Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of OSPF in a network?
What is the primary function of OSPF in a network?
- It monitors network performance metrics.
- It encrypts data packets for secure transmission.
- It serves as a link-state routing protocol for an Autonomous System. (correct)
- It provides firewall protection for network devices.
Which process is involved in the OSPF operation for calculating the best path?
Which process is involved in the OSPF operation for calculating the best path?
- Bellman-Ford algorithm is used.
- Destination-Sequenced Distance-Vector (DSDV) routing is applied.
- Dijkstra’s algorithm is used for path calculation. (correct)
- A hybrid of link-state and distance-vector methods are implemented.
What metric does OSPF use to determine the best routing path?
What metric does OSPF use to determine the best routing path?
- Latency.
- Packet loss rate.
- Cost derived from bandwidth. (correct)
- Distance.
How does OSPF ensure that all routers have the same topology information?
How does OSPF ensure that all routers have the same topology information?
What is the main role of Hello packets in OSPF?
What is the main role of Hello packets in OSPF?
What determines the Router ID (RID) of an OSPF router?
What determines the Router ID (RID) of an OSPF router?
What is the purpose of a Designated Router (DR) in OSPF?
What is the purpose of a Designated Router (DR) in OSPF?
Which of the following describes Single-Area OSPF?
Which of the following describes Single-Area OSPF?
Which component in OSPF holds the link-state information exchanged between routers?
Which component in OSPF holds the link-state information exchanged between routers?
What is the default reference bandwidth used to calculate OSPF metrics?
What is the default reference bandwidth used to calculate OSPF metrics?
OSPF is a distance-vector routing protocol used across different Autonomous Systems.
OSPF is a distance-vector routing protocol used across different Autonomous Systems.
Hello packets are used by OSPF to discover routers and assist in the election of a Designated Router.
Hello packets are used by OSPF to discover routers and assist in the election of a Designated Router.
OSPF calculates the best path using the Bellman-Ford algorithm.
OSPF calculates the best path using the Bellman-Ford algorithm.
The default reference bandwidth for OSPF metrics is $10^8$ bps.
The default reference bandwidth for OSPF metrics is $10^8$ bps.
Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) are only sent to directly connected routers in an OSPF network.
Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) are only sent to directly connected routers in an OSPF network.
A single area OSPF design, known as Area 0, enhances complexity by including multiple areas.
A single area OSPF design, known as Area 0, enhances complexity by including multiple areas.
The Router ID (RID) in OSPF can be manually assigned or determined based on IP addresses.
The Router ID (RID) in OSPF can be manually assigned or determined based on IP addresses.
OSPF uses bandwidth as a cost metric to determine the best routing paths.
OSPF uses bandwidth as a cost metric to determine the best routing paths.
OSPF can only operate in a single area and does not support multi-access networks.
OSPF can only operate in a single area and does not support multi-access networks.
Accumulated cost in OSPF is solely based on the physical distance between routers.
Accumulated cost in OSPF is solely based on the physical distance between routers.
Flashcards
OSPF
OSPF
A link-state routing protocol within an Autonomous System.
Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)
Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)
Messages carrying link state and cost information in OSPF.
OSPF Metric
OSPF Metric
Cost (calculated by reference bandwidth divided by interface bandwidth).
OSPF Router ID
OSPF Router ID
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hello Packets
Hello Packets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Designated Router (DR)
Designated Router (DR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Backup DR
Backup DR
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Area OSPF
Single-Area OSPF
Signup and view all the flashcards
Routing Table
Routing Table
Signup and view all the flashcards
OSPF Link-State Update (LSU)
OSPF Link-State Update (LSU)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is OSPF's core function?
What is OSPF's core function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's OSPF's key advantage?
What's OSPF's key advantage?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does OSPF determine the best route?
How does OSPF determine the best route?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)?
What are Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Designated Router (DR)?
What is a Designated Router (DR)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do routers find each other in OSPF?
How do routers find each other in OSPF?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Router ID (RID)?
What is a Router ID (RID)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Single-Area OSPF?
What is Single-Area OSPF?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does OSPF build the routing table?
How does OSPF build the routing table?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do OSPF routers share routing information?
How do OSPF routers share routing information?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
OSPF Protocol Overview
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a link-state routing protocol within an Autonomous System.
- Key features include fast convergence, scalability, support for Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), and use of cost as a path determination metric.
OSPF Operation
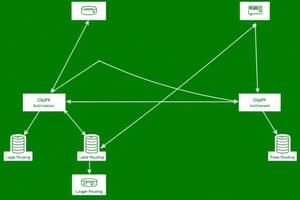
- Link-State Operation: OSPF routers exchange Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) containing link state and cost information. All routers in the area receive this information to maintain a consistent network topology. Routers then build a topology table using Dijkstra's algorithm to calculate the best paths and adding them to the routing table.
- Neighbor Adjacencies: Routers discover and establish adjacencies using Hello packets. In multi-access networks, a Designated Router (DR) and Backup DR (BDR) are elected to manage traffic efficiently.
- OSPF Metrics: Cost is calculated as Reference Bandwidth divided by Interface Bandwidth. Default reference bandwidth is 108 bps but is adjustable. The accumulated cost determines the best route.
OSPF Components
- Router ID (RID): A unique identifier for each OSPF router. It can be manually assigned or derived from the highest IP address on a loopback interface or active physical interface.
- OSPF Packets:
- Hello Packets: Establish neighbor relationships and electing DR/BDR.
- Link-State Updates (LSU): Communicate routing information.
- Areas:
- Single-Area OSPF (Area 0): A simplified design using a single area for all routers.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.