Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary cause of pressure ulcers?
What is the primary cause of pressure ulcers?
- Prolonged pressure on the skin (correct)
- Poor nutrition only
- Inadequate exercise
- Excessive moisture on the skin
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of pressure ulcers?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of pressure ulcers?
- Burning sensation (correct)
- Pus-like draining
- Unusual changes in skin color
- Swelling
Which of these areas is most likely to develop pressure ulcers in individuals who are confined to a bed?
Which of these areas is most likely to develop pressure ulcers in individuals who are confined to a bed?
- Back of the head
- Midsection
- Forehead
- Tailbone (correct)
What is an effective prevention strategy for pressure ulcers?
What is an effective prevention strategy for pressure ulcers?
Which of the following risk factors contributes to the development of pressure ulcers?
Which of the following risk factors contributes to the development of pressure ulcers?
Flashcards
What are pressure ulcers?
What are pressure ulcers?
Injuries to the skin and underlying tissue caused by prolonged pressure.
Where do pressure ulcers commonly occur in wheelchair users?
Where do pressure ulcers commonly occur in wheelchair users?
Areas prone to pressure ulcers in people who use wheelchairs include the tailbone, buttocks, and hips.
Where do pressure ulcers commonly occur in bedridden individuals?
Where do pressure ulcers commonly occur in bedridden individuals?
Areas prone to pressure ulcers in people who are bedridden include the heels, ankles, tailbone, and shoulder blades.
What are some risk factors for pressure ulcers?
What are some risk factors for pressure ulcers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can pressure ulcers be prevented?
How can pressure ulcers be prevented?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores)
- Pressure ulcers are injuries to skin and underlying tissue.
- They result from prolonged pressure on the skin.
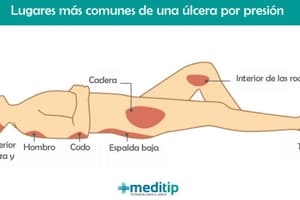
- Common locations include heels, ankles, hips, tailbone.
- They can occur quickly.
- Most heal with treatment, but some do not.
Symptoms of Pressure Ulcers
- Unusual changes in skin color or texture
- Swelling
- Pus-like drainage
- Skin that feels cooler or warmer than other areas
- Tender areas
- Bad odor
Common Pressure Sore Locations
- Wheelchair users: Tailbone, buttocks, shoulder blades, backs of arms and legs (where they rest against the chair)
- Bedridden individuals: Back or sides of head, shoulder blades, hip, lower back, tailbone, heels, ankles, skin behind knees
Risk Factors of Pressure Ulcers
- Stress
- Duration of stress
- Paralysis or spasticity
- Edema
- Moisture
- Lack of nerve supply
- Poor nutrition
Prevention Tips
- Change positions frequently
- Keep skin clean and dry
- Use pillows
- Exercise
Pressure Ulcer Stages (Visual Aids)
- Stage 1: Skin is unbroken but inflamed.
- Stage 2: Skin is broken to the epidermis or dermis.
- Stage 3: Ulcer extends to the subcutaneous fat layer.
- Stage 4: Ulcer extends to muscle or bone. Undermining is likely.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.