Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary concern with oral and enteral medication administration regarding absorption?
What is the primary concern with oral and enteral medication administration regarding absorption?
- They are always more effective than subcutaneous routes.
- They require intravenous access.
- They are affected by the first pass effect. (correct)
- They have a faster onset of action than inhaled medications.
Which route of medication administration bypasses the first pass effect?
Which route of medication administration bypasses the first pass effect?
- Transdermal (correct)
- Intramuscular
- Oral
- Enteral
What happens to medications that are protein-bound in the bloodstream?
What happens to medications that are protein-bound in the bloodstream?
- They become more effective.
- They are excreted unchanged.
- They are considered inactive. (correct)
- They create an action at a receptor site.
In the context of absorption, why is the GI tract a challenging environment for medications?
In the context of absorption, why is the GI tract a challenging environment for medications?
How does the first pass effect influence the dosing of oral medications?
How does the first pass effect influence the dosing of oral medications?
Which administration route directly injects medication into the fat tissue beneath the skin?
Which administration route directly injects medication into the fat tissue beneath the skin?
What is NOT a common route for administering medications?
What is NOT a common route for administering medications?
What is the main advantage of using alternate routes of medication administration?
What is the main advantage of using alternate routes of medication administration?
Why might providers prefer using alternate routes for administering drugs?
Why might providers prefer using alternate routes for administering drugs?
Which statement accurately reflects the impact of the liver on drug absorption?
Which statement accurately reflects the impact of the liver on drug absorption?
What is a significant drawback of transdermal drug delivery?
What is a significant drawback of transdermal drug delivery?
How does intravenous (IV) medication administration differ from other routes?
How does intravenous (IV) medication administration differ from other routes?
In older adults, what physiological change can affect the absorption of medications?
In older adults, what physiological change can affect the absorption of medications?
What common issue arises from subcutaneous and intramuscular injection routes?
What common issue arises from subcutaneous and intramuscular injection routes?
What characteristic of inhaled drug delivery influences its effectiveness?
What characteristic of inhaled drug delivery influences its effectiveness?
What condition can lead to increased drug levels in the bloodstream of neonate and pediatric patients?
What condition can lead to increased drug levels in the bloodstream of neonate and pediatric patients?
Why might patients prefer transdermal patches for long-term medication administration?
Why might patients prefer transdermal patches for long-term medication administration?
Why is the first-pass effect considered detrimental for oral medications?
Why is the first-pass effect considered detrimental for oral medications?
What factor related to aging can affect the absorption of medications delivered via transdermal routes?
What factor related to aging can affect the absorption of medications delivered via transdermal routes?
What unique feature does inhaled insulin need to have for effective administration?
What unique feature does inhaled insulin need to have for effective administration?
Which medication route is least likely to be affected by the first pass effect?
Which medication route is least likely to be affected by the first pass effect?
What is the primary mechanism that reduces the efficacy of orally administered protein-based drugs?
What is the primary mechanism that reduces the efficacy of orally administered protein-based drugs?
Which route of administration allows for a drug to enter systemic circulation while avoiding the gastrointestinal tract?
Which route of administration allows for a drug to enter systemic circulation while avoiding the gastrointestinal tract?
What best describes a potential outcome when a protein drug is administered orally?
What best describes a potential outcome when a protein drug is administered orally?
Which administration route is most effective for drugs requiring rapid effects in the bloodstream with minimal metabolic alteration?
Which administration route is most effective for drugs requiring rapid effects in the bloodstream with minimal metabolic alteration?
Which factor would most likely require a provider to consider alternative administration routes for certain medications?
Which factor would most likely require a provider to consider alternative administration routes for certain medications?
What challenge do drugs face when being absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract?
What challenge do drugs face when being absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract?
What therapeutic strategy can minimize the limitations posed by the first pass effect?
What therapeutic strategy can minimize the limitations posed by the first pass effect?
What is a primary disadvantage of using subcutaneous and intramuscular injections for medication administration?
What is a primary disadvantage of using subcutaneous and intramuscular injections for medication administration?
How does aging impact medication absorption in older adults?
How does aging impact medication absorption in older adults?
Which characteristic of transdermal drug delivery confers its primary advantage?
Which characteristic of transdermal drug delivery confers its primary advantage?
What factor must be considered when utilizing inhaled medication therapies?
What factor must be considered when utilizing inhaled medication therapies?
Which of the following statements about intravenous medications is accurate?
Which of the following statements about intravenous medications is accurate?
What unique challenge does the route of transdermal application face regarding drug molecules?
What unique challenge does the route of transdermal application face regarding drug molecules?
Why is consistency in drug levels critical in medication administration?
Why is consistency in drug levels critical in medication administration?
Which route of medication is particularly valuable for long-term symptom control?
Which route of medication is particularly valuable for long-term symptom control?
What is a notable factor affecting medication absorption in neonate and pediatric patients?
What is a notable factor affecting medication absorption in neonate and pediatric patients?
What is a common limitation of using inhaled insulin therapies?
What is a common limitation of using inhaled insulin therapies?
What is a principal concern with medications administered via the oral route?
