Podcast
Questions and Answers
During which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope disassemble?
During which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope disassemble?
- Prophase
- Anaphase
- Metaphase (correct)
- Telophase
If a cell undergoing mitosis has 46 chromosomes at the beginning of prophase, how many chromosomes will each of the daughter cells have after telophase and cytokinesis?
If a cell undergoing mitosis has 46 chromosomes at the beginning of prophase, how many chromosomes will each of the daughter cells have after telophase and cytokinesis?
- 12
- 46 (correct)
- 92
- 23
During what phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles of the cell?
During what phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles of the cell?
- Prophase
- Telophase
- Anaphase (correct)
- Metaphase
What is the direct result of mitosis?
What is the direct result of mitosis?
In which stage of mitosis do two new nuclei begin to form?
In which stage of mitosis do two new nuclei begin to form?
Which of the following best describes the state of chromosomes during prophase?
Which of the following best describes the state of chromosomes during prophase?
What event typically occurs concurrently with telophase to fully separate the two new daughter cells?
What event typically occurs concurrently with telophase to fully separate the two new daughter cells?
The 'M' in Metaphase stands for?
The 'M' in Metaphase stands for?
What is the primary purpose of the cell cycle in organisms?
What is the primary purpose of the cell cycle in organisms?
A scientist is studying cells that complete their cycle in approximately 8 minutes. Which type of eukaryotic cells are they most likely observing?
A scientist is studying cells that complete their cycle in approximately 8 minutes. Which type of eukaryotic cells are they most likely observing?
Which of the following best describes interphase?
Which of the following best describes interphase?
A cell has just completed DNA replication. In which phase of the cell cycle is this cell most likely to be?
A cell has just completed DNA replication. In which phase of the cell cycle is this cell most likely to be?
What is the relationship between mitosis and the cell cycle?
What is the relationship between mitosis and the cell cycle?
If a scientist introduces a substance that halts cell growth and development, which phase of the cell cycle would be most immediately affected?
If a scientist introduces a substance that halts cell growth and development, which phase of the cell cycle would be most immediately affected?
How does the cell cycle contribute to the healing of a wound?
How does the cell cycle contribute to the healing of a wound?
If a cell with a mutation is unable to complete interphase, what is the most likely outcome?
If a cell with a mutation is unable to complete interphase, what is the most likely outcome?
During mitosis, what ensures that each daughter cell receives the same genetic material as the parent cell?
During mitosis, what ensures that each daughter cell receives the same genetic material as the parent cell?
If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes before mitosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis?
If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes before mitosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis?
Before a cell divides, the genetic material in its nucleus:
Before a cell divides, the genetic material in its nucleus:
A human body cell contains two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. What term describes this number of chromosomes?
A human body cell contains two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. What term describes this number of chromosomes?
In the context of chromosomes, what is a centromere?
In the context of chromosomes, what is a centromere?
Prior to cell division, a chromosome duplicates, resulting in two identical structures. What are these structures called?
Prior to cell division, a chromosome duplicates, resulting in two identical structures. What are these structures called?
A cell is observed to be actively replicating its DNA. In which phase of the cell cycle is this cell most likely to be?
A cell is observed to be actively replicating its DNA. In which phase of the cell cycle is this cell most likely to be?
A cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes DNA replication. How many chromosomes are technically present after replication but before cell division?
A cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes DNA replication. How many chromosomes are technically present after replication but before cell division?
If a certain species has a diploid number of 20, how many chromosomes did each parent contribute to the offspring?
If a certain species has a diploid number of 20, how many chromosomes did each parent contribute to the offspring?
Before a cell enters the mitotic phase, which of the following must occur during interphase to ensure successful cell division?
Before a cell enters the mitotic phase, which of the following must occur during interphase to ensure successful cell division?
During the G2 phase of interphase, what primary activity prepares the cell for the upcoming mitotic phase?
During the G2 phase of interphase, what primary activity prepares the cell for the upcoming mitotic phase?
If a cell fails to replicate its organelles during interphase, what is the most likely consequence for the daughter cells following cell division?
If a cell fails to replicate its organelles during interphase, what is the most likely consequence for the daughter cells following cell division?
