Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
- Dendrites and Axons
- Brain and Spinal Cord
- Central and Peripheral (correct)
- Cranial and Spinal Nerves
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for processing information and making decisions?
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for processing information and making decisions?
- Cranial Nerves
- Central Nervous System (correct)
- Spinal Cord
- Peripheral Nervous System
What are the specialized cells that make up the nervous system called?
What are the specialized cells that make up the nervous system called?
- Spinal Nerves
- Neurons (correct)
- Dendrites
- Axons
Which part of a neuron is responsible for receiving signals?
Which part of a neuron is responsible for receiving signals?
What is the function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the function of the peripheral nervous system?
What is the role of myelin in the nervous system?
What is the role of myelin in the nervous system?
Which part of the nervous system transmits information about sensations like touch and pain to the CNS?
Which part of the nervous system transmits information about sensations like touch and pain to the CNS?
What is the primary function of the limbic system in the brain?
What is the primary function of the limbic system in the brain?
Which area of the cerebral cortex is responsible for learning and decision-making?
Which area of the cerebral cortex is responsible for learning and decision-making?
What is the main function of reflex arcs in the nervous system?
What is the main function of reflex arcs in the nervous system?
Study Notes
Control and Coordination: The Nervous System's Role
The human body is a complex machine, continually carrying out an intricate symphony of actions. Control and coordination form the backbone of this orchestra, ensuring smooth and efficient functioning. At the heart of these essential processes lies the nervous system. In this article, we'll explore the role of the nervous system in control and coordination, delving into the nerves, neurons, and communication pathways that make it all possible.
The Nervous System: An Overview
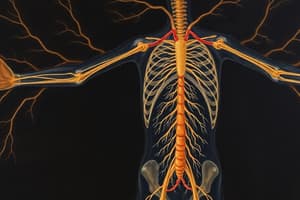
The nervous system is made up of two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS, composed of the brain and spinal cord, is responsible for processing information, making decisions, and coordinating the body's response to internal and external stimuli. The PNS, consisting of cranial nerves and spinal nerves, connects the CNS to the rest of the body, relaying sensory information and transmitting commands to and from the CNS.
Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System
Neurons are the specialized cells that make up the nervous system. They come in different shapes and sizes, each with their unique function. Neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. Each neuron has a cell body, dendrites (receiving ends), and an axon (transmitting end). The axon can be covered by an insulating sheath of myelin, produced by specialized cells called glial cells, which speeds up the transmission of electrical signals.
Communication Pathways: Sensory and Motor Nerves
The nervous system uses sensory nerves to transmit information from the body's sensory organs to the CNS. The sensory nerves convey information about sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain. This sensory information is then processed by the CNS and used to generate appropriate responses.
Motor nerves transmit commands from the CNS to the body's muscles, organs, and glands, causing them to contract, relax, and perform their respective functions. The motor nerves enable the body to carry out complex actions, including walking, talking, and thinking.
Reflexes: Simple Control Mechanisms
Reflexes are simple control mechanisms that allow the body to respond quickly and automatically to external stimuli. A reflex arc is the pathway of communication between a sensory receptor, the spinal cord, and a motor neuron. For example, when you touch a hot object, the nerve cells in your skin send a signal to the spinal cord, which in turn triggers a motor nerve to contract the muscles in your arm and withdraw your hand from the heat source. Reflexes are essential for maintaining homeostasis, which is the body's internal balance.
Higher Functions: The CNS's Complex Role
The CNS, particularly the cerebral cortex, is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. The cerebral cortex is divided into distinct areas, each with its specific function. For instance, the primary motor cortex controls voluntary muscle movements, while the primary sensory cortex processes sensory information.
The limbic system, a group of structures deep within the brain, is responsible for emotional responses and motivation. The hypothalamus, a small region at the base of the brain, regulates vital physiological functions, such as body temperature, hunger, and thirst. The basal ganglia, located deep within the brain, are involved in motor control and cognition.
Conclusion
The nervous system is a complex and interconnected web of cells, nerves, and communication pathways. It plays a vital role in control and coordination, allowing the body to respond to internal and external stimuli, carry out complex actions, and maintain homeostasis. The nervous system is composed of the central and peripheral nervous systems, neurons, and sensory and motor nerves. The CNS is responsible for higher cognitive functions, while the PNS ensures communication between the CNS and the rest of the body. Reflexes are simple control mechanisms that allow the body to respond quickly and automatically to external stimuli. Understanding the nervous system's role in control and coordination is fundamental to comprehending the body's overall functioning and its intricate interactions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the essential role of the nervous system in control and coordination, including the structure of neurons, communication pathways, reflexes, and the higher cognitive functions of the central nervous system (CNS). Learn about the nervous system's components, from the central nervous system (CNS) to the peripheral nervous system (PNS), and how they work together to maintain homeostasis and enable complex actions.