Example
procedure Sumit - Displays the structure of a procedure,
Sumitwith aninparameter and anoutparameter. - Shows a
forloop computing a sum
Sample Function
- Example
function Sumit - Illustrates a function with an
inparameter (e.g., integer N) and a defined return type (e.g., integer). - Shows a
forloop computing a sum, returning a calculated value.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.