Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role do centrioles play in animal cells?
What role do centrioles play in animal cells?
- They produce ATP from glucose.
- They digest waste materials.
- They help organize microtubules. (correct)
- They synthesize proteins.
What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus in animal cells?
What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus in animal cells?
- To store waste products.
- To synthesize cholesterol.
- To produce energy in the form of ATP.
- To process and sort proteins. (correct)
Which component serves as the digestive system of the cell?
Which component serves as the digestive system of the cell?
- Mitochondria
- Vacuoles
- Peroxisomes
- Lysosomes (correct)
What is the main energy currency used in the body?
What is the main energy currency used in the body?
Which organelle is primarily involved in oxidation reactions and lipid biosynthesis?
Which organelle is primarily involved in oxidation reactions and lipid biosynthesis?
What percentage of the body’s energy is generated by the electron transport chain?
What percentage of the body’s energy is generated by the electron transport chain?
Which statement about mitochondrial function is accurate?
Which statement about mitochondrial function is accurate?
Which feature distinguishes the rough endoplasmic reticulum from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Which feature distinguishes the rough endoplasmic reticulum from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
What type of specificity allows an enzyme to catalyze reactions on molecules with specific functional groups?
What type of specificity allows an enzyme to catalyze reactions on molecules with specific functional groups?
Which suffix is commonly used in the names of enzymes responsible for catalyzing reactions?
Which suffix is commonly used in the names of enzymes responsible for catalyzing reactions?
What is the primary role of the enzyme's active site?
What is the primary role of the enzyme's active site?
What happens to enzymes when the temperature exceeds optimal conditions?
What happens to enzymes when the temperature exceeds optimal conditions?
Which category of enzymes is responsible for adding water during hydrolysis reactions?
Which category of enzymes is responsible for adding water during hydrolysis reactions?
What does the 'Lock and Key Theory' illustrate about enzyme function?
What does the 'Lock and Key Theory' illustrate about enzyme function?
What effect does an increase in substrate concentration have on an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, assuming enzyme concentration remains constant?
What effect does an increase in substrate concentration have on an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, assuming enzyme concentration remains constant?
Which type of enzyme specificity refers to action on a specific type of chemical bond regardless of molecular structure?
Which type of enzyme specificity refers to action on a specific type of chemical bond regardless of molecular structure?
What is downregulation in the context of gene expression?
What is downregulation in the context of gene expression?
Which statement accurately describes the epigenome?
Which statement accurately describes the epigenome?
What role do enzymes play in biochemical reactions?
What role do enzymes play in biochemical reactions?
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the human body?
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the human body?
Which of the following best describes upregulation?
Which of the following best describes upregulation?
Which class of biomolecules is primarily stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen?
Which class of biomolecules is primarily stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen?
Which of the following factors is NOT influenced by epigenetic factors?
Which of the following factors is NOT influenced by epigenetic factors?
Which codon specifies the amino acid phenylalanine?
Which codon specifies the amino acid phenylalanine?
How do cofactors relate to enzyme activity?
How do cofactors relate to enzyme activity?
What is biochemistry primarily concerned with?
What is biochemistry primarily concerned with?
What determines the size range of enzymes?
What determines the size range of enzymes?
What is the primary role of transfer RNA (tRNA) in translation?
What is the primary role of transfer RNA (tRNA) in translation?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of enzymes in biochemical processes?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of enzymes in biochemical processes?
Which of the following best describes a human cell based on the context provided?
Which of the following best describes a human cell based on the context provided?
Which of the following is an example of an epigenetic factor that can influence gene expression?
Which of the following is an example of an epigenetic factor that can influence gene expression?
Where does the process of transcription occur?
Where does the process of transcription occur?
What is the initial codon at which the ribosome attaches to mRNA during translation?
What is the initial codon at which the ribosome attaches to mRNA during translation?
What type of molecules are primarily hydrophobic and include triglycerides and cholesterol?
What type of molecules are primarily hydrophobic and include triglycerides and cholesterol?
Which of the following is NOT a type of carbohydrate?
Which of the following is NOT a type of carbohydrate?
Which process is directly responsible for assembling the polypeptide chain?
Which process is directly responsible for assembling the polypeptide chain?
What structure is involved in both the transcription and translation processes?
What structure is involved in both the transcription and translation processes?
In the context of cosmetic products, understanding biochemistry can help individuals evaluate claims regarding:
In the context of cosmetic products, understanding biochemistry can help individuals evaluate claims regarding:
What is formed when a ribosome moves along the mRNA and a peptide bond is created between two amino acids?
What is formed when a ribosome moves along the mRNA and a peptide bond is created between two amino acids?
What is the flow of genetic information in biological systems described by the central dogma?
What is the flow of genetic information in biological systems described by the central dogma?
What type of molecule is primarily composed of fatty acids?
What type of molecule is primarily composed of fatty acids?
Which of the following amino acids must be obtained from the diet?
Which of the following amino acids must be obtained from the diet?
