Podcast
Questions and Answers
A vector is a quantity that is completely specified by its magnitude and its speed.
A vector is a quantity that is completely specified by its magnitude and its speed.
False (B)
The point of application of the muscle force is where the muscle attaches to the skin.
The point of application of the muscle force is where the muscle attaches to the skin.
False (B)
The angle-of-insertion describes the angle formed between a ligament of a muscle and the long axis of the bone.
The angle-of-insertion describes the angle formed between a ligament of a muscle and the long axis of the bone.
False (B)
A force acting without a moment arm cannot potentially translate a body segment.
A force acting without a moment arm cannot potentially translate a body segment.
The perpendicular distance between the Axis of Rotation of a joint and a force is called a moment arm.
The perpendicular distance between the Axis of Rotation of a joint and a force is called a moment arm.
The product of a force and its moment arm produces a torque or a moment.
The product of a force and its moment arm produces a torque or a moment.
Internal torque is defined as the product of the external force and the external moment arm.
Internal torque is defined as the product of the external force and the external moment arm.
External torque is defined as the product of the external force and the external moment arm.
External torque is defined as the product of the external force and the external moment arm.
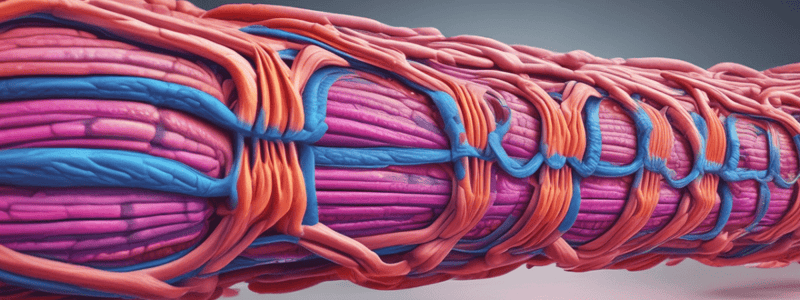
Muscles consist of a single muscle fiber.
Muscles consist of a single muscle fiber.
Contraction of individual muscle fibers is responsible for contraction of the whole muscle.
Contraction of individual muscle fibers is responsible for contraction of the whole muscle.
The epimysium surrounds individual muscle fibers.
The epimysium surrounds individual muscle fibers.
Extracellular connective tissues help transmit contractile forces throughout the muscle.
Extracellular connective tissues help transmit contractile forces throughout the muscle.
Myofilaments consist of the proteins actin and myosin.
Myofilaments consist of the proteins actin and myosin.
The sarcomere is the fundamental unit within each muscle fiber.
The sarcomere is the fundamental unit within each muscle fiber.
Shortening of the muscle fiber generates shortening of the sarcomere.
Shortening of the muscle fiber generates shortening of the sarcomere.
Noncontractile proteins within the sarcomere interact to shorten the muscle fiber.
Noncontractile proteins within the sarcomere interact to shorten the muscle fiber.
The ratio of muscle fibers to nerve fibers is 1:1 for eye muscles.
The ratio of muscle fibers to nerve fibers is 1:1 for eye muscles.
The hamstrings have a 1:300 muscle fiber to nerve fiber ratio.
The hamstrings have a 1:300 muscle fiber to nerve fiber ratio.
The neuromuscular junction is the site where the motor neuron meets the muscle fiber.
The neuromuscular junction is the site where the motor neuron meets the muscle fiber.
The motor end plate is formed by the sarcolemma around the motor neuron.
The motor end plate is formed by the sarcolemma around the motor neuron.
Acetylcholine is released from the muscle fiber to cause an end-plate potential.
Acetylcholine is released from the muscle fiber to cause an end-plate potential.
Rate coding and recruitment are the two primary strategies of the nervous system to activate motor neurons.
Rate coding and recruitment are the two primary strategies of the nervous system to activate motor neurons.
Recruitment involves altering the voltage potential across the membrane of the alpha motor neuron.
Recruitment involves altering the voltage potential across the membrane of the alpha motor neuron.
An action potential is propagated down the axon to the muscle endplate at the neuromuscular junction.
An action potential is propagated down the axon to the muscle endplate at the neuromuscular junction.
Active insufficiency refers to the decrease in torque when a muscle is excessively shortened.
Active insufficiency refers to the decrease in torque when a muscle is excessively shortened.
At the sarcomere level, active insufficiency occurs when the sarcomere length deviates significantly from the optimal length during joint movements.
At the sarcomere level, active insufficiency occurs when the sarcomere length deviates significantly from the optimal length during joint movements.
The influence of the muscle's moment arm and passive restraint of the antagonists may be more important factors than sarcomere length in active insufficiency.
The influence of the muscle's moment arm and passive restraint of the antagonists may be more important factors than sarcomere length in active insufficiency.
Mass and weight are the same measurement.
Mass and weight are the same measurement.
On Earth, an object with a mass of 1 kilogram weighs $9.8\text{ N}$.
On Earth, an object with a mass of 1 kilogram weighs $9.8\text{ N}$.
The references cited in the text are by authors named Neumann, Levangie, and Norkin.
The references cited in the text are by authors named Neumann, Levangie, and Norkin.
The concept of active insufficiency is discussed in the book 'Joint Structure and Function' by Levangie and Norkin.
The concept of active insufficiency is discussed in the book 'Joint Structure and Function' by Levangie and Norkin.
The difference between mass and weight is only relevant on Earth's surface.
The difference between mass and weight is only relevant on Earth's surface.
The pennation angle is always greater than 0 for a muscle.
The pennation angle is always greater than 0 for a muscle.
The contractile (active) proteins within the sarcomeres cause a contraction or shortening of the entire muscle upon stimulation from the nervous system.
The contractile (active) proteins within the sarcomeres cause a contraction or shortening of the entire muscle upon stimulation from the nervous system.
The parallel elastic (PEC) components only include the extracellular connective tissues (i.e., perimysium) and not other structural proteins that surround and support the muscle fiber.
The parallel elastic (PEC) components only include the extracellular connective tissues (i.e., perimysium) and not other structural proteins that surround and support the muscle fiber.
The series elastic components (SEC) of muscle are attached in series with the active proteins, such as tendons and large structural proteins like titin.
The series elastic components (SEC) of muscle are attached in series with the active proteins, such as tendons and large structural proteins like titin.
When a muscle lengthens or shortens, the parallel elastic (PEC) components do not change in length and remain static.
When a muscle lengthens or shortens, the parallel elastic (PEC) components do not change in length and remain static.
The increased resistance to elongation of the perimysium may prevent overstretching of the muscle fiber.
The increased resistance to elongation of the perimysium may prevent overstretching of the muscle fiber.
When sarcomeres shorten from their resting position, the slack collagen fibers within the parallel elastic component become tighter and more rigid.
When sarcomeres shorten from their resting position, the slack collagen fibers within the parallel elastic component become tighter and more rigid.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying