Podcast
Questions and Answers
What do autotrophic bacteria use to synthesize their food?
What do autotrophic bacteria use to synthesize their food?
- Inorganic substances (correct)
- Organic substances
- Parasitic means
- Saprophytic means
Which type of bacteria obtains food from organic substances, living or dead?
Which type of bacteria obtains food from organic substances, living or dead?
- Heterotrophic bacteria (correct)
- Autotrophic bacteria
- Chemosynthetic bacteria
- Photosynthetic bacteria
Which type of oxygen requirement category do bacteria fall into if oxygen inhibits their growth?
Which type of oxygen requirement category do bacteria fall into if oxygen inhibits their growth?
- Obligate aerobe
- Facultative aerobe
- Obligate anaerobe (correct)
- None of the above
Which of the following is a Gram-positive bacterium?
Which of the following is a Gram-positive bacterium?
Which of the following bacteria require oxygen for growth?
Which of the following bacteria require oxygen for growth?
What is suggested to do first?
What is suggested to do first?
What language is used in the main instruction?
What language is used in the main instruction?
What is the main purpose of the given instructions?
What is the main purpose of the given instructions?
Which web button is mentioned to proceed after downloading?
Which web button is mentioned to proceed after downloading?
The instruction suggests the files are:
The instruction suggests the files are:
What component of the bacterial outer wall does the gram stain depend on?
What component of the bacterial outer wall does the gram stain depend on?
What color does Gram-positive bacteria stain?
What color does Gram-positive bacteria stain?
Which type of specimen is used to diagnose respiratory infections in the laboratory?
Which type of specimen is used to diagnose respiratory infections in the laboratory?
What color does Gram-negative bacteria stain?
What color does Gram-negative bacteria stain?
Which type of specimen is used to diagnose urinary tract infections?
Which type of specimen is used to diagnose urinary tract infections?
Which part of a thin blood film is nearest to the drop of blood?
Which part of a thin blood film is nearest to the drop of blood?
What criteria indicate a well-prepared blood smear?
What criteria indicate a well-prepared blood smear?
What is the optimal angle of the spreader slide when making a blood smear?
What is the optimal angle of the spreader slide when making a blood smear?
How long should the blood film be fixed with methyl alcohol before staining?
How long should the blood film be fixed with methyl alcohol before staining?
Which type of stain is used for blood smears?
Which type of stain is used for blood smears?
Which factor does NOT affect the length and thickness of a blood smear?
Which factor does NOT affect the length and thickness of a blood smear?
Which blood group is considered the universal donor?
Which blood group is considered the universal donor?
What antigens are present in the red blood cells of someone with blood group AB?
What antigens are present in the red blood cells of someone with blood group AB?
What antibodies are present in the plasma of someone with blood group A?
What antibodies are present in the plasma of someone with blood group A?
Which blood group has no antibodies in the plasma?
Which blood group has no antibodies in the plasma?
What is the percentage of people with Rh positive blood?
What is the percentage of people with Rh positive blood?
Who can receive blood from both Rh positive and Rh negative donors?
Who can receive blood from both Rh positive and Rh negative donors?
What is the study of microscopic organisms called?
What is the study of microscopic organisms called?
Which of the following is NOT considered a microorganism?
Which of the following is NOT considered a microorganism?
What is the typical size of microorganisms?
What is the typical size of microorganisms?
Which of the following is a shape of bacteria?
Which of the following is a shape of bacteria?
Which microorganism is an example of a rod-shaped bacterium?
Which microorganism is an example of a rod-shaped bacterium?
Which shape describes the appearance of Vibrio cholera?
Which shape describes the appearance of Vibrio cholera?
Which microorganism classification lacks a nuclear membrane?
Which microorganism classification lacks a nuclear membrane?
What is one important role of normal flora in humans?
What is one important role of normal flora in humans?
What percentage of people are Rh positive?
What percentage of people are Rh positive?
Which blood type can Rh positive individuals receive blood from?
Which blood type can Rh positive individuals receive blood from?
Why is it important to determine Rh incompatibility between a mother and her child?
Why is it important to determine Rh incompatibility between a mother and her child?
Which is considered a universal donor blood group?
Which is considered a universal donor blood group?
Which is considered a universal recipient blood group?
Which is considered a universal recipient blood group?
Why must the Rh factor be examined during blood transfusions?
Why must the Rh factor be examined during blood transfusions?
Which blood type has both A and B antigens on the surface of red blood cells?
Which blood type has both A and B antigens on the surface of red blood cells?
Which blood type has neither A nor B antibodies in blood plasma?
Which blood type has neither A nor B antibodies in blood plasma?
Which blood type has A antibodies in blood plasma?
Which blood type has A antibodies in blood plasma?
What antigens and antibodies are present in Blood Type O?
What antigens and antibodies are present in Blood Type O?
Which blood type has B antigens on the surface of red blood cells?
Which blood type has B antigens on the surface of red blood cells?
What are antigens?
What are antigens?
What determines an individual's blood group?
What determines an individual's blood group?
