Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary goal of Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)?
What is the primary goal of Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)?
- To completely remove the knee joint
- To increase the degree of knee flexion beyond normal limits
- To create a permanent fusion of the knee bones
- To replace the worn surfaces of the knee and improve mobility (correct)
Which type of knee implant is most commonly used for Total Knee Replacement?
Which type of knee implant is most commonly used for Total Knee Replacement?
- Tricompartmental implant (correct)
- Unicompartmental implant
- Fully constrained prosthesis
- Bicompartmental implant
Which statement accurately describes the types of knee implants?
Which statement accurately describes the types of knee implants?
- Semiconstrained implants provide little to no support when there is significant soft tissue deformity.
- Fully constrained prostheses are ideal for cases of high bone loss and instability. (correct)
- Unconstrained prostheses allow for maximum mobility without any connection between components.
- Bicompartmental implants are widely preferred due to their effectiveness.
What is an important consideration when choosing fixation techniques for knee implants?
What is an important consideration when choosing fixation techniques for knee implants?
In an ACL reconstruction procedure, what is the first step in preparing for the graft?
In an ACL reconstruction procedure, what is the first step in preparing for the graft?
Which muscles comprise the rotator cuff in the shoulder joint?
Which muscles comprise the rotator cuff in the shoulder joint?
What structure is formed by the fusion of the ilium, pubis, and ischium in the hip bone?
What structure is formed by the fusion of the ilium, pubis, and ischium in the hip bone?
Which ligaments are known to reinforce the knee capsule?
Which ligaments are known to reinforce the knee capsule?
Which part of the humerus connects to the joint capsule of the shoulder?
Which part of the humerus connects to the joint capsule of the shoulder?
What are the two main components of the knee joint's articulations?
What are the two main components of the knee joint's articulations?
What is the primary function of the synovial membrane in joints?
What is the primary function of the synovial membrane in joints?
Which structures are associated with the insertion points in the femur?
Which structures are associated with the insertion points in the femur?
What type of joint is formed by the end of the tibia and fibula at the ankle?
What type of joint is formed by the end of the tibia and fibula at the ankle?
Which material is NOT typically used for suturing tendons or ligaments?
Which material is NOT typically used for suturing tendons or ligaments?
What is a known effect of prolonged exposure to the liquid component of PMMA?
What is a known effect of prolonged exposure to the liquid component of PMMA?
Which agent is applied topically to control bleeding from the bone surfaces?
Which agent is applied topically to control bleeding from the bone surfaces?
What is the primary purpose of a prosthesis in joint replacement surgery?
What is the primary purpose of a prosthesis in joint replacement surgery?
In orthopedic surgeries, when is it important to use double or triple gloves?
In orthopedic surgeries, when is it important to use double or triple gloves?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of plates and screws in fracture fixation?
Which of the following best describes the purpose of plates and screws in fracture fixation?
What is the purpose of mixing Bacitracin with sterile saline in orthopedic procedures?
What is the purpose of mixing Bacitracin with sterile saline in orthopedic procedures?
What is the significance of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation (ASIF) in orthopedic surgery?
What is the significance of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation (ASIF) in orthopedic surgery?
Which protective measure is NOT typically required for orthopedic surgeries?
Which protective measure is NOT typically required for orthopedic surgeries?
During the fixation of a fracture, what is the correct sequence of using instruments?
During the fixation of a fracture, what is the correct sequence of using instruments?
What is the primary benefit of using PMMA impregnated with antibiotics?
What is the primary benefit of using PMMA impregnated with antibiotics?
What should always be done when mixing PMMA to minimize staff exposure?
What should always be done when mixing PMMA to minimize staff exposure?
Which joints are most commonly involved in arthroscopic procedures?
Which joints are most commonly involved in arthroscopic procedures?
Which statement about absorbable sutures is correct?
Which statement about absorbable sutures is correct?
What advantage does arthroscopic surgery provide compared to traditional methods?
What advantage does arthroscopic surgery provide compared to traditional methods?
What is the primary function of saline irrigation during knee arthroscopy?
What is the primary function of saline irrigation during knee arthroscopy?
Why is maintaining strict air flow control important during surgeries?
Why is maintaining strict air flow control important during surgeries?
What is a common reason for performing hip replacement surgery?
What is a common reason for performing hip replacement surgery?
Which statement is true regarding fractures treated by plastic/oral maxillofacial and ENT surgeons?
Which statement is true regarding fractures treated by plastic/oral maxillofacial and ENT surgeons?
What type of screws can be used in fracture fixation?
What type of screws can be used in fracture fixation?
What is the primary goal of fracture surgery?
What is the primary goal of fracture surgery?
Which statement about Closed Reduction is true?
