Podcast
Questions and Answers
Who is the coordinator of the lab classes?
Who is the coordinator of the lab classes?
- Sherwood L.
- dr Szymon Chowanski (correct)
- dr hab.inż. Pawel Marciniak prof.
- Barret et al.
How many lectures are scheduled in the course?
How many lectures are scheduled in the course?
- 5
- 12
- 10 (correct)
- 8
What is the publisher of the Campbell Biology book?
What is the publisher of the Campbell Biology book?
- Cengage Learning
- The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc.
- Benjamin Cummings (correct)
- Thomson Learning
On which date is the first lecture on Nervous system scheduled?
On which date is the first lecture on Nervous system scheduled?
What is the title of the book written by Sherwood L.?
What is the title of the book written by Sherwood L.?
What is the room number of dr hab.inż. Pawel Marciniak prof.?
What is the room number of dr hab.inż. Pawel Marciniak prof.?
What is the typical structure of a multipolar neuron?
What is the typical structure of a multipolar neuron?
What is the function of the myelin sheath in the nervous system?
What is the function of the myelin sheath in the nervous system?
Which type of neuron has a single short process that extends directly from the cell body and looks like a T?
Which type of neuron has a single short process that extends directly from the cell body and looks like a T?
What is the term for the difference in electric potential between the exterior and interior of the cell membrane?
What is the term for the difference in electric potential between the exterior and interior of the cell membrane?
Which ion channel is responsible for the formation of the resting potential?
Which ion channel is responsible for the formation of the resting potential?
What is the function of the Na+/K+ pump?
What is the function of the Na+/K+ pump?
Which type of neuron has processes that are only dendrites, with no axon present?
Which type of neuron has processes that are only dendrites, with no axon present?
What is the term for the ability of neurons to respond to stimuli?
What is the term for the ability of neurons to respond to stimuli?
What is the main function of the axon hillock?
What is the main function of the axon hillock?
What is the term for the period of time during which a neuron is unable to generate another action potential?
What is the term for the period of time during which a neuron is unable to generate another action potential?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Nervous System - Basic Function
- The nervous system is composed of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- CNS: brain and spinal cord
- PNS: nerves that connect CNS to the rest of the body
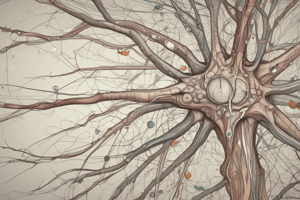
Structure of a Neuron
- Neuron: basic functional unit of the nervous system
- Dendrites: receive signals
- Cell body: contains nucleus
- Axon: transmits signals
- Myelin sheath: insulates and speeds up signal transmission
Types of Neurons
- Multipolar neurons: multiple processes extending from the cell body (most common type)
- Bipolar neurons: two processes extending from the cell body (some special sense neurons)
- Unipolar neurons: single short process extending from the cell body (most sensory neurons)
- Anaxonic neurons: processes are only dendrites, no axon present (interneurons of the CNS)
Important Attribute of Neurons
- Neurons are excitable and easily excited
Membrane Potential
- Resting membrane potential: -70mV (difference in electric potential between exterior and interior of cell membrane)
- Formed by unequal concentrations of K+ and Na+ ions
- Ion channels: allow ions to pass through the cell membrane
- Na+/K+ pump: active transport counter to ions concentrations, requires energy from ATP
Generation of Action Potential
- Stimulus: chemical, physical, or electrical signal
- Depolarization: stimulus raises membrane potential, threshold is -55mV
- Action potential: signal that carries information along the axon (1-2 msec)
- All-or-none response: action potential either occurs or it doesn't, no intermediate responses
Synapses
- Chemical synapse: transmission occurs through neurotransmitters
- Electrical synapse: transmission occurs through electrical signals
- Synaptic transmission: process of transmitting information from one neuron to another
- Postsynaptic potential: response of the postsynaptic cell to neurotransmitters (excitatory or inhibitory)
Synapse Functioning
- Summation of impulses: multiple signals combined to produce a response
- Summation of stimulus: multiple stimuli combined to produce a response
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.