Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is odontogenesis?
What is odontogenesis?
Odontogenesis is the process of tooth development that occurs in multiple stages.
List the morphological stages of tooth development.
List the morphological stages of tooth development.
The morphological stages are dental lamina formation, bud, cap, and bell.
Define dental congenital anomalies.
Define dental congenital anomalies.
Dental congenital anomalies are irregularities in tooth development that occur due to genetic or environmental factors.
What physiological stage follows induction in tooth development?
What physiological stage follows induction in tooth development?
What role do Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and growth factors play in tooth development?
What role do Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and growth factors play in tooth development?
What is the significance of oral biology in dentistry?
What is the significance of oral biology in dentistry?
Explain the difference between morphological and physiological stages of tooth development.
Explain the difference between morphological and physiological stages of tooth development.
Identify two types of dental congenital anomalies.
Identify two types of dental congenital anomalies.
What physiological processes are primarily involved in the bud stage of tooth development?
What physiological processes are primarily involved in the bud stage of tooth development?
How does the ectomesenchyme contribute to the cap stage of tooth development?
How does the ectomesenchyme contribute to the cap stage of tooth development?
What structures make up the tooth germ?
What structures make up the tooth germ?
What shape does the enamel organ take during the cap stage?
What shape does the enamel organ take during the cap stage?
What does the dental sac develop into during tooth formation?
What does the dental sac develop into during tooth formation?
What are the three main components formed during the cap stage of tooth development?
What are the three main components formed during the cap stage of tooth development?
What separates the epithelium from the connective tissue during tooth development?
What separates the epithelium from the connective tissue during tooth development?
What type of proliferation occurs during the cap stage of tooth development?
What type of proliferation occurs during the cap stage of tooth development?
What are the four main morphological stages of tooth development?
What are the four main morphological stages of tooth development?
What is the role of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in odontogenesis?
What is the role of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in odontogenesis?
What structure in tooth development is formed by the bifurcation of the primary epithelial band?
What structure in tooth development is formed by the bifurcation of the primary epithelial band?
At what age does the odontogenic epithelium emerge, and how does it influence mesenchymal tissues?
At what age does the odontogenic epithelium emerge, and how does it influence mesenchymal tissues?
How does the main dental lamina contribute to tooth development?
How does the main dental lamina contribute to tooth development?
What physiological processes are involved in the development of teeth?
What physiological processes are involved in the development of teeth?
What does the vestibular lamina give rise to in the oral cavity?
What does the vestibular lamina give rise to in the oral cavity?
What are the inductive messages sent by the odontogenic epithelium intended to achieve?
What are the inductive messages sent by the odontogenic epithelium intended to achieve?
What are stellate reticulum cells and what is their primary function in the enamel organ?
What are stellate reticulum cells and what is their primary function in the enamel organ?
How do the stellate reticulum cells become star-shaped?
How do the stellate reticulum cells become star-shaped?
What roles do the enamel knot and enamel cord play during tooth development?
What roles do the enamel knot and enamel cord play during tooth development?
Describe the characteristics of the enamel knot.
Describe the characteristics of the enamel knot.
What is the significance of glycosaminoglycans within the extracellular compartment of the enamel organ?
What is the significance of glycosaminoglycans within the extracellular compartment of the enamel organ?
What happens to the enamel knot during the bell stage of tooth development?
What happens to the enamel knot during the bell stage of tooth development?
What is formed when the enamel cord divides the stellate reticulum?
What is formed when the enamel cord divides the stellate reticulum?
In terms of their developmental stage, when do enamel knots appear and disappear?
In terms of their developmental stage, when do enamel knots appear and disappear?
Flashcards
What is Oral Biology?
What is Oral Biology?
Study of the mouth's structures, functions, and related diseases.
Supernumerary teeth
Supernumerary teeth
Extra teeth beyond the normal count.
Teeth fusion
Teeth fusion
Two teeth joined as one.
