Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements accurately describes the anatomical location of the pancreas?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the anatomical location of the pancreas?
- Situated in front of the small intestine, encapsulated by a thick muscle layer.
- Positioned within the abdominal wall, directly connected to the liver.
- Located anterior to the stomach and behind the spleen.
- Lies posterior to the stomach, stretching from the duodenum to the spleen. (correct)
What is the primary function of insulin, produced by the pancreatic islets, in regulating blood sugar levels?
What is the primary function of insulin, produced by the pancreatic islets, in regulating blood sugar levels?
- To facilitate the conversion of proteins into glucose when blood sugar is low.
- To lower blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake by cells. (correct)
- To accelerate the breakdown of complex sugars into simpler forms.
- To raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stored glucose from the liver.
If a patient's pancreas is not producing enough glucagon, which of the following conditions is most likely to occur?
If a patient's pancreas is not producing enough glucagon, which of the following conditions is most likely to occur?
- Hyperglycemia due to an overproduction of insulin.
- Hypoglycemia due to an insufficient release of glucose into the blood. (correct)
- Increased breakdown of proteins into glucose.
- Decreased absorption of glucose from the digestive tract.
Which of the following describes the exocrine function of the pancreas?
Which of the following describes the exocrine function of the pancreas?
What is the role of pancreatic juice secreted by the exocrine cells of the pancreas?
What is the role of pancreatic juice secreted by the exocrine cells of the pancreas?
How does pancreatic alpha-amylase contribute to the digestive process?
How does pancreatic alpha-amylase contribute to the digestive process?
Which enzyme secreted by the pancreas is primarily responsible for the digestion of fats?
Which enzyme secreted by the pancreas is primarily responsible for the digestion of fats?
Damage to the acinar cells of the pancreas would most directly affect which function?
Damage to the acinar cells of the pancreas would most directly affect which function?
What are the expected effects on urine production if the kidneys fail to reabsorb water properly in the collecting duct?
What are the expected effects on urine production if the kidneys fail to reabsorb water properly in the collecting duct?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus?
In which part of the nephron does the majority of reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, water, and salts occur?
In which part of the nephron does the majority of reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, water, and salts occur?
Which of the following correctly describes the function of the peritubular capillaries?
Which of the following correctly describes the function of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the functional significance of the vasa recta in the kidney?
What is the functional significance of the vasa recta in the kidney?
How does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) influence kidney function?
How does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) influence kidney function?
If a patient is diagnosed with glycosuria (glucose in the urine) but does not have diabetes, what other condition might be suspected?
If a patient is diagnosed with glycosuria (glucose in the urine) but does not have diabetes, what other condition might be suspected?
What is the expected effect on blood pressure if the kidneys secrete renin?
What is the expected effect on blood pressure if the kidneys secrete renin?
What is the functional significance of the hypertonic environment in the kidney's medulla?
What is the functional significance of the hypertonic environment in the kidney's medulla?
Which of the following situations would most likely lead to the secretion of erythropoietin (EPO) by the kidneys?
Which of the following situations would most likely lead to the secretion of erythropoietin (EPO) by the kidneys?
What is the role of the afferent arteriole in the glomerulus?
What is the role of the afferent arteriole in the glomerulus?
Which of the following best describes the composition of the filtrate in Bowman's capsule under normal physiological conditions?
Which of the following best describes the composition of the filtrate in Bowman's capsule under normal physiological conditions?
Flashcards
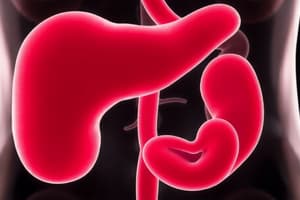
Location of Pancreas
Location of Pancreas
Lies behind the stomach, stretches from the duodenum to the spleen, attached to the posterior abdominal wall, and covered by a thin connective tissue capsule.
Endocrine Function of Pancreas
Endocrine Function of Pancreas
Pancreatic Islets (Islets of Langerhans); Insulin lowers blood sugar while Glucagon raises blood sugar.
