Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the nephron components with their functions:
Match the nephron components with their functions:
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) = Reabsorbs water depending on ADH Collecting Duct = Transport urine to the ureter Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) = Increases permeability of nephron parts Nephron = Filters blood to produce urine
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
ADH = Released from the pituitary gland Collecting Duct = Connects several nephrons Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) = Follows the nephron loop Kidneys = Regulate blood volume and waste removal
Match the process with its effect:
Match the process with its effect:
Water reabsorption = Decreases urine output Filtration = Produces urine ADH action = Increases water permeability of nephron Nephron function = Maintains homeostasis
Match the following hormones with their roles:
Match the following hormones with their roles:
Match the following effects with their triggers:
Match the following effects with their triggers:
Match the parts of the nephron with their functions:
Match the parts of the nephron with their functions:
Match the components of the kidney with their descriptions:
Match the components of the kidney with their descriptions:
Match the filtration process with its characteristics:
Match the filtration process with its characteristics:
Match the nephron parts with their specific functions:
Match the nephron parts with their specific functions:
Match the nephron functions with their importance:
Match the nephron functions with their importance:
Match the processes in kidney function with their descriptions:
Match the processes in kidney function with their descriptions:
Match specific nephron locations with the substances associated with them:
Match specific nephron locations with the substances associated with them:
Match the terms with their definitions related to nephron physiology:
Match the terms with their definitions related to nephron physiology:
Flashcards
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
The part of the nephron after the nephron loop where water diffusion depends on ADH.
Collecting Duct
Collecting Duct
A tube that collects urine from several nephrons and transports it to the ureter.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
A hormone released by the pituitary gland that increases water permeability in the DCT and collecting duct.
Filtration
Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reabsorption
Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a nephron?
What is a nephron?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the renal cortex?
What is the renal cortex?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the renal medulla?
What is the renal medulla?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the glomerulus?
What is the glomerulus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is filtration?
What is filtration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is filtrate?
What is filtrate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is reabsorption?
What is reabsorption?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
What is the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
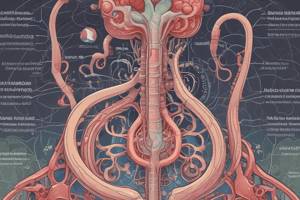
Nephron Function
- The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and producing urine.
- Millions of nephrons are located in the renal pyramids, found within the renal medulla and cortex.
- Each nephron is surrounded by blood vessels that supply blood to the kidneys.
Renal Cortex and Medulla
- The renal cortex is the outer layer of the kidney located above a diagram's dotted line.
- The renal medulla is the inner layer of the kidney located below the dotted line in a diagram.
Blood Vessels and Filtration
- Blood enters the nephron via a branch of the renal artery.
- The renal artery branches into a fine capillary network called the glomerulus, situated within Bowman's capsule.
- The glomerulus has thinner vessel walls compared to the renal artery, creating increased pressure and forcing fluid out of the glomerulus.
Filtration Process
- Filtration moves fluid from the glomerulus into Bowman's capsule.
- Approximately 20% of blood plasma is filtered into Bowman's capsule.
- Red blood cells, white blood cells, and large proteins remain in the bloodstream due to their size.
Filtrate
- The fluid that filters from the glomerulus is called filtrate.
- The filtrate moves through the rest of the nephron and is no longer considered blood plasma.
Reabsorption
- Reabsorption returns filtered substances from the nephron back into the bloodstream.
- Reabsorption occurs throughout the nephron.
- This process is vital for maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance and conserving essential nutrients.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- The PCT is the first segment of the nephron after Bowman's capsule.
- About two-thirds of the filtered water is reabsorbed from the PCT back into the blood.
- Important nutrients like sugars and vitamins are also reabsorbed from the PCT.
- The remaining filtrate proceeds to the nephron loop.
The Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle)
- The nephron loop dips into the saltier renal medulla.
- The descending limb is permeable to water, allowing water to leave due to osmosis.
- The ascending limb is impermeable to water but actively pumps out sodium and chloride ions, making the medulla salty and driving osmosis in the descending limb.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- The DCT is the segment of the nephron after the nephron loop.
- Water reabsorption in the DCT is influenced by Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH).
Collecting Duct
- Several nephrons connect to a single collecting duct.
- Water reabsorption in the collecting duct is also regulated by ADH.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
- ADH, or vasopressin, is released from the pituitary gland in the brain.
- ADH increases the permeability of the DCT and collecting duct to water, thus boosting water reabsorption and reducing urine output.
Overview
- The nephron filters blood and creates urine, which travels through the collecting duct, ureter, and bladder.
- The kidneys control blood volume, electrolyte balance, and waste removal.
- Filtration and reabsorption are critical for maintaining homeostasis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.