Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a potential cause of brachial plexus injury in the supine position?
What is a potential cause of brachial plexus injury in the supine position?
- Shoulder brace placed too anterior
- Arm abduction < 90 degrees on armboard
- Thorax pressure exertion on dependent shoulder and axilla
- Arm abduction > 90 degrees on armboard (correct)
In the Trendelenburg position, what can cause brachial plexus injury?
In the Trendelenburg position, what can cause brachial plexus injury?
- Shoulder braces placed too medial or lateral (correct)
- Arm abduction and lateral flexion of the head to the same side
- Arm abduction and lateral flexion of the head to the opposite side
- Shoulder braces placed too posterior
What is a potential cause of brachial plexus injury in the lateral position?
What is a potential cause of brachial plexus injury in the lateral position?
- Arm abduction < 90 degrees on armboard
- Thorax pressure exertion on non-dependent shoulder and axilla
- Thorax pressure exertion on dependent shoulder and axilla (correct)
- Shoulder brace placed too anterior
What can cause brachial plexus injury in the prone position?
What can cause brachial plexus injury in the prone position?
What is a common mechanism of brachial plexus injury in multiple positions?
What is a common mechanism of brachial plexus injury in multiple positions?
Which of the following positions is most likely to cause brachial plexus injury due to arm abduction alone?
Which of the following positions is most likely to cause brachial plexus injury due to arm abduction alone?
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of brachial plexus injury in the Trendelenburg position?
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of brachial plexus injury in the Trendelenburg position?
What is a potential cause of brachial plexus injury that can occur in both supine and lateral positions?
What is a potential cause of brachial plexus injury that can occur in both supine and lateral positions?
Which of the following positions is least likely to cause brachial plexus injury due to arm falls off the table edge and is abducted and externally rotated?
Which of the following positions is least likely to cause brachial plexus injury due to arm falls off the table edge and is abducted and externally rotated?
In which position is a well-padded shoulder brace recommended to be placed over the acromioclavicular joint?
In which position is a well-padded shoulder brace recommended to be placed over the acromioclavicular joint?
What is the primary reason for not abducting the arm more than 90 degrees in the supine position?
What is the primary reason for not abducting the arm more than 90 degrees in the supine position?
In which position is it most important to support the head to maintain neutral alignment?
In which position is it most important to support the head to maintain neutral alignment?
What is the purpose of placing a roll caudad to the axilla in the lateral position?
What is the purpose of placing a roll caudad to the axilla in the lateral position?
In the prone position, what is the recommended approach to arm abduction?
In the prone position, what is the recommended approach to arm abduction?
What is the primary purpose of ensuring arms are adequately secured in the supine position?
What is the primary purpose of ensuring arms are adequately secured in the supine position?
What is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury when a patient's arm is positioned at the side?
What is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury when a patient's arm is positioned at the side?
Which of the following arm positions can cause ulnar nerve injury?
Which of the following arm positions can cause ulnar nerve injury?
What is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury when a patient's arm is secured at the side?
What is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury when a patient's arm is secured at the side?
Which of the following is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury?
Which of the following is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury?
What can cause ulnar nerve injury?
What can cause ulnar nerve injury?
Which of the following is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury when a patient's arms are folded across their abdomen or chest?
Which of the following is a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury when a patient's arms are folded across their abdomen or chest?
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury?
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of ulnar nerve injury?
What is a key consideration when positioning a patient's arm at their side to prevent ulnar nerve injury?
What is a key consideration when positioning a patient's arm at their side to prevent ulnar nerve injury?
Which of the following arm positions can cause ulnar nerve injury due to inadequate padding?
Which of the following arm positions can cause ulnar nerve injury due to inadequate padding?
Why is it recommended to supinate the forearm on a padded armboard?
Why is it recommended to supinate the forearm on a padded armboard?
What is a potential consequence of folding a patient's arms across their abdomen or chest?
What is a potential consequence of folding a patient's arms across their abdomen or chest?
What is the primary purpose of having the draw sheet up above the elbow and tucking it between the patient and the mattress?
What is the primary purpose of having the draw sheet up above the elbow and tucking it between the patient and the mattress?
What is a potential consequence of flexing the elbow more than 90 degrees when positioning a patient?
What is a potential consequence of flexing the elbow more than 90 degrees when positioning a patient?
Why is it recommended to avoid flexing the elbow more than 90 degrees when positioning a patient?
Why is it recommended to avoid flexing the elbow more than 90 degrees when positioning a patient?
What is the primary purpose of placing sufficient padding around the elbow during patient positioning?
What is the primary purpose of placing sufficient padding around the elbow during patient positioning?
Why is it recommended to not flex the elbow beyond 90 degrees during patient positioning?
Why is it recommended to not flex the elbow beyond 90 degrees during patient positioning?
Which of the following nerve injuries can occur due to inadequate padding of a malnourished patient in the supine or sitting position?
Which of the following nerve injuries can occur due to inadequate padding of a malnourished patient in the supine or sitting position?
What can cause radial or circumflex nerve injury during surgery?
What can cause radial or circumflex nerve injury during surgery?
In which position can suprascapular nerve injury occur due to shoulder circumduction?
In which position can suprascapular nerve injury occur due to shoulder circumduction?
What can cause sciatic nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What can cause sciatic nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of radial or circumflex nerve injury?
What is a potential cause of radial or circumflex nerve injury?
In which position can suprascapular nerve injury occur due to patient rolling?
In which position can suprascapular nerve injury occur due to patient rolling?
What can cause sciatic nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What can cause sciatic nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of nerve injury in a malnourished patient?
What is a potential cause of nerve injury in a malnourished patient?
Which of the following nerve injuries can occur due to patient positioning in the sitting position?
Which of the following nerve injuries can occur due to patient positioning in the sitting position?
What is the recommended preventative measure to reduce the risk of radial or circumflex nerve injury?
What is the recommended preventative measure to reduce the risk of radial or circumflex nerve injury?
In which position can suprascapular nerve injury occur if not properly stabilized?
In which position can suprascapular nerve injury occur if not properly stabilized?
What is the primary purpose of generous soft padding under the buttock when supine or sitting?
What is the primary purpose of generous soft padding under the buttock when supine or sitting?
What is the recommended approach to prevent sciatic nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is the recommended approach to prevent sciatic nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Common Peroneal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Common Peroneal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Posterior tibial nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Posterior tibial nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
In which position can Common Peroneal nerve injury occur due to undue pressure on the downside leg?
In which position can Common Peroneal nerve injury occur due to undue pressure on the downside leg?
What is a potential cause of Common Peroneal nerve injury in the lateral position?
What is a potential cause of Common Peroneal nerve injury in the lateral position?
What is a common mechanism of peroneal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a common mechanism of peroneal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
In the lithotomy position, what is the primary preventative measure to reduce the risk of Common Peroneal nerve injury?
In the lithotomy position, what is the primary preventative measure to reduce the risk of Common Peroneal nerve injury?
What is a potential cause of Posterior tibial nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Posterior tibial nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
In the lateral position, what is the primary preventative measure to reduce the risk of Common Peroneal nerve injury?
In the lateral position, what is the primary preventative measure to reduce the risk of Common Peroneal nerve injury?
What is a common preventative measure for both Common Peroneal and Posterior tibial nerve injuries in the lithotomy position?
What is a common preventative measure for both Common Peroneal and Posterior tibial nerve injuries in the lithotomy position?
Which nerve is most likely to be injured due to excessive pressure on the medial aspect of the leg from 'knee crutch' stirrups in the lithotomy position?
Which nerve is most likely to be injured due to excessive pressure on the medial aspect of the leg from 'knee crutch' stirrups in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following is a potential cause of pudendal nerve injury?
Which of the following is a potential cause of pudendal nerve injury?
Which nerve is most likely to be injured due to excessive flexion of the thigh at the hip in the lithotomy position?
Which nerve is most likely to be injured due to excessive flexion of the thigh at the hip in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following nerves is NOT typically injured in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following nerves is NOT typically injured in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Saphenous nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Saphenous nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Pudendal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Pudendal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Obturator nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a potential cause of Obturator nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is a common feature of nerve injury prevention in the lithotomy position?
What is a common feature of nerve injury prevention in the lithotomy position?
Which nerve injury can be prevented by ensuring sufficient padding between the legs and vertical bar in the lithotomy position?
Which nerve injury can be prevented by ensuring sufficient padding between the legs and vertical bar in the lithotomy position?
What is the recommended preventative measure to reduce the risk of Pudendal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
What is the recommended preventative measure to reduce the risk of Pudendal nerve injury in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following nerve injuries can be prevented by ensuring minimal hip flexion in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following nerve injuries can be prevented by ensuring minimal hip flexion in the lithotomy position?
What is the primary reason for recommending generous padding between the legs and vertical bar in the lithotomy position?
What is the primary reason for recommending generous padding between the legs and vertical bar in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following nerve injuries can occur due to inadequate padding between the stirrup and leg in the lithotomy position?