Macrodontia
Macrodontia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microdontia
Microdontia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morphological stages
Morphological stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiological stages
Physiological stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sonic hedgehog (Shh)
Sonic hedgehog (Shh)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shh signaling
Shh signaling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dental lamina initiation
Dental lamina initiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Odontogenic epithelium
Odontogenic epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural crest cells
Neural crest cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main dental lamina
Main dental lamina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior proliferation of main dental lamina
Posterior proliferation of main dental lamina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lingual Proliferation
Lingual Proliferation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibular lamina
Vestibular lamina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bud stage
Bud stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Induction at bud stage
Induction at bud stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cap stage
Cap stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectomesenchyme fate
Ectomesenchyme fate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tooth germ
Tooth germ
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel organ cell organization
Enamel organ cell organization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stellate reticulum function
Stellate reticulum function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bell Stage
Bell Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel Knot
Enamel Knot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel Cord
Enamel Cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel knot description
Enamel knot description
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enamel cord description
Enamel cord description
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Oral Biology
Importance of Oral Biology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Key Topics in Oral Biology
Key Topics in Oral Biology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Oral Biology
- Oral biology provides a basis for dental subjects and practice.
- Oral biology is the study of the structure, function, and diseases that relate to the mouth and its surrounding structures.
Topics Studied
- Tooth development
- Enamel structure and amelogenesis
- Dentin structure and Dentinogensis
- Cementum structure and cementogenesis
- Pulp structure
- PDL structure
- Alveolar bone and osteointegration
- Radiographic interpretation to the maxillary and mandibular landmarks
Dental Congenital Anomalies
- Supernumerary teeth: Extra teeth
- Teeth fusion: Two teeth are joined together
- Macrodontia: Abnormally large teeth
- Microdontia: Abnormally small teeth
Tooth Development Stages
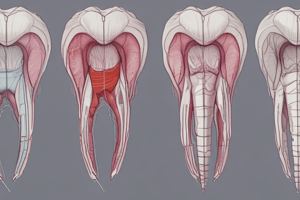
- Morphological Stages: Dental lamina formation, bud, cap, and bell
- Physiological Stages: Induction, proliferation, morpho-differentiation, histo-differentiation, apposition, and maturation.
- Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and different types of growth factors are responsible for the development of teeth, their numbers, and their specific morphology.
Shh Signaling
- Shh is secreted by the odontogenic epithelium.
- Shh diffuses to the dental ectomesenchyme.
Morphological Stages of Tooth Development
- Dental lamina initiation: Starts at 5 weeks in utero.
- The odontogenic epithelium covers mesenchymal tissues rich in Shh.
- Neural crest cells differentiate into odontogenic cells.
- The primary epithelial band forms.
- The band bifurcates into the general (main) dental and vestibular laminae.
- Main dental lamina gives rise to deciduous dentition.
- Posterior proliferation of the main dental lamina gives rise to permanent molars.
- Lingual proliferation gives rise to successional dental laminae.
- Vestibular lamina forms the vestibular mucosa.
- Induction and proliferation are the key physiological processes.
- Bud stage: Begins at 6 weeks in utero.
- The dental lamina induces dental placodes to form buds.
- Induction and Proliferation are the key physiological processes.
- Cap stage:
- The bud shows unequal growth, forming a cap shape called the enamel organ.
- The ectomesenchyme divides into the dental papilla and dental sac.
- The basement membrane separates the epithelium from the connective tissue.
- Enamel organ, dental papilla, and dental sac form the tooth germ.
- Proliferation is the key physiological process.
- Cells within the enamel organ are organized into the outer and inner enamel epithelium and stellate reticulum.
- The stellate reticulum cells are polygonal and synthesize glycosaminoglycans, pulling water into the enamel organ.
- Bell stage:
- The enamel organ develops into a bell shape.
- This stage is subdivided into early bell and late bell.
- The enamel knot is a signaling center for cuspal morphogenesis.
- The enamel cord is a strand of cells extending from the stratum intermedium to the outer enamel epithelium.
Transitory Structures
- Enamel knot: A cluster of non-dividing epithelial cells that appear in the cap stage and bulge into the dental papilla.
- Enamel cord: A strand of cells seen at the early bell stage, extending from the stratum intermedium to the outer enamel epithelium.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.