Exocrine Function of Pancreas
Exocrine Function of Pancreas
Acinar cells + Duct epithelial cells. Secretes pancreatic juice (digestive enzymes + bicarbonate). Helps digest proteins, fats, and carbs in the small intestine
Pancreatic Alpha-Amylase
Pancreatic Alpha-Amylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Lipase
Pancreatic Lipase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleases
Nucleases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proteolytic Enzymes
Proteolytic Enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main Functions of the Kidneys
Main Functions of the Kidneys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration
Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretion
Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reabsorption
Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration in Kidney
Filtration in Kidney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretion in Kidney
Secretion in Kidney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reabsorption in Kidney
Reabsorption in Kidney
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle's function
Loop of Henle's function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arterioles
Arterioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus and Bowman's Capsule
Glomerulus and Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- These notes cover the pancreas, kidney function, adrenal glands, and blood vessels of the kidney, as well as their key functions and structures.
Location of the Pancreas
- The pancreas is located behind (posterior) to the stomach
- It stretches from the duodenum to the spleen
- The pancreas is attached to the posterior abdominal wall
- It is covered by a thin connective tissue capsule
Functions of the Pancreas
- The pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine functions
Endocrine Function
- Endocrine cells in the Pancreatic Islets (Islets of Langerhans) produce hormones
- Insulin lowers blood sugar levels
- Glucagon raises blood sugar levels
Exocrine Function
- Exocrine cells, consisting of Acinar cells and duct epithelial cells, produce enzymes
- The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice (digestive enzymes and bicarbonate)
- This juice helps digest proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the small intestine
Pancreatic Enzymes
- Pancreatic Alpha-Amylase is a carbohydrase that breaks down carbs into starches
- It produces simple sugars like maltose
- Similar to salivary amylase, it continues carbohydrate breakdown that starts in the mouth
- Pancreatic Lipase is a lipase that breaks down fats
- It breaks down complex lipids (fats) into fatty acids and monoglycerides, which are easily absorbed
- It works with bile to digest fats in the small intestine
- Nucleases are enzymes that break down nucleic acids
- They break down DNA/RNA into nucleotides (building blocks of nucleic acids)
- Proteolytic enzymes include proteases and peptidases
- Proteases break large proteins into smaller parts
- Peptidases break small peptides into amino acids
- 70% of pancreatic enzyme production is for protein digestion
Main Functions of the Kidneys
- Kidneys filter blood
- They remove waste
- Kidneys maintain fluid, electrolyte, and pH balance
- They regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production
Filtration in the Kidneys
- Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (part of the nephron)
- Blood enters the glomerulus under pressure
- Water, ions, glucose, and small molecules are filtered out of the blood into Bowman's capsule
- Blood cells and proteins stay in the bloodstream because they are too large to filter
Secretion in the Kidneys
- Secretion mainly occurs in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
- The body actively transports waste (like H+, K+, ammonia, drugs) from the blood into the nephron
- Secretion helps maintain pH balance and remove toxins.