Which of the following nerve injuries can occur due to inadequate padding between the stirrup and leg in the lithotomy position?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
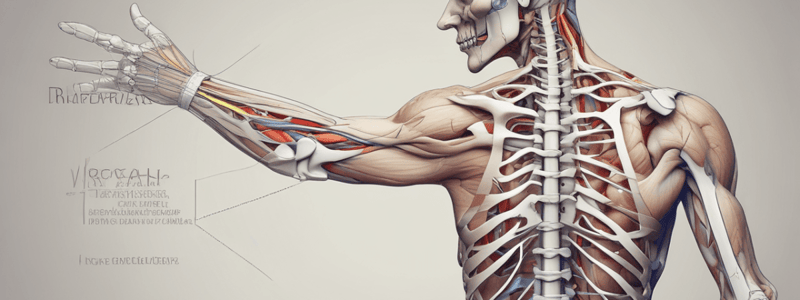
Nerve Injuries: Brachial Plexus
Potential Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
- In Supine, Trendelenburg, or lithotomy positions:
- Arm abducted more than 90 degrees on the armboard
- Arm falls off the table edge, resulting in abduction and external rotation
- Arm abduction and lateral flexion of the head to the opposite side
- In Trendelenburg position:
- Shoulder braces placed too medial or lateral
- In a lateral position:
- Thorax pressure exertion on the dependent shoulder and axilla
- In Prone position:
- Arms abducted more than 90 degrees
Nerve Injuries: Brachial Plexus
Potential Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
- In Supine, Trendelenburg, or lithotomy positions:
- Arm abducted more than 90 degrees on the armboard
- Arm falls off the table edge, resulting in abduction and external rotation
- Arm abduction and lateral flexion of the head to the opposite side
- In Trendelenburg position:
- Shoulder braces placed too medial or lateral
- In a lateral position:
- Thorax pressure exertion on the dependent shoulder and axilla
- In Prone position:
- Arms abducted more than 90 degrees
Brachial Plexus Nerve Injuries: Positioning Recommendations
Supine, Trendelenburg, or Lithotomy Position
- Avoid abducted arm > 90 degrees to prevent nerve injury
- Ensure arms are securely fastened to prevent movement
- Maintain neutral head alignment with support to prevent strain on the brachial plexus
Trendelenburg Position
- Use a well-padded shoulder brace over the acromioclavicular joint to provide support
- Avoid using a shoulder brace if possible to minimize pressure on the brachial plexus
Lateral Position
- Place a roll caudad to the axilla to support the upper thorax and reduce pressure on the brachial plexus
Prone Position
- Abduct arms minimally to prevent strain on the brachial plexus and minimize the risk of nerve injury
Brachial Plexus Nerve Injuries: Positioning Recommendations
Supine, Trendelenburg, or Lithotomy Position
- Avoid abducted arm > 90 degrees to prevent nerve injury
- Ensure arms are securely fastened to prevent movement
- Maintain neutral head alignment with support to prevent strain on the brachial plexus
Trendelenburg Position
- Use a well-padded shoulder brace over the acromioclavicular joint to provide support
- Avoid using a shoulder brace if possible to minimize pressure on the brachial plexus
Lateral Position
- Place a roll caudad to the axilla to support the upper thorax and reduce pressure on the brachial plexus
Prone Position
- Abduct arms minimally to prevent strain on the brachial plexus and minimize the risk of nerve injury
Ulnar Nerve Injuries
- The ulnar nerve can be injured due to improper arm positioning during medical procedures.
- Arm pronation on an armboard can cause ulnar nerve injury.
- Folding arms across the abdomen or chest with elbows flexed at more than 90 degrees can lead to ulnar nerve injury.
- Inadequate padding at the elbow when securing arms at the side can cause ulnar nerve injury.
- Inadequate securing of arms at the side, allowing elbows to extend over the table edge, can also lead to ulnar nerve injury.
Ulnar Nerve Injuries
- The ulnar nerve can be injured due to improper arm positioning during medical procedures.
- Arm pronation on an armboard can cause ulnar nerve injury.
- Folding arms across the abdomen or chest with elbows flexed at more than 90 degrees can lead to ulnar nerve injury.
- Inadequate padding at the elbow when securing arms at the side can cause ulnar nerve injury.
- Inadequate securing of arms at the side, allowing elbows to extend over the table edge, can also lead to ulnar nerve injury.
Ulnar Nerve Injuries
- Potential causes of ulnar nerve injury include:
- Pronating the arm on an armboard
- Folding arms across the abdomen or chest with elbows flexed more than 90 degrees
- Securing arms at the side with inadequate padding at the elbow
- Inadequately securing arms at the side with elbows extended over the table edge
Preventative Positioning Recommendations
- To prevent ulnar nerve injury, the forearm should be supinated on a padded armboard
- Elbows should not be flexed more than 90 degrees
- Sufficient padding should be placed around the elbow
- The draw sheet should extend above the elbow and be tucked between the patient and the mattress
Ulnar Nerve Injuries
- To prevent ulnar nerve injuries, the forearm should be supinated on a padded armboard.