What happens when incompatible blood groups are mixed?
What happens when incompatible blood groups are mixed?
How many genetically determined blood group systems are known today?
How many genetically determined blood group systems are known today?
What blood types are included in the ABO blood typing system?
What blood types are included in the ABO blood typing system?
What antibodies are present in the blood plasma of an individual with blood group A?
What antibodies are present in the blood plasma of an individual with blood group A?
Which type of blood cell carries oxygen throughout the body?
Which type of blood cell carries oxygen throughout the body?
What is the main purpose of a blood smear test?
What is the main purpose of a blood smear test?
Which condition is NOT a reason for conducting a blood smear test?
Which condition is NOT a reason for conducting a blood smear test?
Which of the following is a type of blood film used for the detection of parasites like malaria?
Which of the following is a type of blood film used for the detection of parasites like malaria?
What is the function of platelets in the blood?
What is the function of platelets in the blood?
Which step is NOT involved in preparing a thin blood film?
Which step is NOT involved in preparing a thin blood film?
What is the angle at which the spreader (another slide) should be placed near the drop of blood?
What is the angle at which the spreader (another slide) should be placed near the drop of blood?
Why is fixation NOT used in thick blood film preparation?
Why is fixation NOT used in thick blood film preparation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
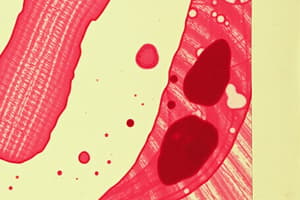
Parts of a Thin Blood Film
- A peripheral blood film consists of three parts: Head (portion of blood film near the drop of blood), Body (main part of the blood film), and Tail (tapering end of the blood film)
Features of a Good Blood Smear
- A well-prepared smear covers about three-fourths of the slide and should show a gradual transition from thick to thin
- It should have a smooth appearance, with no holes or ridges, and a feathered edge (about 1.5 cm long) at the thin end of the smear
- When the smear is examined microscopically, the cells should be evenly distributed, with an area at the thin end of the smear where RBCs are not overlapping
Factors Affecting Blood Smear Quality
- The length and thickness of the smear are affected by the size of the drop of blood (medium size), the angle of the spreader slide (30-45 degrees), and the speed at which the smear is made
Fixing of Blood Films
- Before staining, the blood film needs to be fixed with methyl alcohol for 0.5 to 2 minutes to prevent hemolysis
Staining Blood Smears
- There are many types of blood staining, including Giemsa stain, Wright's stain, and Leishman stain
Bacterial Nutrition
Autotrophic Bacteria
- Synthesize all their food from inorganic substances (CO2 and hydrogen donor)
- Include two types: photosynthetic bacteria and chemosynthetic bacteria
Heterotrophic Bacteria
- Obtain their ready-made food from organic substances, living or dead
- Include three types: saprophytic bacteria, parasitic bacteria, and symbiotic bacteria
Oxygen Requirements
- Obligate aerobe: require O2
- Facultative aerobe: O2 not required but better growth when present
- Obligate anaerobe: O2 inhibits bacterial growth
Reaction to the Gram Stain
- Bacteria are divided into two groups according to the reaction with Gram stain
- Gram-positive bacteria: Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Bacillus, and Clostridium
- Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, etc.
Gram Stain
- Gram-positive: peptidoglycan (cell wall) = blue
- Gram-negative: lipopolysaccharide (cell wall) = red
Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Disease
- It depends on clinical specimens reaching the lab
- Examples of specimens: Blood, Urine, Stool, Sputum, Vaginal swabs, Nose & ear swabs, Cerebral spinal fluid, Food & vomit
Introduction to Microbiology
- Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms
- Microorganisms (MOs) include protozoa, algae, fungi, bacteria, and viruses
- MOs are present in vast numbers everywhere on the bodies of animals and humans, on plant surfaces, in the air, food, water, dust, soil
- MOs include normal flora, which prevents the spread and growth of fungi and harmful bacteria
Bacteria
- Bacteria (prokaryotes, together with Archaea) share many common features
- Common features: lack of a nuclear membrane, unicellularity, division by binary-fission, and generally small size
- Species can be differentiated through the comparison of several characteristics, allowing their identification and classification
Classification of Bacteria
- Depends on the shape of bacteria
- Examples:
- Cocci (Spherical): Diplococci, Chain (Cocci), Cluster or Grape like shape
- Bacilli: Lactobacillus.spp. (rod shaped)
- Spiral shape: Helicobacter pylori
- Comma shape: Vibrio cholera
Blood Smear
- A blood smear is a blood test used to look for abnormalities in blood cells
- The test focuses on the number and shape of red cells, white cells, and platelets
- Provides information on the number and shape of these cells, which can help diagnose certain blood disorders or other medical conditions
Why is a Blood Smear Done?
- To diagnose conditions that are causing unexplained jaundice, unexplained anemia, sudden weight loss, severe infection, skin rashes or cuts, bone pain
- A blood film report can provide rapidly and at low cost, useful information about a patient's condition
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.