Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscles are primarily responsible for scapular winging?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for scapular winging?
- Rhomboids and serratus anterior (correct)
- Pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi
- Upper trapezius and internal oblique
- Cervical spine extensors and rectus abs
What condition is indicated by noticeable protrusion of the inferior angle of the scapulae?
What condition is indicated by noticeable protrusion of the inferior angle of the scapulae?
- Shoulder adduction
- Scapular protraction
- Kyphosis
- Winged scapulae (correct)
Which observation is associated with tightness in the pectoralis minor and internal oblique muscles?
Which observation is associated with tightness in the pectoralis minor and internal oblique muscles?
- Kyphosis and depressed chest (correct)
- Asymmetry to midline
- Forward-head position
- Protracted shoulders
In an individual with a forward-head position, which muscle group is likely to be tight?
In an individual with a forward-head position, which muscle group is likely to be tight?
What is the most common muscle group implicated in shoulders that are protracted?
What is the most common muscle group implicated in shoulders that are protracted?
What condition may indicate quadriceps and hip flexor dominance during movement initiation at the knees?
What condition may indicate quadriceps and hip flexor dominance during movement initiation at the knees?
Which factor contributes to an inability to keep heels in contact with the floor?
Which factor contributes to an inability to keep heels in contact with the floor?
What could a lack of parallelism between the tibia and torso imply?
What could a lack of parallelism between the tibia and torso imply?
What might a deficiency in gluteus group activation suggest?
What might a deficiency in gluteus group activation suggest?
Which issue is related to tightness in the plantar flexors?
Which issue is related to tightness in the plantar flexors?
What is the likely effect of poor mechanics during movement?
What is the likely effect of poor mechanics during movement?
Which problem could result from insufficient activation of hip extensors?
Which problem could result from insufficient activation of hip extensors?
What is a common effect of an inability to achieve heel contact during movement?
What is a common effect of an inability to achieve heel contact during movement?
What does excessive arching of the lumbar spine indicate?
What does excessive arching of the lumbar spine indicate?
Which group of muscles is primarily involved in stabilizing the movement despite weakness?
Which group of muscles is primarily involved in stabilizing the movement despite weakness?
What can result from weakness in the back of the knee and calves?
What can result from weakness in the back of the knee and calves?
What is a likely outcome of poor mechanics in the back?
What is a likely outcome of poor mechanics in the back?
Which muscle group does NOT typically help with the lowering phase of movement?
Which muscle group does NOT typically help with the lowering phase of movement?
What is a consequence of weakness in the core during movement?
What is a consequence of weakness in the core during movement?
The hamstrings play a crucial role in which phase of movement?
The hamstrings play a crucial role in which phase of movement?
Which condition could be implicated by weak hamstrings and poor mechanics?
Which condition could be implicated by weak hamstrings and poor mechanics?
What muscle coupling relationship is associated with anterior pelvic tilt due to tight hip flexors?
What muscle coupling relationship is associated with anterior pelvic tilt due to tight hip flexors?
Which muscles are generally suspected to be lengthened during posterior pelvic tilt?
Which muscles are generally suspected to be lengthened during posterior pelvic tilt?
How many degrees of motion are attributed to the scapulothoracic region during shoulder movements?
How many degrees of motion are attributed to the scapulothoracic region during shoulder movements?
What is the consequence of foot pronation on pelvic tilt and lumbar lordosis?
What is the consequence of foot pronation on pelvic tilt and lumbar lordosis?
What occurs at the ASIS during anterior pelvic tilt?
What occurs at the ASIS during anterior pelvic tilt?
Which lifestyle habit is commonly associated with tight hip flexors leading to anterior pelvic tilt?
Which lifestyle habit is commonly associated with tight hip flexors leading to anterior pelvic tilt?
What is the primary action of the shoulder girdle during combined movements at the glenohumeral and scapulothoracic joints?
What is the primary action of the shoulder girdle during combined movements at the glenohumeral and scapulothoracic joints?
What commonly leads to compensations in shoulder movement?
What commonly leads to compensations in shoulder movement?
What substance is formed during glycolysis that contributes to muscle fatigue?
What substance is formed during glycolysis that contributes to muscle fatigue?
Which metabolic processes are involved in the oxidative system?
Which metabolic processes are involved in the oxidative system?
How does the oxidative system compare to the glycolytic system in terms of ATP production speed?
How does the oxidative system compare to the glycolytic system in terms of ATP production speed?
During which type of exercise would the glycolytic system be primarily utilized?
During which type of exercise would the glycolytic system be primarily utilized?
What happens to blood sugar during exercise when intense activity occurs?
What happens to blood sugar during exercise when intense activity occurs?
What is the heart rate zone for warm-up or recovery training?
What is the heart rate zone for warm-up or recovery training?
Which of the following is true about the duration of activities for the oxidative system?
Which of the following is true about the duration of activities for the oxidative system?
What is the average resting heart rate (RHR) of an adult human?
What is the average resting heart rate (RHR) of an adult human?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
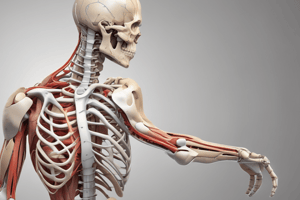
Movement Mechanics and Joint Relationships
- Sagittal plane analysis reveals issues like inability to keep heels down, indicating plantar flexor weakness.
- Hip and knee initiation often points to quadriceps and hip flexor dominance, potentially indicating gluteus group activation insufficiency.
- Tibia and torso relationship can show poor mechanics due to tight dorsiflexors leading to an inability to parallel the tibia and torso.
- Lumbar and thoracic spine issues may be characterized by excessive arching or rounding, which can involve core and hip muscles.
Pelvic Tilting
- Anterior pelvic tilt is common in sedentary individuals with tight hip flexors, leading to tight erector spinae as part of Lower-Cross Syndrome.
- Posterior pelvic tilt is associated with tight rectus abdominis and hamstrings, indicating muscle imbalances.
- Foot pronation and internal femoral rotation may contribute to anterior pelvic tilt, enhancing lumbar lordosis.
Shoulder and Thoracic Spine
- Shoulder movement limitations arise from complex girdle design, requiring collaboration between glenohumeral joint and scapulothoracic movements.
- Tight upper trapezius, levator scapulae, and rhomboids manifest as shoulder height differences or postural asymmetries.
- Scapular protraction and winging indicate compromised scapula stabilizers like rhomboids and serratus anterior.
- A forward head position often results from tight cervical extensors and upper trapezius, misaligning the earlobe from the acromion.
Energy Systems
- Glycolytic system relies on rapid carbohydrate breakdown for ATP production, effective for high-intensity efforts lasting 1-2 minutes.
- Lactate and hydrogen ions accumulation from glycolysis contribute to muscle fatigue and burning sensation.
- Oxidative system utilizes oxygen, carbs, fats, and proteins for longer-duration energy output but works slower than glycolytic and phosphagen systems.
- It is crucial for sustained efforts like marathon running.
Heart Rate Zones
- Resting heart rate averages between 60-80 beats per minute (BPM) and increases with exercise to meet muscle oxygen and nutrient demands.
- Five distinct heart rate zones correspond to different exercise responses and benefits, starting from low-intensity warm-up/recovery in Zone 1.
- Training in different zones enhances cardiovascular fitness and overall exercise performance.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.