- Elbows should not be flexed more than 90 degrees to prevent injury.
- Sufficient padding should be placed around the elbow to prevent compression.
- The draw sheet should be extended above the elbow and tucked between the patient and the mattress to prevent pressure on the nerve.
Ulnar Nerve Injuries
- To prevent ulnar nerve injuries, the forearm should be supinated on a padded armboard.
- Elbows should not be flexed more than 90 degrees to prevent injury.
- Sufficient padding should be placed around the elbow to prevent compression.
- The draw sheet should be extended above the elbow and tucked between the patient and the mattress to prevent pressure on the nerve.
Nerve Injuries
- Radial or circumflex nerve injury can occur when the arm is pressed against a vertical positioning or retractor post or the pole securing the ether screen.
Causes of Suprascapular Nerve Injury
- Lateral position rolls semi-prone onto dependent arm with shoulder circumduction can cause suprascapular nerve injury.
Causes of Sciatic Nerve Injury
- Malnourished or emaciated patients in supine or sitting position on inadequately padded tables are at risk of sciatic nerve injury.
- Legs straight in a sitting position can also cause sciatic nerve injury.
- In lithotomy position, externally rotated legs with knees extended can cause sciatic nerve injury.
Nerve Injuries
- Radial or circumflex nerve injury can occur when the arm is pressed against a vertical positioning or retractor post or the pole securing the ether screen.
Causes of Suprascapular Nerve Injury
- Lateral position rolls semi-prone onto dependent arm with shoulder circumduction can cause suprascapular nerve injury.
Causes of Sciatic Nerve Injury
- Malnourished or emaciated patients in supine or sitting position on inadequately padded tables are at risk of sciatic nerve injury.
- Legs straight in a sitting position can also cause sciatic nerve injury.
- In lithotomy position, externally rotated legs with knees extended can cause sciatic nerve injury.
Nerve Injury Prevention
Radial and Circumflex Nerve
- Ensure adequate padding between the arm and vertical posts or poles to prevent pressure on the nerve
- Prevent the arm from pressing against vertical posts or poles to minimize nerve injury risk
Suprascapular Nerve
- Stabilize patients in a lateral position to protect the suprascapular nerve
Sciatic Nerve
- Use generous soft padding under the buttock to cushion the nerve
- Flex the table at the knees to reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve
- In lithotomy position, maintain minimal external rotation of the legs and keep the knees flexed to minimize nerve injury risk
Nerve Injuries
Common Peroneal Nerve Injuries
- Can occur in lithotomy position when the fibular neck rests against the vertical bar of the lithotomy stirrup
- Also occurs when knees are extended and legs are externally rotated in lithotomy position
- Can also occur in lateral position due to undue pressure on the downside leg
Posterior Tibial Nerve Injuries
- Can occur in lithotomy position when "knee crutch" stirrups support the posterior aspect of knees
Nerve Injuries Prevention
Common Peroneal Nerve
- To prevent injury in lithotomy position, ensure adequate padding between the leg and stirrup, and flex knees with minimal external rotation.
- In lateral position, padding under the fibular head is essential to prevent injury.
Posterior Tibial Nerve
- In lithotomy position, generous padding under the knees is crucial to prevent injury.
- Avoid using knee crutch stirrups for prolonged procedures to prevent posterior tibial nerve injury.
Nerve Injuries
- Saphenous nerve injuries can occur due to lithotomy positioning, where the foot is suspended outside a vertical bar and the leg rests on the bar, resulting in excessive pressure on the medial aspect of the leg from "knee crutch" stirrups.
Causes of Obturator Nerve Injuries
- Excessive flexion of the thigh at the hip during lithotomy positioning can cause obturator nerve injuries.
Causes of Pudendal Nerve Injuries
- Pudendal nerve injuries can result from traction of the legs against the perineal post or orthopedic fracture table.
Nerve Injuries
- Saphenous nerve injuries can be prevented by ensuring sufficient padding between the legs and vertical bar, and between the stirrup and leg during lithotomy position.
Nerve Protection
- To protect the obturator nerve, minimal hip flexion should be maintained during lithotomy position.
- Generous padding should be placed between the perineum and post to prevent pudendal nerve injuries.
Preventative Positioning for Nerve Injuries
Saphenous Nerve
- To prevent injury in Lithotomy position, ensure sufficient padding between:
- Legs and vertical bar
- Stirrup and leg
Obturator Nerve
- To prevent injury in Lithotomy position, maintain:
- Minimal hip flexion
Pudendal Nerve
- To prevent injury, use:
- Generous padding between perineum and post
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.