Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which factor is NOT a physical determinant of population density?
Which factor is NOT a physical determinant of population density?
- Climate type
- Soil quality
- Political stability (correct)
- Physical accessibility
Why might a country with a declining annual population growth rate still experience an increase in total population?
Why might a country with a declining annual population growth rate still experience an increase in total population?
- A large 'bump' of people reaching reproductive age (correct)
- Decreased emigration rates
- Increased death rates
- Reduced access to healthcare
Which of the following is the most accurate definition of doubling time?
Which of the following is the most accurate definition of doubling time?
- The time it takes for the annual growth rate to double
- The time it takes for a population to double in size (correct)
- The time it takes for the Earth's resources to be depleted
- The time it takes for a population to increase by one billion people
How does increased access to technology and healthcare impact population dynamics?
How does increased access to technology and healthcare impact population dynamics?
Why is it difficult to compare population data across all countries?
Why is it difficult to compare population data across all countries?
What is a potential disadvantage of relying solely on crude birth and death rates to understand population trends?
What is a potential disadvantage of relying solely on crude birth and death rates to understand population trends?
According to the demographic transition model (DTM), what characterizes Stage 2?
According to the demographic transition model (DTM), what characterizes Stage 2?
What is a key limitation of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
What is a key limitation of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
What information can be derived from a population pyramid?
What information can be derived from a population pyramid?
A population pyramid with a broad base and a rapidly narrowing top indicates:
A population pyramid with a broad base and a rapidly narrowing top indicates:
In a population pyramid, a significant bulge in the middle age groups suggests:
In a population pyramid, a significant bulge in the middle age groups suggests:
What might a population pyramid for Qatar in 2022, reveal based on the text?
What might a population pyramid for Qatar in 2022, reveal based on the text?
Which factor is considered a 'push' factor in migration?
Which factor is considered a 'push' factor in migration?
Which of the following is the best example of an intervening obstacle in migration?
Which of the following is the best example of an intervening obstacle in migration?
What is a potential economic benefit for the place of origin due to international migration?
What is a potential economic benefit for the place of origin due to international migration?
What is the primary cause of forced migration?
What is the primary cause of forced migration?
Which of the following is the best definition of 'land grabbing'?
Which of the following is the best definition of 'land grabbing'?
What is a key characteristic of an 'ageing population'?
What is a key characteristic of an 'ageing population'?
What is a potential economic challenge posed by an ageing population?
What is a potential economic challenge posed by an ageing population?
What is a potential strategy to address the challenges of an ageing population?
What is a potential strategy to address the challenges of an ageing population?
What best describes a pro-natalist policy?
What best describes a pro-natalist policy?
Which of the following statements best reflects the impact of China's one-child policy?
Which of the following statements best reflects the impact of China's one-child policy?
What is the demographic dividend?
What is the demographic dividend?
Which of these factors has contributed most too declining crude birth rate and child mortality rate?
Which of these factors has contributed most too declining crude birth rate and child mortality rate?
What is a potential benefit for local communities resulting from the movement of older people into the area?
What is a potential benefit for local communities resulting from the movement of older people into the area?
Flashcards
Crude birth rate
Crude birth rate
The number of live births per 1,000 people in a given area per year.
Crude death rate
Crude death rate
Total deaths per 1,000 people in a given area per year.
Natural increase
Natural increase
The difference between the crude birth rate and crude death rate.
