Podcast
Questions and Answers
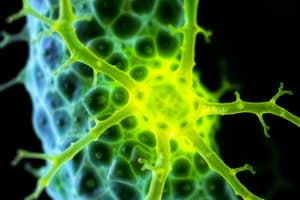
Quale typo de tissu connectiv es presentate in le prime imagine?
Quale typo de tissu connectiv es presentate in le prime imagine?
Mesenchymatic connective tissue
Quale cellulas es presente in le prime imagine? (Selecte tote que applica.)
Quale cellulas es presente in le prime imagine? (Selecte tote que applica.)
- Fibroblastos
- Cellulas adipose
- Cellulas de musculo
- Mesenchymatic cellulas (correct)
- Cellulas de nervo
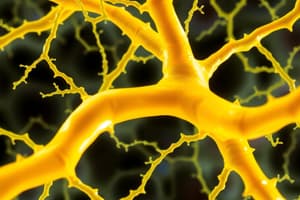
Quale typo de tissu es presentate in le secunde imagine?
Quale typo de tissu es presentate in le secunde imagine?
- Tissu connectiv areolar
- Tissu connectiv dense regular
- Tissu connectiv dense irregular
- Tissu connectiv mucous (correct)
Quale typo de fibra es presentate in le tertie imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presentate in le tertie imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presente in le octave imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presente in le octave imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presente in le undecime imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presente in le undecime imagine?
Quale typo de tissu connectiv es presentate in le duodecimo imagine?
Quale typo de tissu connectiv es presentate in le duodecimo imagine?
Quale typo de tissu connectiv es presentate in le tertiedecimo imagine?
Quale typo de tissu connectiv es presentate in le tertiedecimo imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presente in le quartedecimo imagine?
Quale typo de fibra es presente in le quartedecimo imagine?
Quale typo de cellula es presente in le quintedecimo imagine?
Quale typo de cellula es presente in le quintedecimo imagine?
Quale typo de cellula es presente in le septiendecimo imagine?
Quale typo de cellula es presente in le septiendecimo imagine?
Flashcards
Tissu connectivo mesenchymate
Tissu connectivo mesenchymate
Un tissu connectivo que es trovate in le corpore del adulto, e que contine fibras collagene, elastic, e reticular.
Cellulas mesenchymate
Cellulas mesenchymate
Cellulas specialisate que forma le tissu connectivo mesenchymate.
Tissu connectivo mucose o gelatinose
Tissu connectivo mucose o gelatinose
Un typo de tissu connectivo que es trovate in le cordon umbilical e in le gelatina de Wharton.
Fibroblastos
Fibroblastos
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibras collagene
Fibras collagene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Substantias fundamental
Substantias fundamental
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissu connectivo areolare o lose
Tissu connectivo areolare o lose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibras elastic
Fibras elastic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tendone
Tendone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibras collagene dense regular
Fibras collagene dense regular
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelle
Pelle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grande arteria elastic (Aorta)
Grande arteria elastic (Aorta)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glandula adrenal
Glandula adrenal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nodo lymphatic
Nodo lymphatic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibras reticular
Fibras reticular
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissu adipose blanc
Tissu adipose blanc
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissu adipose brun
Tissu adipose brun
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ligamento
Ligamento
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mastocytas
Mastocytas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellulas plasmatic
Cellulas plasmatic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophagos
Macrophagos
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Connective Tissue Overview
- Connective tissue comprises a diverse group of tissues that support, connect, and separate different types of tissues and organs within the body.
- It is characterized by the presence of cells embedded within an extracellular matrix, which can be liquid, gel-like, or solid.
- The matrix is composed of fibers (like collagen and elastic fibers) and ground substance.
- Different types of connective tissues have varying proportions of cells and extracellular matrix components.
Types of Connective Tissue
-
Mesenchymal Connective Tissue:
- Found in embryos
- Contains mesenchymal cells, which are embryonic connective tissue cells.
-
Mucous or Gelatinous Connective Tissue:
- Characterized by a jelly-like ground substance.
- Predominantly found in the umbilical cord of fetuses (Wharton's jelly)
- Contains collagen fibers, fibroblast cells, and ground substance.
-
Areolar Connective Tissue (Loose Connective Tissue):
- This is the most widespread connective tissue.
- It contains a loose arrangement of fibers, cells, and ground substance.
- Collagen and elastic fibers are present, along with various types of cells like fibroblasts, mast cells, and immune cells (e.g., macrophages, lymphocytes).
- Important for support and flexibility in skin and other tissues.
-
Dense Connective Tissue:
- Can be either regular or irregular depending on the arrangement of fibers.
- Dense Regular Connective Tissue: Fibers are arranged in parallel bundles, providing high tensile strength, e.g., tendons and ligaments.
- Dense Irregular Connective Tissue: Fibers are arranged in a tangled meshwork, providing strength in multiple directions, e.g., skin's dermis.
- Both types contain collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and ground substance.
-
Adipose Tissue:
- Stores energy in the form of fat.
- White Adipose Tissue: Predominantly stores triglycerides as large fat droplets. Abundant in most parts of the body.
- Brown Adipose Tissue: Found in infants and some animals. Generates heat through thermogenesis.
-
Elastic Connective Tissue:
- Primarily composed of elastic fibers.
- Provides elasticity and flexibility. Found in structures requiring stretching, like the walls of arteries and parts of the lungs.
-
Reticular Connective Tissue:
- Composed of a network of reticular fibers.
- Forms a supportive framework for many organs like the spleen and lymph nodes.
-
Cartilage:
- Cartilage tissue is a type of supporting connective tissue that plays an essential role in providing structural support, cushioning, and flexibility to joints, structures, and other tissues.
-
Bone Tissue:
- Bone tissue is a type of connective tissue that provides rigid support to the skeleton.
-
Blood:
- Blood is a liquid connective tissue that transports essential substances throughout the body.
Specific Tissue Components
- Fibroblasts: Cells that produce the extracellular matrix components, including collagen and elastin.
- Collagen fibers: Provide tensile strength to connective tissue. Fibers can vary in maturity or morphology.
- Elastic fibers: Allow tissues to stretch and recoil.
- Ground substance: A gel-like substance that fills spaces between cells and fibers.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.