Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is one primary purpose of systems documentation?
What is one primary purpose of systems documentation?
- Describing business processes (correct)
- Training employees on software
- Designing user interfaces
- Creating marketing materials for products
What percentage of public companies emphasized reading or preparing systems documentation post-Sarbanes-Oxley Act?
What percentage of public companies emphasized reading or preparing systems documentation post-Sarbanes-Oxley Act?
- 82% (correct)
- 72%
- 92%
- 62%
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of using a process map?
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of using a process map?
- Enhancing product marketing strategies (correct)
- Highlighting workflow inefficiencies
- Identifying opportunities to streamline processes
- Promoting awareness of employee responsibilities
What symbol in a process map represents the transformation of inputs into outputs?
What symbol in a process map represents the transformation of inputs into outputs?
What method is considered less effective for gathering information for a process map?
What method is considered less effective for gathering information for a process map?
In developing a process map, what does the term 'trigger' refer to?
In developing a process map, what does the term 'trigger' refer to?
What is the purpose of swim lanes in a process map?
What is the purpose of swim lanes in a process map?
What does a process flow line in a process map indicate?
What does a process flow line in a process map indicate?
Which of the following roles would likely be included in a process map for order fulfillment?
Which of the following roles would likely be included in a process map for order fulfillment?
Which term describes the outcomes that come from decision points in a process map?
Which term describes the outcomes that come from decision points in a process map?
What should be the focus when assessing a process for non value-added steps?
What should be the focus when assessing a process for non value-added steps?
What is a primary risk associated with handoffs in a process?
What is a primary risk associated with handoffs in a process?
Which issue is likely to cause delays by limiting the performance of an entire system?
Which issue is likely to cause delays by limiting the performance of an entire system?
What does cycle time refer to in process evaluation?
What does cycle time refer to in process evaluation?
What is a common problem that arises from role ambiguity?
What is a common problem that arises from role ambiguity?
What should be avoided to prevent unnecessary delays in a process?
What should be avoided to prevent unnecessary delays in a process?
Which of the following best describes data duplication in process mapping?
Which of the following best describes data duplication in process mapping?
In process mapping, what should the roles retain throughout the map?
In process mapping, what should the roles retain throughout the map?
What is a significant contributor to cycle time delays?
What is a significant contributor to cycle time delays?
What should be included when starting with a high-level process map?
What should be included when starting with a high-level process map?
Flashcards
Handoff
Handoff
A process map component that illustrates a transfer of responsibility from one role to another in the map. This transfer can increase the potential for errors or delays.
Bottleneck
Bottleneck
A point in a process where multiple activities flow into one single activity, potentially causing slowdowns or complete process stoppage.
Cycle Time
Cycle Time
The time a process takes from start to finish. It's a key measure of process efficiency.
Flow Time
Flow Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-Value-Added Step
Non-Value-Added Step
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systems Diagrams
Systems Diagrams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systems Documentation
Systems Documentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Process Map
Process Map
Signup and view all the flashcards
Activities
Activities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decision Points
Decision Points
Signup and view all the flashcards
Process Flow Lines
Process Flow Lines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Data Stores
Data Stores
Signup and view all the flashcards
Swim Lanes
Swim Lanes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigger
Trigger
Signup and view all the flashcards
Group Interview Method
Group Interview Method
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Modern ERP: Systems Diagramming and Process Mapping
- Systems Documentation has three basic purposes: describing business processes, assessing internal control procedures, and evaluating/designing/changing information systems.
- Systems Diagrams graphically represent systems, including flowcharts, ER diagrams, and other techniques.
- Importance of systems diagramming: A recent study highlighted increased emphasis on reading and preparing systems documentation for 72% of private and 82% of public companies since the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. A 2006 study found that 77% considered the ability to read system diagrams "very important" or "somewhat important," and 66% felt likewise about the ability to prepare such diagrams.