Immigration
Immigration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emigration
Emigration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Life expectancy
Life expectancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertility rate
Fertility rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infant mortality rate
Infant mortality rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Child mortality rate
Child mortality rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Doubling Time
Doubling Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Refugees
Refugees
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internally displaced people (IDPs)
Internally displaced people (IDPs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Push factors
Push factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pull factors
Pull factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intervening obstacles
Intervening obstacles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aging Population
Aging Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
Youthful Population
Youthful Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Pyramid
Population Pyramid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stages of DTM
Stages of DTM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Demographic Dividend
Demographic Dividend
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pro-natalist policy
Pro-natalist policy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anti-natalist policy
Anti-natalist policy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Female infanticide
Female infanticide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Remittance
Remittance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The issues surrounding population are intricate, and the impact of population growth on the future is a significant concern for humanity
- The need to understand where people live and why is essential
Population Distribution and Density
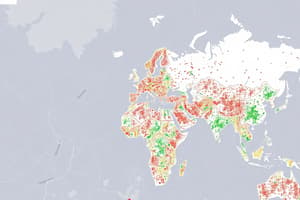
- Many regions have sparse populations due to extreme climates, poor soil, mountainous terrain, or remoteness
- Only a third of Earth's land surface is inhabited
- Of that, only a third is inhabited by more than 20 people per square kilometer
- Deeper colors or more dots on a population density map indicates a higher concentration of people per square kilometer
- Lightly colored areas indicate sparsely populated regions
- Physical factors like land relief, soil quality, climate, vegetation, water access, and accessibility all affect population distribution
- Human factors include economic, political, and technological influences
Measuring Population Growth
- Population trends are determined by examining Crude birth rate and Crude death rate
- Crude birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people per year
- Crude death rate is the total deaths per 1,000 people per year
- Natural increase or decrease is the difference between crude birth and death rates
- Population change is also affected if people are Immigrating or Emigrating
- Life expectancy is the average number of years a person is expected to live in a region at birth
- World life expectancy in 2017 was 71 years, compared to 52 years in 1969
- Fertility rate is the average number of children a woman gives birth to in her lifetime
- Infant mortality rate measures the number of infants who die before age one
- Child mortality rate measures the number of children who die before age five
- Data collection methods vary by country, leading to potential inaccuracies in population representation
Population Trends and Patterns
- Population data reveals trends, patterns, and comparisons between countries
- Doubling time shows how quickly a population is growing
- The highest annual growth rate occurred between 1950 and 1990, peaking at 2.1% around 1970
- More people giving birth, rather than an increased global fertility rate, is why world population still grows, even though annual growth rate has declined
- World population doubled in 125 years from 1803 and 1928
- The time to double again from 1975 took only 76 years
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
- The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) illustrates how birth and death rates affect population growth
- Stage 1: High birth rate and high death rate, resulting in a stable population
- Stage 2: High birth rate but falling death rate, leading to population increase
- Stage 3: Declining birth rate while total population continues to increase
- Stage 4: Low birth and death rates, resulting in a high total population
- Stage 5: Death rate exceeds birth rate, causing population decline
- The DTM focuses on birth and death rates and does not include migration
Population Structure
- Population distribution that accounts for percentage of males and females is shown on an age sex pyramid
- On age-sex pyramids, males are shown on the left and females on the right
- Age is shown in five-year bands
- Ethiopia's broad base on a population pyramid indicates a high fertility rate
- The older population starts to decline at around 80 years, which indicates a low life expectancy.
- At each of the childhood age sections, the total population decreases, showing a high infant and child mortality rate
- A higher cultural preference for boys can be inferred if the population born of males exceeds females
- Studying population pyramids discern the factors that affect population in certain countries
Managing Population
- Youthful age groups are 0-15 years of age
- Elderly age groups are over 60 years of age
- Working age groups are People 15–59 years
- Governments and policymakers need to plan how to meet societal needs with regard to its population demographics
Migration
- Migration, along with births and deaths, is a factor that directly affects population growth
- Immigration is movement of people into a country
- Emigration is movement of people out of the country
- Internal migration is when a person moves within a country's border
- International migration is when a person is moving across borders
- Voluntary migration: when the person chooses to move
- Forced migration: when a person is obliged to move because their life is threatened or endangered
- Push factors are negative reasons which explain a person leaving their place of origin
- Pull factors are positive reasons that attract the person to move to the place of destination
- When large scales of people migrate there are significant impacts on both origin and destination
- Remittance: money sent home to the family to spend on education
- A large percentage of the world's displaced come from conflict, climate change and land grabbing
- An unprecedented 68.5 million people around the world have been forced from home
- 25.4 million refugees, over half of whom are under the age of 18
- 10 million stateless people who have been denied a nationality and access to basic rights
- Nearly 1 person is forcibly displaced every two seconds as a result of conflict or persecution
- Conflict between countries or civil war has been the primary cause of refugees
- Climate change examples include: Sub-Saharan Africa and The Pacific Islands
- Land grabbing examples include: Amazonian indigenous groups
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.