Podcast
Questions and Answers
Can animals be asymmetric?
Can animals be asymmetric?
Yes, animals can be asymmetric; for example, sponges are mostly asymmetric.
What is radial symmetry?
What is radial symmetry?
Symmetry around a central point; for example, a sea star.
What is the difference between the oral and the aboral side of an animal?
What is the difference between the oral and the aboral side of an animal?
The oral side is where the mouth is located; the aboral side is the surface that is furthest away from the mouth.
What is bilateral symmetry?
What is bilateral symmetry?
How do animals with bilateral symmetry differ from animals who have radial symmetry, and how are these animals' perspectives different?
How do animals with bilateral symmetry differ from animals who have radial symmetry, and how are these animals' perspectives different?
Is either form of symmetry superior?
Is either form of symmetry superior?
Define these terms: anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral, proximal, distal, superior, inferior, lateral.
Define these terms: anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral, proximal, distal, superior, inferior, lateral.
When do animals appear for the first time in the fossil record?
When do animals appear for the first time in the fossil record?
Why did 19th century biologists view the Cambrian period as the starting point of animal life?
Why did 19th century biologists view the Cambrian period as the starting point of animal life?
What is interesting about the Cambrian Period?
What is interesting about the Cambrian Period?
What is interesting about the Burgess Shale?
What is interesting about the Burgess Shale?
Approximately when did the first animals appear in the fossil record?
Approximately when did the first animals appear in the fossil record?
What is the importance of the Cambrian explosion?
What is the importance of the Cambrian explosion?
What is unusual about the animal fossils found at the Burgess Shale?
What is unusual about the animal fossils found at the Burgess Shale?
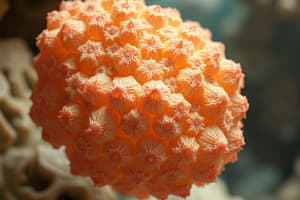
Briefly characterize the phylum Porifera.
Briefly characterize the phylum Porifera.
Are sponges symmetric, asymmetric, or both? Explain.
Are sponges symmetric, asymmetric, or both? Explain.
What kind of cell types exist in a sponge, and briefly describe them and their role?
What kind of cell types exist in a sponge, and briefly describe them and their role?
Sponges are considered to lack tissues. Explain. What kind of experiment would demonstrate that sponges lack tissues?
Sponges are considered to lack tissues. Explain. What kind of experiment would demonstrate that sponges lack tissues?
Describe the structure and function of the choanocyte/collar cell.
Describe the structure and function of the choanocyte/collar cell.
How does a sponge feed? What do they feed on?
How does a sponge feed? What do they feed on?
What are spicules, what are they made of, and what is their function?
What are spicules, what are they made of, and what is their function?
Do all sponges have spicules? What are spongin fibers?
Do all sponges have spicules? What are spongin fibers?
All the cells in a sponge are genetically identical. Why is this important?
All the cells in a sponge are genetically identical. Why is this important?
What are the differences between asconoid, syconoid, and leuconoid sponges?
What are the differences between asconoid, syconoid, and leuconoid sponges?
Many species within the phylum are hermaphrodites. Explain.
Many species within the phylum are hermaphrodites. Explain.
Briefly describe the life cycle of a typical sponge.
Briefly describe the life cycle of a typical sponge.
Can sponges move at any time in their life cycle? When?
Can sponges move at any time in their life cycle? When?
Several research groups are actively extracting chemicals from different sponge species. What is the purpose of these studies?
Several research groups are actively extracting chemicals from different sponge species. What is the purpose of these studies?
Flashcards
What is Phylum Porifera?
What is Phylum Porifera?
Phylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges, includes approximately 5,500 described species found mostly in marine environments.
Describe the structure of sponges.
Describe the structure of sponges.
Sponges are asymmetrical organisms lacking true tissues and organs, but possess specialized cells for specific functions.
What symmetry do sponges exhibit?
What symmetry do sponges exhibit?
Symmetry in animals refers to the arrangement of body parts. Sponges are asymmetrical, lacking any specific body plan.
What are the types of symmetry in animals?
What are the types of symmetry in animals?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When did animals first appear in the fossil record?
When did animals first appear in the fossil record?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Cambrian Explosion?
What is the Cambrian Explosion?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Burgess Shale?
What is the Burgess Shale?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main cell types in sponges?
What are the main cell types in sponges?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are choanocytes and their function?
What are choanocytes and their function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are pinacocytes and their function?
What are pinacocytes and their function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are amoebocytes and their function?
What are amoebocytes and their function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are spicules and their function?
What are spicules and their function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do sponges reproduce?
How do sponges reproduce?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the reproductive advantage of hermaphroditism in sponges?
What is the reproductive advantage of hermaphroditism in sponges?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the mobility of sponges?
Describe the mobility of sponges?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are sponge larvae important?
Why are sponge larvae important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain the different canal systems in sponges.
Explain the different canal systems in sponges.
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do sponge canal systems evolve?
How do sponge canal systems evolve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the potential medical applications of sponges?
What are the potential medical applications of sponges?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do bioactive compounds from sponges contribute to medical research?
How do bioactive compounds from sponges contribute to medical research?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a key characteristic of Porifera?
What is a key characteristic of Porifera?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain the evolutionary significance of Porifera.
Explain the evolutionary significance of Porifera.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the ecological importance of sponges in marine ecosystems?
What is the ecological importance of sponges in marine ecosystems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a unique feature of sponges?
What is a unique feature of sponges?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where can sponges be found?
Where can sponges be found?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Phylum Porifera Overview
- Porifera, commonly known as sponges, includes approximately 5,500 described species, predominantly marine and mostly asymmetrical.
- Sponges lack true tissues and organs but possess specialized cells that perform distinct functions, indicating a primitive structure in evolution.
Symmetry in Animals
- Animals can exhibit various forms of symmetry: asymmetry (e.g., sponges), radial symmetry (e.g., sea stars), and bilateral symmetry (e.g., humans and worms).
- Bilateral symmetry allows for a clear distinction between anterior (head) and posterior (rear) ends, promoting directional movement, while radial symmetry typically results in a sessile lifestyle.
Cambrian Period Significance
- The Cambrian Period marks the first appearance of animals in the fossil record, approximately 540 to 550 million years ago, characterized by a rapid increase in species diversity known as the "Cambrian Explosion."
- The Burgess Shale is a key fossil site from the Cambrian Period, offering insights into early animal evolution with fossils that represent original body plans.
Sponge Structure and Function
- Sponges feature three main cell types:
- Choanocytes (collar cells) with flagella that facilitate digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Pinacocytes, which form the outer layer of the sponge.
- Amoebocytes, which transport food, create spicules, and produce gametes.
- Spicules, composed of calcium carbonate or silica, provide structural support, aiding in species identification.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
- Sponges can reproduce sexually (sperm release and fertilization) and asexually (fragmentation, budding, or producing gemmules).
- Many species are hermaphrodites, possessing both male and female sex cells to enhance reproductive success.
Sponge Mobility and Ecology
- Adult sponges are primarily sessile or slow-moving, while sponge larvae are free-swimming and planktonic, crucial for understanding reproduction strategies.
- The evolution of various canal systems in sponges (asconoid, syconoid, and leuconoid) reflects adaptations to environmental factors like light and water turbidity.
Chemical Research and Applications
- Ongoing research involves extracting bioactive compounds from sponges for potential medical applications, particularly in treating diseases like cancer by inhibiting cell growth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.