Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the ACE Scanner?
What is the primary function of the ACE Scanner?
- To scan documents and images (correct)
- To analyze financial data
- To enhance digital security
- To perform optical character recognition
Which of the following features is least likely to be associated with the ACE Scanner?
Which of the following features is least likely to be associated with the ACE Scanner?
- High-resolution scanning
- Real-time data processing
- Batch scanning capabilities
- Secure data encryption (correct)
How does the ACE Scanner most likely improve efficiency in document management?
How does the ACE Scanner most likely improve efficiency in document management?
- By offering customizable scanning resolutions
- By integrating with other management systems
- By providing automatic text recognition (correct)
- By reducing file sizes automatically
In terms of output quality, which aspect is crucial for the ACE Scanner's operation?
In terms of output quality, which aspect is crucial for the ACE Scanner's operation?
What potential issue might arise during the use of the ACE Scanner?
What potential issue might arise during the use of the ACE Scanner?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
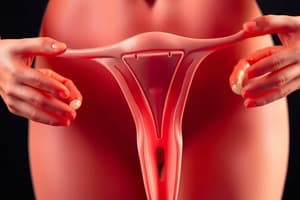
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- PCOS is a hormonal condition affecting women, causing higher-than-normal male hormone levels.
- This imbalance leads to skipped menstrual periods and difficulty getting pregnant.
- PCOS also causes increased hair growth on the face and body, as well as baldness.
- It can contribute to long-term health issues like heart disease.
- PCOS involves fluid-filled sacs (follicles) inside the ovaries.
- These sacs contain immature eggs, preventing ovulation.
- This disruption alters hormone levels (estrogen, progesterone, FSH, LH) and increases male hormone levels.
- Women with PCOS tend to have fewer periods than usual.
Pathophysiology of PCOS
- Doctors don't fully understand the causes of PCOS.
- High male hormone levels, genes, insulin resistance, and inflammation are believed to be linked to excess male hormone production in PCOS.
- Genetic factors may play a role in PCOS development (runs in families).
Insulin Resistance in PCOS
- Up to 70% of women with PCOS have insulin resistance.
- This means cells cannot properly utilize insulin.
- Insulin resistance causes the body to produce more insulin to compensate.
- Increased insulin triggers the ovaries to produce more male hormones.
- Obesity is a major cause of insulin resistance.
- Both obesity and insulin resistance increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
PCOS Symptoms
- Irregular Periods: Fewer than eight periods a year and unpredictable bleeding cycles are common.
- Heavy Bleeding: Periods with heavier flow than normal are sometimes seen.
- Hair Growth: More than 70% of women with PCOS experience increased hair growth on their face, body (hirsutism), back, belly, chest.
- Acne: Increased oil production and breakouts are common, particularly on the face, chest, and upper back.
- Weight Gain: PCOS is often linked to weight gain, with approximately 80% of women with the condition overweight or obese.
- Male-pattern Baldness: Hair thinning or loss on the scalp.
- Skin Changes: Darkening of skin in body folds (neck, groin, under breasts).
- Headaches: Hormone changes can trigger headaches.
PCOS and Fertility
- Ovulation is necessary for pregnancy.
- Women with PCOS often don't ovulate regularly. This significantly impacts fertility.
- This is one of the leading causes of infertility in women.
PCOS and Metabolic Syndrome
- Up to 80% of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
- PCOS increases the risk of high blood sugar, high blood pressure, low "good" cholesterol (HDL), and high "bad" cholesterol (LDL).
- These conditions create a metabolic syndrome, further raising the risk of heart disease, diabetes and stoke.
PCOS and Sleep Apnea
- Sleep apnea, which causes repeated pauses in breathing, is more common in obese women who also have PCOS.
- The risk is 5-10 times higher in women with PCOS.
PCOS and Endometrial Cancer
- Irregular ovulation can lead to uterine lining thickening.
- A thickened uterine lining increases endometrial cancer risk.
Diagnosis of PCOS
- Doctors typically diagnose PCOS in women showing at least two of these three symptoms:
- High androgen levels
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Cysts in the ovaries
PCOS Management
- Treatment often starts with lifestyle changes focusing on diet, exercise, and weight loss.
- Losing 5-10% body weight can improve menstrual regularity, insulin levels, and cholesterol.
- Low glycemic index (low-GI) diets emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help regulate menstrual cycles more effectively.
- Medical treatments (birth control pills, metformin, anti-androgens) help manage specific symptoms.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.