What is a principal concern with medications administered via the oral route?
What challenge do injectable medications typically pose for patients?
What challenge do injectable medications typically pose for patients?
Which of the following best describes how drug accumulation in the body can occur?
Which of the following best describes how drug accumulation in the body can occur?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Absorption in Pharmacokinetics
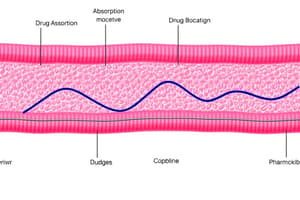
- Absorption is the first stage of pharmacokinetics, involving drug transition from the administration site into circulation.
- Various administration routes include oral, enteral, rectal, inhalation, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and transdermal.
Oral and Enteral Administration
- Oral and enteral routes face challenges, especially in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
- Protein medications may be inactivated by stomach enzymes.
- First pass effect occurs when drugs are metabolized by liver enzymes after absorption, reducing bioavailability.
- Multiple doses may be required for effective therapy due to the effects of liver metabolism.
Alternative Administration Routes
- Bypassing the first pass effect can be achieved through alternative routes: dermal, nasal, inhalation, injection, and intravenous.
- Intravenous (IV) medications enter the bloodstream directly, offering full bioavailability without absorption.
Transdermal Drug Delivery
- Transdermal patches provide slow, steady drug delivery, avoiding liver metabolism.
- Useful for prolonged symptom management (e.g., fentanyl for pain, scopolamine for motion sickness, nitroglycerin for chest pain).
- Limitations include only small drug molecules being absorbable through the skin.
Inhalation Route
- Inhalation techniques deliver medication rapidly while bypassing liver metabolism.
- Metered-dose inhalers are commonly used for asthma; nasal steroids address allergies and sinus issues.
- Emerging options include inhaled insulin, such as Afrezza®, designed for optimal particle size for absorption.
Lifespan Considerations
- Neonate and pediatric gastric absorption is different; immature stomach acids and irregular peristalsis affect absorption.
- Neonates exhibit higher plasma drug levels due to decreased first-pass elimination.
- In older adults, decreased GI blood flow, altered gastric pH, and variations in plasma proteins can impact absorption.
- Decreased body fat in older adults may also hinder transdermal patch effectiveness.
Route Considerations Summary
- Oral/Enteral: Convenient, but impacted by factors like food, gastric pH, and the first pass effect.
- Injection (Subcutaneous/Intramuscular): Can be painful and difficult; risk of infection and fluctuations in drug levels.
- Intravenous: Immediate effect with full bioavailability, but requires sterile technique and has a higher infection risk.
- Inhalation: Quick absorption dependent on particle size; effective for respiratory treatments.
- Topical/Transdermal: Topical for local effects; transdermal for systemic effects with steady absorption avoiding the first pass effect.
Absorption in Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption is the first stage of pharmacokinetics, involving drug transition from the administration site into circulation.
- Various administration routes include oral, enteral, rectal, inhalation, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and transdermal.
Oral and Enteral Administration
- Oral and enteral routes face challenges, especially in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
- Protein medications may be inactivated by stomach enzymes.
- First pass effect occurs when drugs are metabolized by liver enzymes after absorption, reducing bioavailability.
- Multiple doses may be required for effective therapy due to the effects of liver metabolism.
Alternative Administration Routes
- Bypassing the first pass effect can be achieved through alternative routes: dermal, nasal, inhalation, injection, and intravenous.
- Intravenous (IV) medications enter the bloodstream directly, offering full bioavailability without absorption.
Transdermal Drug Delivery
- Transdermal patches provide slow, steady drug delivery, avoiding liver metabolism.
- Useful for prolonged symptom management (e.g., fentanyl for pain, scopolamine for motion sickness, nitroglycerin for chest pain).
- Limitations include only small drug molecules being absorbable through the skin.
Inhalation Route
- Inhalation techniques deliver medication rapidly while bypassing liver metabolism.
- Metered-dose inhalers are commonly used for asthma; nasal steroids address allergies and sinus issues.
- Emerging options include inhaled insulin, such as Afrezza®, designed for optimal particle size for absorption.
Lifespan Considerations
- Neonate and pediatric gastric absorption is different; immature stomach acids and irregular peristalsis affect absorption.
- Neonates exhibit higher plasma drug levels due to decreased first-pass elimination.
- In older adults, decreased GI blood flow, altered gastric pH, and variations in plasma proteins can impact absorption.
- Decreased body fat in older adults may also hinder transdermal patch effectiveness.
Route Considerations Summary
- Oral/Enteral: Convenient, but impacted by factors like food, gastric pH, and the first pass effect.
- Injection (Subcutaneous/Intramuscular): Can be painful and difficult; risk of infection and fluctuations in drug levels.
- Intravenous: Immediate effect with full bioavailability, but requires sterile technique and has a higher infection risk.
- Inhalation: Quick absorption dependent on particle size; effective for respiratory treatments.
- Topical/Transdermal: Topical for local effects; transdermal for systemic effects with steady absorption avoiding the first pass effect.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.