What is the structural unit of nucleic acids?
What is the structural unit of nucleic acids?
Which nitrogenous base is not found in DNA?
Which nitrogenous base is not found in DNA?
Which statement accurately describes DNA?
Which statement accurately describes DNA?
What is the primary function of RNA?
What is the primary function of RNA?
Which best describes the sugar component in RNA?
Which best describes the sugar component in RNA?
In the context of proteins, what do ribosomes do?
In the context of proteins, what do ribosomes do?
What is the relationship between DNA and RNA in protein synthesis?
What is the relationship between DNA and RNA in protein synthesis?
Which of the following correctly pairs the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
Which of the following correctly pairs the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
Flashcards
Transcription
Transcription
The process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA.
Translation
Translation
The process of decoding RNA to synthesize proteins.
What is biochemistry?
What is biochemistry?
Biochemistry is the study of the chemical substances and vital processes occurring in live organisms. It explains the chemical basis of life.
Codon
Codon
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are carbohydrates?
What are carbohydrates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are lipids?
What are lipids?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ribosome
Ribosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the human cell like?
What is the human cell like?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is glycogen?
What is glycogen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initiation Codon (AUG)
Initiation Codon (AUG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stop Codon
Stop Codon
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is ATP?
What is ATP?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are enzymes?
What are enzymes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cofactors?
What are cofactors?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fatty Acid-Based Lipids
Fatty Acid-Based Lipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-Fatty Acid Lipids
Non-Fatty Acid Lipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amino Acids
Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Essential Amino Acids
Essential Amino Acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peptides
Peptides
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proteins
Proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signaling Molecules (Hormones)
Signaling Molecules (Hormones)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamins
Vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Co-factors
Co-factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Downregulation
Downregulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upregulation
Upregulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genome
Genome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epigenome
Epigenome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epigenetic factors
Epigenetic factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enzymes
Enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gene regulation
Gene regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is an enzyme?
What is an enzyme?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the active site?
What is the active site?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a substrate?
What is a substrate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a product?
What is a product?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is enzyme specificity?
What is enzyme specificity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is activation energy?
What is activation energy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enzyme inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enzyme cofactor
Enzyme cofactor
Signup and view all the flashcards
ATP
ATP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electron transport chain
Electron transport chain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Co-enzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone)
Co-enzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrioles
Centrioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Principles of Biochemistry
- Biochemistry studies chemical substances and processes in living organisms.
- Topics covered include DNA replication and transcription, enzymes and cofactors, ATP production and energy production.
Introduction
- Lectures cover how cosmetic products affect skin biochemistry.
- Some cosmetic products claim to enhance or decrease the activities of cellular organelles or to supply compounds that decline with age.
- Understanding biochemistry helps appreciate how these cosmetic products work.
What is Biochemistry?
- Biochemistry is the study of the chemical substances and processes occurring in live organisms.
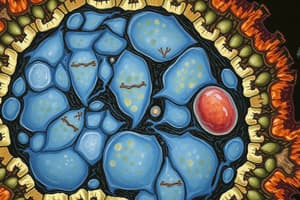
Structure of an Animal Cell
- A diagram of an animal cell illustrates its various components.
- Components like mitochondria, peroxisome, secretory vesicle, ribosomes, smooth/rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, plasma membrane, lysosomes and vacuoles are present.
- A brief explanation of each component is included at the end of the slide presentation.
Human Cell - The Complex Bioreactor
- A human cell is a complex "reactor" that carries out essential processes for survival, growth and reproduction.
Human Cell-The Complex Bioreactor (Diagram)
- A complex diagram shows numerous biochemical pathways in a human cell.
- The diagram details various metabolic pathways such as metabolism of cofactors, vitamins, lipids and proteins .
- Other biochemical pathways include the synthesis and degradation of numerous molecules including but not limited to steroids, carbohydrates, lipids and nitrogen containing compounds.
Biomolecules - Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Carbohydrates provide a primary energy source and are stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
- They are water-soluble and present in cytoplasm and extra-cellular space.
Biomolecules - Lipids
- Lipids are organic molecules composed mostly of hydrophobic chemical components like fatty acids, sterols.
- Major lipids include triglycerides, phospholipids, and ceramides.
- Other lipids include cholesterol, testosterone, and estrogen.
Biomolecules - Amino acids, Peptides and Proteins
- There are 21 different amino acids in humans. 9 are essential amino acids, not synthesized in the body and must be present in diet.
- Amino acids have an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and a variable R-group.
- Amino acids form peptides and proteins.
- Proteins have complex structures including primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures
Biomolecules - Other Small Molecules
-
- Important molecules include adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy carrier in living cells, crucial for metabolism and energy transfer. Signalling molecules like cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), nitric oxide (NO), and hydrocortisone facilitate intercellular communication, regulating processes like inflammation and growth. Vitamins are essential organic compounds acting as coenzymes and antioxidants, influencing biochemical reactions. Minerals such as sodium and potassium maintain cellular functions, while magnesium supports over 300 enzymatic reactions. Key trace elements like zinc, calcium, and iron play roles in immune function, bone health, and oxygen transport. Urea, a metabolic waste product, is excreted by kidneys to remove excess nitrogen.
