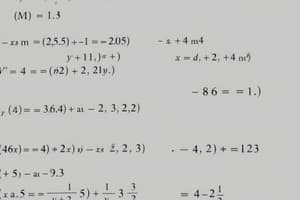Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the standard form representation of 0.000456?
What is the standard form representation of 0.000456?
- 45.6 x 10⁻⁵
- 4.56 x 10⁻⁴ (correct)
- 4.56 x 10⁻³
- 4.56 x 10³
Which of the following is NOT a quantity typically expressed in standard form?
Which of the following is NOT a quantity typically expressed in standard form?
- Three megajoules (MJ)
- Six microcoulombs (µC)
- One kilometer (km)
- A dog's speed (correct)
What is 16800 expressed in standard form?
What is 16800 expressed in standard form?
- 1.68 x 10³
- 1.68 x 10²
- 16.8 x 10³
- 1.68 x 10⁴ (correct)
What is the standard form representation of 0.000000023?
What is the standard form representation of 0.000000023?
If a value is expressed as $7.5 \times 10^{-6}$, what is that number in decimal form?
If a value is expressed as $7.5 \times 10^{-6}$, what is that number in decimal form?
What are the two components that make up a physical quantity?
What are the two components that make up a physical quantity?
Which of the following is NOT considered a base quantity in the SI system?
Which of the following is NOT considered a base quantity in the SI system?
What is the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature?
What is the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature?
What is the correct prefix for $10^9$?
What is the correct prefix for $10^9$?
Which of the following best describes the primary focus of Physics?
Which of the following best describes the primary focus of Physics?
Which of the following represents the smallest unit?
Which of the following represents the smallest unit?
Why is it necessary to have standardized units like the SI units?
Why is it necessary to have standardized units like the SI units?
According to the provided text, what is a crucial aspect of scientific experiments in Physics?
According to the provided text, what is a crucial aspect of scientific experiments in Physics?
What is the SI unit for the amount of substance?
What is the SI unit for the amount of substance?
How is 0.001 meters best expressed using a prefix?
How is 0.001 meters best expressed using a prefix?
Which of these is NOT an area of study within Physics, as listed in the text?
Which of these is NOT an area of study within Physics, as listed in the text?
What is the correct symbol for the prefix 'micro-'?
What is the correct symbol for the prefix 'micro-'?
Which of the following prefixes represents the smallest value?
Which of the following prefixes represents the smallest value?
What role do 'Disciplinary Ideas' play in the study of Physics?
What role do 'Disciplinary Ideas' play in the study of Physics?
A distance of one million meters can be conveniently expressed as
A distance of one million meters can be conveniently expressed as
What does the prefix 'kilo' (k) represent?
What does the prefix 'kilo' (k) represent?
In the context of chemistry, what does one mole contain?
In the context of chemistry, what does one mole contain?
How are matter and energy related?
How are matter and energy related?
What does the text indicate about the process of gaining knowledge in Physics?
What does the text indicate about the process of gaining knowledge in Physics?
Based on the diagram, which field is NOT directly connected to the study of matter's properties?
Based on the diagram, which field is NOT directly connected to the study of matter's properties?
What is the function of models in the context of Physics, as mentioned in the text?
What is the function of models in the context of Physics, as mentioned in the text?
What is the SI unit for length?
What is the SI unit for length?
Which of the following is the closest order of magnitude to the diameter of a wire?
Which of the following is the closest order of magnitude to the diameter of a wire?
What would be the least suitable instrument to measure the diameter of a tree trunk?
What would be the least suitable instrument to measure the diameter of a tree trunk?
Which of these has the smallest order of magnitude?
Which of these has the smallest order of magnitude?
Approximately what is the order of magnitude of the length of a football field?
Approximately what is the order of magnitude of the length of a football field?
Which part of the digital micrometer screw gauge is responsible for ensuring the spindle makes contact with the object?
Which part of the digital micrometer screw gauge is responsible for ensuring the spindle makes contact with the object?
What is the smallest division measurable by a digital micrometer screw gauge as shown in the table?
What is the smallest division measurable by a digital micrometer screw gauge as shown in the table?
When recording a measurement from a digital micrometer screw gauge, to what level of precision should you record?
When recording a measurement from a digital micrometer screw gauge, to what level of precision should you record?
How would you determine the thickness of a single sheet of paper?
How would you determine the thickness of a single sheet of paper?
According to the provided content, which instrument has the smallest measuring range?
According to the provided content, which instrument has the smallest measuring range?
What is the precision of measurement for a digital caliper, as mentioned in the instructions for recording measurements?
What is the precision of measurement for a digital caliper, as mentioned in the instructions for recording measurements?
Which of these instruments typically measures volumes of liquids to the nearest 0.05 cm³?
Which of these instruments typically measures volumes of liquids to the nearest 0.05 cm³?
What is the precision of a metre rule according to the content?
What is the precision of a metre rule according to the content?
Why is it important to position your eyes directly above a meter rule when taking a measurement?
Why is it important to position your eyes directly above a meter rule when taking a measurement?
A meter rule has wear at the zero mark. What is the recommended method to use this ruler for accurate measurements?
A meter rule has wear at the zero mark. What is the recommended method to use this ruler for accurate measurements?
What is the term for a complete back-and-forth movement of a pendulum?
What is the term for a complete back-and-forth movement of a pendulum?
