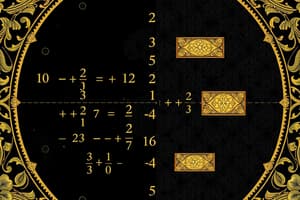
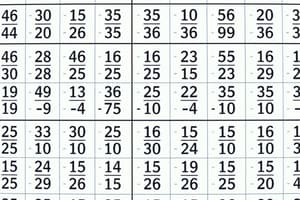
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the area of an object represent?
What does the area of an object represent?
- The thickness of the object
- The height of the object
- The weight of the object
- The amount of space occupied by its surface (correct)
How is the area of a rectangle calculated?
How is the area of a rectangle calculated?
- Dividing its length by its width
- Subtracting its length from its width
- Adding its length and width
- Multiplying its length and width (correct)
Why is understanding multiplication crucial in calculating area?
Why is understanding multiplication crucial in calculating area?
- It helps in visualizing the dimensions of an object
- It allows for faster calculations
- It enables precise measurement of area
- It simplifies the process of finding the area (correct)
How are parallelograms and triangles handled when calculating their area?
How are parallelograms and triangles handled when calculating their area?
In the area model for multiplication, what do the sides of a rectangle represent?
In the area model for multiplication, what do the sides of a rectangle represent?
What does each intersection in the grid used for multiplication represent?
What does each intersection in the grid used for multiplication represent?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Measuring Area with Multiplication
Measuring area with multiplication is a fundamental mathematical concept that describes the relationship between a surface and its dimensions. The area of an object is the amount of space occupied by its surface, typically measured in square units, such as square meters or square feet. Multiplying the length and width of an object gives its area, making it a crucial aspect of understanding multiplication and geometry.
For instance, consider a rectangle with a length of 4 units and a width of 3 units. By multiplying these two numbers, we get the area of the rectangle: 4 * 3 = 12 square units. This concept can be extended to more complex shapes, such as parallelograms and triangles, by breaking them down into simpler shapes like rectangles.
The principles of multiplication and area are closely linked. When multiplying numbers, we can visualize the process as filling a grid with the digits of the numbers being multiplied. For example, to multiply 43 by 218, we might draw a 2 × 3 grid and fill it with the digits of 43 along the right side and those of 218 along the top. Each intersection in the grid corresponds to a product formed when multiplying corresponding digits.
The area model for multiplication provides a visual representation of multiplication, helping students understand the concept better. In this model, the factors are represented by the sides of a rectangle, and their product is the area of the rectangle. This approach is particularly effective for teaching children and reinforcing their understanding of multiplication and area relationships.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.