Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is Class Osteichthyes commonly known as?
What is Class Osteichthyes commonly known as?
- Cartilaginous fish
- Jawless fish
- Freshwater fish
- Bony fish (correct)
What are the characteristics of bony fishes?
What are the characteristics of bony fishes?
- They possess gills (correct)
- They are all freshwater species
- They have no fins
- They have a strong, lightweight skeleton (correct)
What type of fish are most commonly found?
What type of fish are most commonly found?
Ray-finned fish
What adaptation allows bony fish to detect vibrations in water?
What adaptation allows bony fish to detect vibrations in water?
What is the function of the swim bladder in bony fish?
What is the function of the swim bladder in bony fish?
All bony fish have swim bladders.
All bony fish have swim bladders.
What type of circulation do bony fish exhibit?
What type of circulation do bony fish exhibit?
What are the main components of fish characteristics?
What are the main components of fish characteristics?
What structure covers the gills of bony fish?
What structure covers the gills of bony fish?
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from high to low _________.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from high to low _________.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
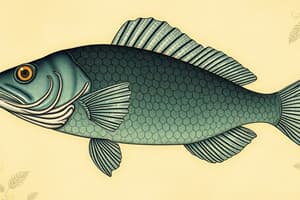
Class Osteichthyes
- Recognized as bony fish with over 27,000 species.
- Characterized by strong, lightweight skeletons; the order Teleostei includes notable examples like cod and tuna.
- Annually, 77 million metric tons of bony fishes are harvested from oceans.
Types of Fishes
-
Ray-Finned Fish:
- Majority of fishes fall in this category, with fins supported by bony rays.
- Teleosts represent the most advanced ray-finned fish, featuring symmetrical tails and flexible fins.
-
Lobe-Finned Fish:
- Have long, fleshy fins supported by a central core of bones, suggesting a link to amphibian ancestors.
- Examples include coelacanth and lungfish.
Fish Characteristics
- Possess gills for respiration, a backbone made of vertebrae, paired fins, and a two-chambered heart that supports single loop circulation.
Skin Structure
- Covered in bony scales resembling roof shingles, providing waterproof protection.
- Mucous glands in the skin secrete mucus, protecting fish from infections; handling fish can remove this crucial coating.
Gills Functionality
- Feathery structures located on the head permit oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide expulsion.
- Healthy fish exhibit bright red gills due to high oxygen content; gills are protected by a bony operculum.
Respiratory Process
- Water flows over gills as fish opens its mouth; water moves against blood flow ensuring efficient oxygen transfer.
- Gills consist of thousands of filaments covered by opercula for protection.
Circulatory System
- Two-chambered heart facilitates single-loop circulation where blood passes through gills to collect oxygen before reaching the body and returning to the heart.
Fin Structure and Function
- Fins aid in swimming and may offer protection; they can be paired (pectoral and pelvic) or unpaired (dorsal, anal, caudal).
Adaptations in Bony Fish
- Lateral Line System: Detects vibrations and helps in orientation within the water, running alongside the fish's body.
- Operculum: The gill cover allows for more efficient water flow through movement.
- Swim Bladder: A gas-filled sac that helps maintain buoyancy; absent in sharks.
Osmotic Considerations
- For Marine Teleosts: They maintain lower internal salt concentrations compared to their marine environment, leading to a hypotonic state which requires effective osmoregulation to prevent water loss.
Osmotic Mechanism in Sharks
- Sharks utilize urea to balance osmotic pressure, preventing excess water loss.
- Urea contributes to the bitter taste of shark flesh unless adequately soaked.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.