Reabsorption in the Kidneys
- Reabsorption mainly occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, and collecting duct
- The nephron reabsorbs useful substances (like glucose, amino acids, water, and salts) back into the blood
- Reabsorption prevents the loss of essential nutrients
- It is controlled by hormones like ADH (water reabsorption) and aldosterone (Na+ reabsorption)
Adrenal Glands
- Two small glands sit on top of each kidney
- They help control stress, energy, blood pressure, and metabolism
- The adrenal cortex (outer layer) makes steroid hormones
Cortisol
- Cortisol ("Stress Hormone") helps the body handle stress
- It controls blood sugar and reduces inflammation
Aldosterone
- Aldosterone ("Salt & Water Balance") controls blood pressure by regulating sodium & potassium
Adrenal Medulla
- The adrenal medulla (inner layer) mediates the fight or flight response
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine) increases heart rate, breathing, and energy when stressed
Peritubular Capillaries
- They surround the proximal and distal tubules of the nephron, mainly in the cortex of the kidney
- They help with reabsorption and secretion
- These capillaries take back useful substances like water, glucose, and salts into the blood
- They let go of waste or extra substances (like H+, drugs) into the nephron
Vasa Recta
- Vasa Recta surrounds the Loop of Henle (in juxtamedullary nephrons, deeper in the kidney)
- They help maintain the concentration of urine
- These vessels work with the loop to reabsorb water and keep the body from losing too much
- They are important for creating concentrated urine (when you're dehydrated)
Glomerulus
- A tiny ball of capillaries is inside the Bowman's capsule
- Its main job is to filter blood to form urine
Afferent Arteriole
- The afferent arteriole ("Arriving") brings blood into the glomerulus
- The blood is under high pressure to push fluid into Bowman's capsule
- It is larger than the efferent arteriole to create pressure
Efferent Arteriole
- The efferent arteriole ("Exiting") takes blood away from the glomerulus
- Blood has been filtered
- It leads to peritubular capillaries or vasa recta for further processing
Filtration in the Glomerulus
- Water, glucose, salts, and urea pass into Bowman's capsule
- Blood cells and proteins stay in the bloodstream because they are too big to filter
Nephron Structure
- A nephron is the basic filtering unit of the kidney
- Each kidney has about 1 million nephrons
Bowman's Capsule
- A cup-shaped structure surrounds the glomerulus
- It collects the filtered fluid (filtrate) from the blood
Glomerulus (Nephron)
- A bundle of capillaries is inside the Bowman's capsule
- It is where blood is filtered
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- A twisty tube is right after the Bowman's capsule
- It reabsorbs nutrients, water, and salts back into the blood
Loop of Henle
- A long loop dives into the kidney medulla
- The descending limb reabsorbs water
- The ascending limb reabsorbs salts (Na+, Cl-)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- Another twisty tube helps with secretion (removes more waste like H+, drugs)
- It also fine-tunes salt and water balance
Collecting Duct
- This duct collects urine from many nephrons
- Reabsorbs water (controlled by ADH)
- It sends urine to the renal pelvis, then the ureter, and finally the bladder
Blood Supply Around the Nephron
- The Afferent arteriole brings blood into the glomerulus
- The Efferent arteriole takes filtered blood out
- It leads to Peritubular capillaries (around tubules) and Vasa recta (around the loop of Henle in juxtamedullary nephrons)
Key Functions and Components of the Kidney
- Glomerulus filters blood
- Bowman's Capsule catches the filtrate
- PCT reabsorbs water, glucose, and salts
- Loop of Henle reabsorbs water & salts
- DCT secretes waste and fine-tunes balance
- Collecting Duct reabsorbs water and forms final urine
Additional Notes
- Glycosuria indicates glucose in the urine and may indicate high blood sugar or diabetes
- Proteinuria indicates protein (albumin) in the urine and may indicate kidney damage, disease, or infections
- Cells in urine indicate something is wrong with the kidneys or urinary tract
- Cortex is the outer part of the kidney
- Medulla is the inner part of the kidney
- The medulla is hypertonic, meaning it has a high concentration of solutes, especially sodium (salt)
Arteriole Bloodflow
- Afferent arteriole bringing oxygenated blood to get filtered
- Efferent arteriole carrying partially deoxygenated blood away
- Kidney's nephrons acts like second endocrine gland secreting hormones
Summary of the Kidney's Activities
- Cortex less concentrated
- Medulla more concentrated = hypertonic
- Nephron the filtering unit responsible for filtering blood and forming urine
Kidney Functions
- Filter waste products and excess substances (like water, salts, and urea) from the blood to form urine
- Control blood pressure by adjusting the volume of water and sodium in the body and secreting renin
- Maintain the acid-base balance by secreting hydrogen ions (H+) and reabsorbing bicarbonate (HCO3) Regulate the levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate in the blood
- Produce erythropoietin (EPO), which stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells in response to low oxygen levels.
- Convert inactive vitamin D into its active form (calcitriol), which helps with calcium absorption in the intestines and bone health.
- Excrete toxins, drugs, and metabolic waste products like urea and creatinine through urine.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.