Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the types of degeneration with their descriptions:
Match the types of degeneration with their descriptions:
Wallerian degeneration = Breakdown of the axon after injury leading to cell death Retrograde degeneration = Breakdown of the axon still attached to the cell body Chromatolysis = Loss of Nissl substances in the neuron Transsynaptic degeneration = Death of connected neurons due to synaptic relationships
Match the types of cells with their functions:
Match the types of cells with their functions:
Ependymal cells = Secretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Schwann cells = Support axons and produce myelin sheaths Neurons in PNS = Ability to repair and regenerate after degeneration Neurons in CNS = Inability to reverse degeneration effects
Match the terms with their definitions:
Match the terms with their definitions:
Axon = Long projection that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body Nissl substances = Ribosomal RNA involved in protein synthesis in the cell body Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) = Fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord Myelin sheath = Insulating layer that accelerates electrical signal transmission
Match the following processes with their outcome:
Match the following processes with their outcome:
Match the following types of neurodegeneration with their location:
Match the following types of neurodegeneration with their location:
Match the parts of a neuron with their functions:
Match the parts of a neuron with their functions:
Match the types of neurons according to their structure:
Match the types of neurons according to their structure:
Match the functional classification of neurons:
Match the functional classification of neurons:
Match the supporting cells in the nervous system with their functions:
Match the supporting cells in the nervous system with their functions:
Match the definitions with the parts of the neuron:
Match the definitions with the parts of the neuron:
Match the terms related to neuron functions with their descriptions:
Match the terms related to neuron functions with their descriptions:
Match the types of neurons with their roles:
Match the types of neurons with their roles:
Match the key neuron structures with their characteristics:
Match the key neuron structures with their characteristics:
Match the types of glial cells with their primary function:
Match the types of glial cells with their primary function:
Match each neuron type with its description:
Match each neuron type with its description:
Match the following neuronal functions with their types:
Match the following neuronal functions with their types:
Match the neuron types with their common locations:
Match the neuron types with their common locations:
Match the following neuron types according to their function:
Match the following neuron types according to their function:
Match glial cells with their roles in the CNS:
Match glial cells with their roles in the CNS:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
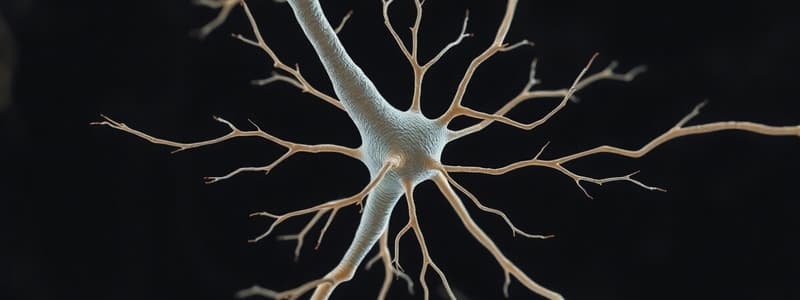
Neuron
- The neuron is the fundamental unit of the nervous system, responsible for processing and transmitting information.
- It consists of a soma (cell body), dendrites, an axon, and terminal buttons.
- The soma contains the nucleus and vital machinery for the neuron’s life processes.
- Dendrites receive neural messages from other neurons, resembling a tree-like structure.
- The axon is a long, slender tube that carries information from the soma to the terminal buttons.
- Terminal buttons are located at the ends of branches extending from the axon, responsible for transmitting messages to other neurons.
- The junction between a terminal button and a dendrite or soma is known as a synapse, where neural transmission occurs.
Reflex Arc
- A reflex arc is the pathway for nerve impulse conduction to and from the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
Neuron Types (Structure)
- Multipolar Neuron: The most common type in the CNS, characterized by one axon and multiple dendrites.
- Bipolar Neuron: Possesses one axon and one dendritic tree at opposite ends of the soma, often found in sensory neurons.
- Unipolar Neuron: Has a single stalk extending from the soma that branches into two extensions, one functioning as a dendrite and the other as an axon. Also known as pseudo-unipolar neurons.
Neuron Types (Function)
- Afferent (Sensory) Neurons: Transmit nerve impulses towards the spinal cord or brain.
- Efferent (Motor) Neurons: Transmit impulses away from the brain or spinal cord towards muscles or glands.
- Interneurons: Connect various neurons within the brain or spinal cord, facilitating communication between afferent and efferent neurons.
Supporting Cells (Glia)
- Astrocytes (Star Cells): Provide structural support to neurons, clear debris in the brain, chemically buffer fluid surrounding neurons, and supply nutrients and dispose of waste products.
- Microglia: Smaller glia cells that act as phagocytes, engulfing dead neurons.
- Oligodendroglia: Provide support to axons and produce myelin sheaths in the CNS.
- Ependymal Cells: Epithelial cells that monitor cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) composition, with specialized cells participating in CSF secretion.
- Schwann Cells: Support axons and produce myelin sheaths in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Degeneration
- Wallerian Degeneration: Occurs when an axon is injured, causing the severed section to die due to lack of sustenance.
- Retrograde Degeneration: The breakdown of the axon portion still attached to the cell body.
- Chromatolysis: The cell body loses its Nissl substances and eventually loses its ability to sustain itself.
Degenerative Responses
- Neurons in the PNS can sometimes reverse the effects of degeneration, repairing their structure and growing a new axon.
- Neurons in the CNS are generally unable to reverse the degenerative process.
- Transsynaptic Degeneration: Neurons that form synapses with dying neurons may also die as a consequence.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.