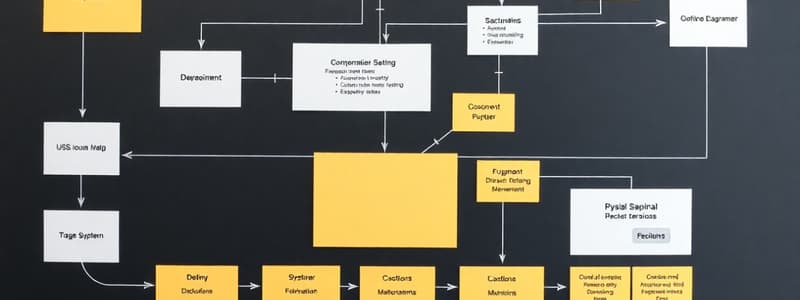
Process Maps
- A process map, also called a cross-functional flowchart, documents, analyzes, streamlines, and redesigns business activities.
- Benefits:
- Defines the "as is" process and clarifies changes needed for the "to be" process.
- Determines if "as is" measures are appropriate.
- Promotes awareness of employee responsibilities.
- Shows the impact of a role's performance on upstream/downstream activities in the process.
- Highlights workflow inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
- Pinpoints internal controls needing audit testing.
Process Map Symbols
- Activities (events) transform inputs into outputs.
- Decision points represent yes/no outcomes, depicting alternatives.
- Process flow lines connect symbols, labeled to show information flow.
- Data stores support the process.
- Termination points mark the end of the process.
- On-page connectors reduce clutter, used when processes are on a single page.
- Off-page connectors manage processes spanning multiple pages.
Gathering Information for a Process Map
- Group interview method: All process participants are interviewed together using a skilled facilitator to promote unbiased discussions that question conventional wisdom.
- One-on-one interview method: Less effective than group interviews because each person is interviewed individually.
- Walkthrough: A physical review of the process scope to confirm if the documented process accurately reflects the current workflow.
Guidelines for Developing a Process Map
- Define the purpose and explain it to participants.
- Identify the process scope.
- Determine participating roles and assign them to swim lanes (horizontal bands).
- The trigger event initiates the process (first swim lane).
- Events move from left-to-right or top-to-bottom chronologically.
- Information exchange details are on the flow lines.
- Decision points end with a question mark, outcomes labeling flow lines emerging.
- The last swim lane accommodates information systems supporting the process.
Process Map Example
- Example of an electric city order fulfillment process map. (a diagram of the specific steps)
Hints for Constructing Process Maps
- Maintain consistent effort level across the map.
- Start with a high-level map and use detailed documentation for activities.
- Create glossary of process acronyms.
- Use humps where flow lines intersect.
- Maintain consistent role assignments (swim lanes) even across multiple pages.
- Terminate the process in the final swim lane.
Advanced Process Map Example
- Examples of Monster Furniture warehouse order-to-cash process maps (diagrams). (two pages)
Process Problems to Uncover
- Handoffs: Transferring responsibility can lead to mistakes, miscommunication, and delay.
- Bottlenecks: Multiple flows converging to a single activity can limit system performance and delay processes.
- Rework: Time spent fixing errors during processes.
- Role ambiguity: Lack of clarity on roles/responsibilities leads to confusion among participants.
- Data duplication: Excessive flows between information systems can mean unnecessary data exists in multiple places.
- Cycle time: measuring the time consumed during process flow from start to finish.
- Flow time: measures time between activities, identifies delays and underutilization.
- Non-value-added steps: customer workflow is examined. Unnecessary or repeated steps are often problematic.
Process Decision Issues to Uncover
- Authority ambiguity: Defining who has decision-making authority.
- Decision necessity: Avoid unnecessary decisions that lead to delays in the process.
- Decisions made too early/too late: potential errors.
Developing the "To-be" Process
- Identifying the customer, their needs, and willingness to pay.
- Determining performance expectations and satisfaction levels.
- Defining process start and end points (optimal).
- Identifying crucial/added-value process steps.
- Deciding/differentiating what can be changed (in scope) from what cannot (out of scope).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.