Podcast
Questions and Answers
Active transport moves solutes from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration and requires ATP.
Active transport moves solutes from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration and requires ATP.
False (B)
How many sodium and potassium would be moved to the appropriate locations if 3 ATP are used?
How many sodium and potassium would be moved to the appropriate locations if 3 ATP are used?
9 sodium out, 6 potassium in
What is osmosis?
What is osmosis?
Passive transport of water following solute concentration.
Voltage gated channels are a form of active transport.
Voltage gated channels are a form of active transport.
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
What is the sodium-potassium pump?
What is facilitated diffusion?
What is facilitated diffusion?
Explain the difference between active and passive transport.
Explain the difference between active and passive transport.
What is cotransport?
What is cotransport?
The force driving simple diffusion is ______, while the energy source for active transport is ______.
The force driving simple diffusion is ______, while the energy source for active transport is ______.
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell even when the concentration outside is much lower. This transport is an example of __________.
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell even when the concentration outside is much lower. This transport is an example of __________.
The voltage across a membrane is called the ______.
The voltage across a membrane is called the ______.
What does a sodium-potassium pump do?
What does a sodium-potassium pump do?
How could a cell increase the concentration of phosphate in the cytosol if the concentration outside is 0.1 mM and inside is 2.0 mM?
How could a cell increase the concentration of phosphate in the cytosol if the concentration outside is 0.1 mM and inside is 2.0 mM?
What is exocytosis?
What is exocytosis?
What is endocytosis?
What is endocytosis?
Both endocytosis and exocytosis require cellular energy.
Both endocytosis and exocytosis require cellular energy.
The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that ______.
The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that ______.
White blood cells engulf bacteria using ______.
White blood cells engulf bacteria using ______.
What is diffusion?
What is diffusion?
What is the process by which substances are transported across cell membranes by protein carrier molecules?
What is the process by which substances are transported across cell membranes by protein carrier molecules?
What is active transport?
What is active transport?
Passive diffusion is either _____________
Passive diffusion is either _____________
What is passive transport?
What is passive transport?
What is simple diffusion?
What is simple diffusion?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Molecular Transport Concepts
-
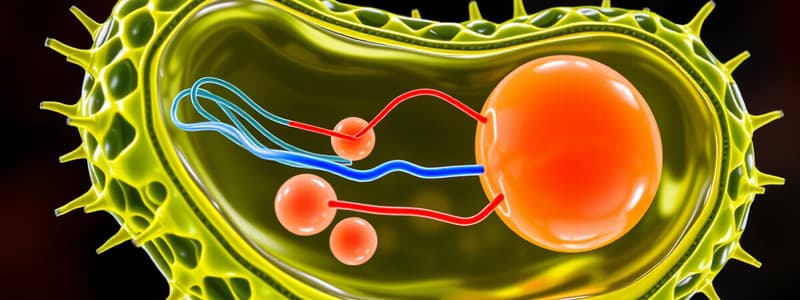
Active Transport
- Moves solutes from low to high concentration against the gradient.
- Requires energy in the form of ATP.
- Example: Sodium-Potassium pump (3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in) uses 1 ATP per cycle.
-
Passive Transport
- Moves substances from high to low concentration without energy input.
- Examples include diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis.
- Operates down the concentration gradient.
Key Transport Mechanisms
-
Osmosis
- Passive movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, following solute concentration.
-
Facilitated Diffusion
- Specific proteins help transport solutes across the membrane without energy.
- Utilizes channel or carrier proteins (e.g., GLUT1 transporter).
-
Voltage-Gated Channels
- Allow ions to move across membranes without energy usage when opened by voltage changes.
-
Cotransport
- Energy for moving one solute against its gradient is provided by another solute moving down its gradient.
Types of Endocytosis and Exocytosis
-
Endocytosis
- Forms vesicles from membrane folding, bringing substances into the cell.
- Decreases surface area of the plasma membrane.
-
Exocytosis
- Fuses vesicles with the plasma membrane to secret large molecules outside the cell.
- Increases plasma membrane surface area.
-
Phagocytosis
- A type of endocytosis where white blood cells engulf bacteria.
-
Pinocytosis vs. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
- Pinocytosis is nonselective; receptor-mediated is selective for specific molecules.
Important Definitions
-
Membrane Potential
- Voltage difference across a membrane due to differences in ion distribution.
-
Diffusion
- Movement of substances across membranes without intermediaries.
-
Active vs. Passive Transport
- Active transport requires energy to move substances against the gradient; passive transport does not.
-
Osmotic Pressure
- The pressure required to prevent water from moving into a solution.
Concentration Examples
- If cytosolic phosphate concentration is 2.0 mM and surrounding fluid is 0.1 mM, active transport is necessary to increase cytosolic phosphate concentration.
Summary of Transport Types
- Active Transport: Uses energy; moves against the gradient.
- Passive Diffusion: Moves down the gradient; no energy needed (includes simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.