Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the synovial fluid in a joint affected by osteoarthritis?
What is the function of the synovial fluid in a joint affected by osteoarthritis?
- To help lubricate and protect the joint's movement (correct)
- To provide structural support to the joint
- To promote bone regeneration
- To prevent the breakdown of articular cartilage
What happens to the joint space in osteoarthritis?
What happens to the joint space in osteoarthritis?
- It remains unchanged
- It becomes narrowed (correct)
- It disappears completely
- It widens
What is the result of the breakdown of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis?
What is the result of the breakdown of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis?
- Progressive damage to the underlying bone (correct)
- Formation of new cartilage
- Decreased joint movement
- Increased production of synovial fluid
What contributes to the progression of osteoarthritis?
What contributes to the progression of osteoarthritis?
What are osteophytes in the context of osteoarthritis?
What are osteophytes in the context of osteoarthritis?
What is the role of articular cartilage in a joint affected by osteoarthritis?
What is the role of articular cartilage in a joint affected by osteoarthritis?
How has the understanding of osteoarthritis pathophysiology evolved?
How has the understanding of osteoarthritis pathophysiology evolved?
What can occur in addition to degeneration in osteoarthritis?
What can occur in addition to degeneration in osteoarthritis?
What is the primary function of the subchondral bone in a joint?
What is the primary function of the subchondral bone in a joint?
How does obesity contribute to the risk of osteoarthritis?
How does obesity contribute to the risk of osteoarthritis?
What is the medical term for the death of tissue due to insufficient blood supply?
What is the medical term for the death of tissue due to insufficient blood supply?
Which materials are commonly used in joint replacements?
Which materials are commonly used in joint replacements?
What is the purpose of cemented fixation in joint replacement surgery?
What is the purpose of cemented fixation in joint replacement surgery?
What factors should be considered when deciding on a particular fixation technique for joint replacement?
What factors should be considered when deciding on a particular fixation technique for joint replacement?
What are the expected outcomes for patients undergoing joint replacement surgery?
What are the expected outcomes for patients undergoing joint replacement surgery?
What is the purpose of the American Joint Replacement Registry (AJRR)?
What is the purpose of the American Joint Replacement Registry (AJRR)?
What is associated with decreased hospital length of stay and improved balance and gait function after joint replacement surgery?
What is associated with decreased hospital length of stay and improved balance and gait function after joint replacement surgery?
What has led to earlier hospital discharge and quicker recovery after joint replacement surgery?
What has led to earlier hospital discharge and quicker recovery after joint replacement surgery?
What is the purpose of the data generated from the American Joint Replacement Registry (AJRR)?
What is the purpose of the data generated from the American Joint Replacement Registry (AJRR)?
What is the purpose of total joint arthroplasty, also known as total joint replacement?
What is the purpose of total joint arthroplasty, also known as total joint replacement?
What is the most prominent modifiable risk factor for osteoarthritis?
What is the most prominent modifiable risk factor for osteoarthritis?
Which clinical manifestation is characteristic of osteoarthritis?
Which clinical manifestation is characteristic of osteoarthritis?
What diagnostic tool may show narrowing of joint space in osteoarthritis?
What diagnostic tool may show narrowing of joint space in osteoarthritis?
Which intervention is beneficial for preventing osteoarthritis progression?
Which intervention is beneficial for preventing osteoarthritis progression?
What is the focus of nursing management for osteoarthritis?
What is the focus of nursing management for osteoarthritis?
Which type of exercise can prevent osteoarthritis progression?
Which type of exercise can prevent osteoarthritis progression?
What is the potential benefit of wedged insoles, knee braces, and orthotic devices for osteoarthritis?
What is the potential benefit of wedged insoles, knee braces, and orthotic devices for osteoarthritis?
Which type of therapies are used by osteoarthritis patients?
Which type of therapies are used by osteoarthritis patients?
In which stage of osteoarthritis might surgical interventions like osteotomy and arthroplasty be used?
In which stage of osteoarthritis might surgical interventions like osteotomy and arthroplasty be used?
What is not useful for diagnosing osteoarthritis?
What is not useful for diagnosing osteoarthritis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Osteoarthritis: Risk Factors, Clinical Manifestations, Assessment, and Management
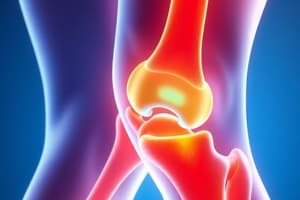
- Osteoarthritis (OA) risk factors include aging, obesity, joint overuse, previous injuries, muscle weakness, genetic predisposition, and certain diseases.
- Obesity is the most prominent modifiable risk factor for OA, reducing both quality and quantity of life when combined with OA.
- Clinical manifestations of OA include joint pain aggravated by movement, brief morning stiffness, insidious onset, and physical signs such as joint enlargement and decreased range of motion.
- Blood tests and joint fluid examination are not useful for diagnosing OA, but X-rays may show narrowing of joint space, osteophyte formation, and thickened subchondral bone.
- Management goals for OA are to decrease pain and stiffness and maintain or improve joint mobility.
- Exercise, particularly cardiovascular aerobic exercise and lower extremity strength training, can prevent OA progression and decrease symptoms.
- Weight loss is beneficial for OA as it decreases excess load on the joint.
- Occupational and physical therapy can help patients adopt self-management strategies for OA.
- Wedged insoles, knee braces, orthotic devices, and walking aids are being evaluated as potential OA therapies to treat biomechanical abnormalities.
- Complementary, alternative, and integrative health therapies such as massage, yoga, and acupuncture are used by OA patients, and research is ongoing to determine their effectiveness.
- Nursing management of OA focuses on pain management, functional ability, education, and understanding of disease process and symptoms.
- Surgical interventions such as osteotomy and arthroplasty may be used in moderate to severe OA with severe pain or loss of function.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.