Biomolecules - Nucleic Acids
- DNA and RNA are nucleic acids.
- DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid, and RNA is ribonucleic acid.
- The structural unit of nucleic acids is a nucleotide.
Nucleotides
- Nucleotides consist of phosphate group, pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base.
- The phosphate group is negatively charged.
The Nitrogenous Bases
- There are 5 different nitrogen-containing bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil.
- Purines (A & G) are large, two-ringed bases.
- Pyrimidines (C, T & U) are smaller, single-ringed bases.
DNA
- DNA is a double-stranded molecule.
- Alternating sugar and phosphate molecules form the DNA backbone.
- Sugar is deoxyribose.
- Nucleotides are joined by a phosphodiester linkage.
- Base pairs (A-T, C-G) are joined by hydrogen bonds.
DNA
- The two strands of DNA form a double helix
- The sequence of one strand is complementary to the other.
RNA
- RNA is a single-stranded molecule
- The sugar in RNA is ribose.
- Bases include A, U, C & G
- There are three types of RNA: tRNA, rRNA, mRNA.
Summary – DNA vs RNA
- DNA is located in the nucleus, while RNA is found in the cytoplasm.
- DNA's main function is directing protein synthesis and replication. RNA carries out genetic instructions for protein synthesis.
- DNA has deoxyribose sugar, and RNA has ribose sugar.
- DNA bases are A-T, C-G, and RNA bases are A-U, C-G.
- DNA is a double helix, and RNA is a single straight or folded strand.
DNA → RNA → amino acids
- DNA is the master blueprint for protein synthesis.
- Genes are segments of DNA that code for polypeptides.
- DNA sequence determines the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide chain.
- Codons are triplets of bases that "encode" amino acids.
- Processes involved in protein synthesis include transcription and translation.
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
- Explains the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
- Two steps: transcription and translation.
- Transcription produces an RNA copy of a DNA segment.
- Translation converts the RNA information into proteins.
Transcription - RNA Synthesis
- DNA never leaves the nucleus, but proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm.
- A copy of the gene (mRNA) is made and carries the genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- The process of copying the genetic information in the DNA to mRNA is referred to as transcription.
Translation - Protein Synthesis
- Translation occurs in ribosomes, either free or bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) is crucial for linking mRNA codons to amino acids.
- Ribosomes translate mRNA's codons into amino acids, to synthesise a polypeptide chain (protein).
Mechanism of Enzyme Activity
- Enzymes follow three basic steps: binding of substance to active site, internal rearrangement to form products and release of products, to initiate the next cycle.
- Enzyme specificity is described by four types: absolute, group, linkage and stereochemical specificity.
Lock and Key Theory
- Enzyme's 3D structure determines the active site's shape, influencing its specificity.
- The lock-and-key model describes that substrates fit into active sites like a key into a lock, a mechanism used by enzymes to regulate biochemical reactions.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Temperature, pH, concentration of enzyme & substrate, and inhibitors affect enzyme activity.
- Optimal temperature and pH are crucial for enzyme function.
- Enzyme denaturation occurs at high temperatures.
- Concentration increases reaction rate up to a point.
- Inhibitors can affect enzyme activity.
Enzymes and Cofactors
- Enzyme cofactors are needed for enzyme function.
- Cofactors can be inorganic (metals) or organic (coenzymes).
- Examples of cofactors include thiamine pyrophosphate, flavin adenine nucleotide, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, pyridoxal phosphate.
Enzymes and Collagen Synthesis
- Collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, is a component of connective tissues (skin, bones, cartilage).
- Collagen has a triple helical structure.
- Enzyme-catalyzed hydroxylation of proline residues is necessary for collagen's triple helix configuration. Specific enzymes, reduced iron (Fe+2) and ascorbate (vitamin C) are crucial in this process.
ATP and Energy Production
- ATP is the main energy currency of the body.
- Energy from food is stored in ATP's bonds
- ATP has a molecular weight of 507 Da
- ATP is water-soluble.
Cellular Respiration
- Cellular respiration converts glucose into ATP (energy).
- The process involved includes Glycolysis, Tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
- Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the mitochondria via the electron transport chain.
Co-enzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone)
- A fat-soluble compound found primarily in the mitochondria.
- It is part of the electron transport chain and plays a role in energy production.
Components of an Animal Cell
- Structures within an animal cell like centrioles, peroxisomes, smooth/rough ER, Golgi complex plays different roles in the functioning of the cell.
- Other components include lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria, nucleus and nuclear envelope.
Additional Information
- Links to videos about protein synthesis and respiration are provided.
- Articles that discuss the importance of protease enzymes in the skin have been cited.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.