If an experiment involving a pendulum is carried out, and a fixed error is found associated with the equipment, what can be said of this error?
If an experiment involving a pendulum is carried out, and a fixed error is found associated with the equipment, what can be said of this error?
Which of the following is the key difference between random errors and systematic errors?
Which of the following is the key difference between random errors and systematic errors?
Which measuring instrument is most suitable for determining the circumference of a cylindrical object?
Which measuring instrument is most suitable for determining the circumference of a cylindrical object?
What is the primary purpose of the locking screw on digital calipers?
What is the primary purpose of the locking screw on digital calipers?
Which part of the digital calipers is used to measure the depth of a hole?
Which part of the digital calipers is used to measure the depth of a hole?
If you needed to measure the internal diameter of a pipe or tube, which part of the digital calipers would you use?
If you needed to measure the internal diameter of a pipe or tube, which part of the digital calipers would you use?
What is the main purpose of the zero button on digital calipers?
What is the main purpose of the zero button on digital calipers?
Which measurement is typically taken using a metre rule?
Which measurement is typically taken using a metre rule?
What is the most accurate way to measure the external width of a book?
What is the most accurate way to measure the external width of a book?
Why should you be careful when using digital calipers to grip an object?
Why should you be careful when using digital calipers to grip an object?
Flashcards
Physical Quantity
Physical Quantity
A quantity that can be measured. It consists of two parts: a numerical magnitude and a unit.
SI Units
SI Units
A system of standardised units used for measurements worldwide.
Numerical Magnitude
Numerical Magnitude
The numerical part of a measurement.
Unit
Unit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meter (m)
Meter (m)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kilogram (kg)
Kilogram (kg)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second (s)
Second (s)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Milli (m)
Milli (m)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Physics?
What is Physics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matter
Matter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Energy
Energy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Force
Force
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wave
Wave
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conservation Laws
Conservation Laws
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microscopic Models
Microscopic Models
Signup and view all the flashcards
General Physics
General Physics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Standard Form
Standard Form
Signup and view all the flashcards
1.3 x 10^-5 m
1.3 x 10^-5 m
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Usain Bolt's average speed?
What is Usain Bolt's average speed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Converting m/s to km/h
Converting m/s to km/h
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expressing Avogadro's number in standard form
Expressing Avogadro's number in standard form
Signup and view all the flashcards
Giga (G)
Giga (G)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nano (n)
Nano (n)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mega (M)
Mega (M)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micro (µ)
Micro (µ)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kilo (k)
Kilo (k)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diameter of a Curved Object
Diameter of a Curved Object
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Ruler?
What is a Ruler?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Measuring Tape?
What is Measuring Tape?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Meter?
What is a Meter?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How to Measure Curved Length
How to Measure Curved Length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digital Micrometer Screw Gauge
Digital Micrometer Screw Gauge
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precision of an Instrument
Precision of an Instrument
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anvil (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Anvil (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spindle (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Spindle (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ratchet (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Ratchet (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digital Display (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Digital Display (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thimble (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Thimble (Micrometer Screw Gauge)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estimating Paper Thickness
Estimating Paper Thickness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meter rule
Meter rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Measuring tape
Measuring tape
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digital calipers
Digital calipers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inside jaws
Inside jaws
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outside jaws
Outside jaws
Signup and view all the flashcards
Locking screw
Locking screw
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digital display
Digital display
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tail
Tail
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parallax Error
Parallax Error
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Pendulum
Simple Pendulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Random Errors
Random Errors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systematic Errors
Systematic Errors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Taking Multiple Readings
Taking Multiple Readings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Standard Form
- Another convenient way of expressing physical quantities is to use standard form.
- A standard form is a way of writing numbers, in which a number between 1 to 10 is multiplied by an appropriate power of 10.
- Example: 0.00567 = 5.67 x 10-3, 16 800 = 1.68 x 104
Prefixes for SI Units
-
Using decimal notation, the distance between air molecules can be expressed as 0.000 000 001 m.
-
Instead of using decimal notation, it is more convenient to use prefixes to represent quantities.
-
Example: For example, when measuring short distances such as 1/1,000,000 of a metre, we simply express it as one micrometre.
-
1 x 10-6 m (micrometre)
-
If you have 1 000 000 000 metres, we simply express it as one terametre.
-
1 x 1012 m (terametre)
Table 1.2 Some common prefixes and their symbols
| Multiplies | Factor | Prefix | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1012 | 1012 | tera- | T |
| 109 | 109 | giga- | G |
| 106 | 106 | mega- | M |
| 103 | 103 | kilo- | k |
| 10-1 | 10-1 | deci- | d |
| 10-2 | 10-2 | centi- | c |
| 10-3 | 10-3 | milli- | m |
| 10-6 | 10-6 | micro- | μ |
| 10-9 | 10-9 | nano- | n |
Physical Quantities
- A physical quantity typically consists of a numerical magnitude and a unit.
- Example: 4.5 m (4.5 is the numerical magnitude, and m is the unit).
Base Quantities and SI Units
| Base Quantity | SI Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| length | metre | m |
| mass | kilogram | kg |
| time | second | s |
| electric current | ampere | A |
| thermodynamic temperature | kelvin | K |
| amount of substance | mole | mol |
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the standard form representation of numbers and the SI unit system with this quiz. It covers various aspects of physics, including base quantities, prefixes, and the importance of standardized units. Ideal for students looking to reinforce their understanding of these fundamental concepts in physics.