Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of muscles are described as wider in the center and taper off at the ends?
What type of muscles are described as wider in the center and taper off at the ends?
- Parallel Muscles
- Triangular Muscles
- Pennate Muscles
- Fusiform Muscles (correct)
What is an example of fusiform muscle architecture?
What is an example of fusiform muscle architecture?
Biceps brachii
Parallel muscles have fibers that are perpendicular to the force-generating axis.
Parallel muscles have fibers that are perpendicular to the force-generating axis.
False (B)
Name an example of parallel muscles.
Name an example of parallel muscles.
What is a defining feature of triangular (convergent) muscles?
What is a defining feature of triangular (convergent) muscles?
Provide an example of a triangular (convergent) muscle.
Provide an example of a triangular (convergent) muscle.
What characterizes pennate muscles?
What characterizes pennate muscles?
Name an example of a pennate muscle.
Name an example of a pennate muscle.
What is the shape of circular muscles?
What is the shape of circular muscles?
Which of the following is an example of a circular muscle?
Which of the following is an example of a circular muscle?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
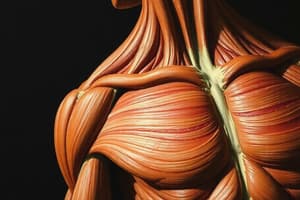
Muscle Shapes
-
Fusiform Muscles
- Characterized by a spindle shape, wider in the center and tapering at the ends.
- The line of action runs straight between attachment points, usually tendons.
- Force generated is concentrated in a small area.
- Example: Biceps brachii.
-
Parallel Muscles
- Muscle fibers run parallel to the force-generating axis.
- Ideal for fast and extensive movements.
- Measured by anatomical cross-sectional area.
- Examples: Sartorius and Sternocleidomastoid.
-
Triangular (Convergent) Muscles
- Origin is broader than the insertion point, allowing maximum force production.
- Fiber arrangement contributes to effective force generation.
- Example: Pectoralis Major.
-
Pennate Muscles
- Fibers are arranged at an angle to the force-generating axis (known as pennation angle).
- Fibers typically insert into a central tendon.
- Example: Deltoid muscle in the shoulder.
-
Circular Muscles (Sphincters)
- Circular muscle shape, functioning as sphincters surrounding openings.
- Control passage through openings in the body.
- Examples: Obicularis Oris (surrounding the mouth) and Obicularis Oculi (surrounding the eyes).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.