Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the pinna?
What is the primary function of the pinna?
- To decode and analyze electrical nerve signals
- To amplify sound
- To protect the eardrum from shocks
- To direct sound waves towards the tympanic membrane (correct)
What is the length of the auditory canal?
What is the length of the auditory canal?
- 1.5 cm
- 3.5 cm
- 2.5 cm (correct)
- 4.5 cm
What is the function of the auditory canal?
What is the function of the auditory canal?
- To decode and analyze electrical nerve signals
- To amplify sound by acting as a resonator (correct)
- To convert mechanical pulses into electrical signals
- To transmit sound waves to the inner ear
What is the role of the middle ear?
What is the role of the middle ear?
What is the function of the inner ear?
What is the function of the inner ear?
How does the auditory system work?
How does the auditory system work?
What is the role of the outer ear?
What is the role of the outer ear?
What is the function of the tympanic membrane?
What is the function of the tympanic membrane?
What is the purpose of the auditory cortex?
What is the purpose of the auditory cortex?
What is the primary function of the ear?
What is the primary function of the ear?
What is the velocity of sound in air?
What is the velocity of sound in air?
What is the frequency of sound wave that enhances the sensitivity of the ear?
What is the frequency of sound wave that enhances the sensitivity of the ear?
What is the main function of the tympanic membrane?
What is the main function of the tympanic membrane?
What happens to the acoustical signal when it hits the eardrum?
What happens to the acoustical signal when it hits the eardrum?
What is the ratio of the force on the oval window to the force on the eardrum?
What is the ratio of the force on the oval window to the force on the eardrum?
What is the area of the oval window compared to the area of the eardrum?
What is the area of the oval window compared to the area of the eardrum?
What is the function of the middle ear bones?
What is the function of the middle ear bones?
Why is most of the incoming wave intensity lost for the hearing process?
Why is most of the incoming wave intensity lost for the hearing process?
What is the frequency range in which the ear is most sensitive?
What is the frequency range in which the ear is most sensitive?
What is the role of the tympanic membrane in sound wave transmission?
What is the role of the tympanic membrane in sound wave transmission?
What is the primary function of the inner ear?
What is the primary function of the inner ear?
What structure connects the cochlea to the middle ear?
What structure connects the cochlea to the middle ear?
What is the purpose of the basilar membrane?
What is the purpose of the basilar membrane?
What type of sensory cells are found along the basilar membrane?
What type of sensory cells are found along the basilar membrane?
What happens when sound energy is transmitted to the cochlea?
What happens when sound energy is transmitted to the cochlea?
What is the result of the hair cells shearing on the tectorial membrane?
What is the result of the hair cells shearing on the tectorial membrane?
Where do high frequency sounds produce the greatest motion of the basilar membrane?
Where do high frequency sounds produce the greatest motion of the basilar membrane?
What is the purpose of the Reissner membrane?
What is the purpose of the Reissner membrane?
What does the cochlea resemble in shape?
What does the cochlea resemble in shape?
What type of testing is represented by the symbol 'O' in the figure?
What type of testing is represented by the symbol 'O' in the figure?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
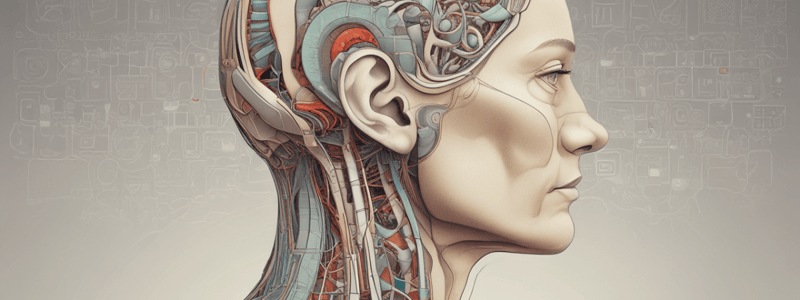
Hearing System
- The ear is the organ that detects sound and aids in balance and body position.
- It consists of three parts: outer, middle, and inner ears.
- The ear is a converter of weak mechanical waves in air into electrical pulses in the auditory nerve.
Parts of the Ear
- Outer Ear:
- Collects and directs sound waves towards the tympanic membrane.
- Consists of pinna, auditory canal, and tympanic membrane.
- Pinna:
- Collects sound, acting as a funnel to amplify sound and directing sound toward the ear canal.
- Protects the eardrum from shocks and prevents harmful items from entering the ear canal.
- Auditory canal:
- A tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear.
- Functions:
- Protects the ear from excessive vibrations.
- Amplifies sound by acting as a resonator.
- Middle Ear:
- Transfers sound from the outer ear to the inner ear.
- Consists of hammer, anvil, and stirrup.
- Functions:
- Acts as a lever system to amplify the pressure on the oval window.
- Filter out noise generated in the body.
- Inner Ear:
- Transforms the energy of compressional waves into nerve impulses.
- Consists of:
- Cochlea: a snail-shaped structure that converts sound waves into electrical signals.
- Vestibular chamber, middle chamber, and tympanic chamber.
- Basilar membrane: separates the scala media from the scala tympani.
- Hair cells: respond to the frequency of sound waves.
- Functions:
- High frequency sounds produce the greatest motion of the basilar membrane near the oval window.
- Low frequency sounds produce the greatest motion of the basilar membrane farthest from the apex.
- Different nerve cells produce electrical pulses depending on the frequency of sound waves.
Hearing Loss (Deafness)
- Not covered in this lecture.
Hearing Test (Audiometer)
- Not covered in this lecture.
Additional Notes
- The velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s.
- The resonance of the ear canal enhances the sensitivity of the ear in the higher frequency range (2000-10000 Hz).
- The best sensitivity of the ear is in the region 2000-4000 Hz.
- Reflection and transmission of acoustical signals at the tympanic membrane occur due to impedance mismatch.
- The middle ear bones act as a lever system to amplify the pressure on the oval window.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.