Which statement about Closed Reduction is true?
When is External Fixation typically used?
When is External Fixation typically used?
What is a notable advantage of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)?
What is a notable advantage of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)?
What materials are commonly used in internal fixation during ORIF?
What materials are commonly used in internal fixation during ORIF?
What type of fracture treatment uses K-wires or Steinman Pins?
What type of fracture treatment uses K-wires or Steinman Pins?
Which option correctly describes the use of Intramedullary (IM) rods?
Which option correctly describes the use of Intramedullary (IM) rods?
What is a major benefit of using IM rods over traditional fixation methods?
What is a major benefit of using IM rods over traditional fixation methods?
In which case would Internal Fixation be the treatment of choice?
In which case would Internal Fixation be the treatment of choice?
Which of the following is NOT an example of ORIF procedures?
Which of the following is NOT an example of ORIF procedures?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
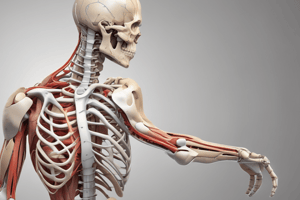
Bone Repair and Anatomy
- Periosteal elevators are used to strip away the periosteal layer during fracture repair.
- The synovial membrane covers all articulating surfaces of joints.
- Cortical (hard) bone is contrasted with cancellous (spongy) bone in anatomy.
Shoulder and Upper Extremity
- The shoulder features a ball-and-socket joint, supported by four rotator cuff muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
- Humerus is the longest bone in the upper arm, connecting to the shoulder capsule at the proximal end and the ulna and radius at the distal end.
Wrist and Hand Structure
- The wrist and hand consist of three parts: 8 carpals, 14 metacarpals, and phalanges.
- There are two sides: radial and ulnar; the median nerve travels through the palm and wrist.
Hip Joint Components
- The hip joint is stabilized by a capsule, ligaments, and muscles.
- Comprised of ilium, pubis, and ischium, the acetabulum connects with the head of the femur.
- The greater and lesser trochanters on the femur serve as insertion points for hip muscles.
Knee Anatomy and Function
- The knee contains two articulations: one between the femur and tibia, and another between the patella and femur.
- Key stabilizing structures include the medial (MCL) and lateral collateral ligaments (LCL), as well as the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
- Two menisci (medial and lateral) provide cushioning and stability between femur and tibia.
Ankle Joint Characteristics
- The ankle is a hinge joint formed by the tibia and fibula, contributing to movements of the foot.
- Surgical site infections (SSI) may occur due to airborne bacteria; maintaining sterile techniques is crucial.
Suture Material and Bone Cement
- Suture materials are selected for tensile strength and minimal degradability; absorbable sutures are utilized for softer tissues while non-absorbable sutures are used for tougher tissues.
- Bone cement (PMMA) combines a powder and liquid to create a radiopaque substance, with precautions in handling to avoid flammability and respiratory irritation.
Medications in Orthopedic Surgery
- Use of antibiotics, hemostatics, and antibacterial agents is common; antibiotics can be applied intravenously or locally.
- Bone wax and topical thrombin aid in controlling bleeding during procedures.
Protective Measures in Surgery
- Extra precautions in orthopedic cases include double or triple gloving, face shields, and care to avoid strike-through contamination.
- X-ray gowns are required for personnel if imaging equipment is being used.
Prosthesis Handling and Fracture Surgery Goals
- Careful handling of prostheses is essential to avoid damage or contamination.
- The primary objective of fracture surgery is to restore bone alignment, length, and functionality.
Techniques for Fracture Fixation
- Closed reduction involves non-surgical manipulation with radiographic confirmation; splints or casts are used for immobilization.
- External fixation offers rigid stabilization without the need for a cast, useful in severe fractures or soft tissue injuries.
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) involves surgical exposure and application of devices like plates and screws to align broken bones.
Arthroscopy Overview
- Arthroscopies are utilized for diagnosis and treatment of joint injuries, commonly performed in the knee, shoulder, and wrist.
- Normal saline is used for irrigation, and multiple small incisions allow for insertion of arthroscopic instruments.
Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
- Total knee replacements primarily address degenerative, rheumatoid, or traumatic arthritis to enhance joint mobility.
- Types of knee implants include unicompartmental, bicompartmental, and tricompartmental; the latter is the most commonly used.
- Constraint levels of implants vary and implantation techniques can be cemented or non-cemented, influenced by bone condition and patient factors.
Summary of Instrumentation for Fixation
- Hold bone with a holder for stabilization.
- Drill to create holes for screws, followed by tapping for threaded stability.
- Depth gauging ensures appropriate screw length before insertion with a screwdriver.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.