A researcher observes a cell with a significantly reduced amount of available energy. Which phase of interphase would be most affected by this condition?
A researcher observes a cell with a significantly reduced amount of available energy. Which phase of interphase would be most affected by this condition?
Chromosomes are composed of DNA and proteins. What is the primary purpose of organizing DNA into chromosomes before cell division?
Chromosomes are composed of DNA and proteins. What is the primary purpose of organizing DNA into chromosomes before cell division?
A toxin is introduced that halts the production of proteins and lipids within a cell. Which process would be directly inhibited?
A toxin is introduced that halts the production of proteins and lipids within a cell. Which process would be directly inhibited?
What distinguishes the G1 phase from the G2 phase in the cell cycle?
What distinguishes the G1 phase from the G2 phase in the cell cycle?
What is the primary function of mitosis in multicellular organisms?
What is the primary function of mitosis in multicellular organisms?
During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur, resulting in the formation of sister chromatids?
During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur, resulting in the formation of sister chromatids?
What would be the most likely outcome if the centromere did not function correctly during mitosis?
What would be the most likely outcome if the centromere did not function correctly during mitosis?
A cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many chromosomes will each daughter cell have?
A cell with 46 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many chromosomes will each daughter cell have?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between chromosomes, DNA, and sister chromatids?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between chromosomes, DNA, and sister chromatids?
A researcher observes a cell undergoing mitosis but notices that the chromosomes are not aligned in the middle of the cell. Which stage of mitosis is most likely affected?
A researcher observes a cell undergoing mitosis but notices that the chromosomes are not aligned in the middle of the cell. Which stage of mitosis is most likely affected?
Which statement accurately contrasts mitosis and cytokinesis?
Which statement accurately contrasts mitosis and cytokinesis?
If a toxin interferes with the function of the mitotic spindle, which stage of mitosis would be directly affected?
If a toxin interferes with the function of the mitotic spindle, which stage of mitosis would be directly affected?
Flashcards
Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle
The repeating series of growth, development, and division that cells go through.
Cell Cycle Purpose
Cell Cycle Purpose
To grow and develop, replace old/damaged cells, and produce new cells.
Main Cell Cycle Phases
Main Cell Cycle Phases
Interphase and the Mitotic Phase.
Mitosis
Mitosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Cycle Length
Cell Cycle Length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interphase
Interphase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Cell Cycle
Human Cell Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interphase Stages
Interphase Stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
G1 Stage
G1 Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
S Stage
S Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
G2 Stage
G2 Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitotic Phase (Mitosis)
Mitotic Phase (Mitosis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organelle Replication
Organelle Replication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromosomes
Chromosomes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleus
Nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sister Chromatids
Sister Chromatids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centromere
Centromere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitotic Phase
Mitotic Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Replication
Replication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Daughter Cells
Daughter Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goal of Mitosis
Goal of Mitosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diploid number
Diploid number
Signup and view all the flashcards
Copied chromosome
Copied chromosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
DNA
DNA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human chromosome sets
Human chromosome sets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromosomes (human)
Chromosomes (human)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Replacement
Cell Replacement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prophase
Prophase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metaphase
Metaphase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anaphase
Anaphase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Telophase
Telophase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Result of Mitosis
Result of Mitosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The goal of this lesson is to understand the cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis, and each phase of cell division.
- Success in this lesson is achieved by describing the phases of the cell cycle and cell division, as well as understanding the difference between mitosis and meiosis.
- Weather changes in a regular pattern each year.
- Some areas experience four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and fall.
- As seasons change, temperature, precipitation, and the number of hours of sunlight also change in a regular cycle.
- Just like the seasons, cells have a life cycle.
- Most cells in an organism go through a cycle of growth, development, and division called the cell cycle.
- The cell cycle makes it possible for organisms to grow, develop, and replace old and damaged cells and to produce new cells
- Mitosis involves the division of body cells.
Phases of the Cell Cycle
- The goal of the cell cycle is to create new identical cells.
- There are two main phases in the cell cycle: interphase and mitotic phase.
- The time it takes a cell to complete the cell cycle depends on the type that is dividing.
- For some eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle might take only around eight minutes, while in others it is up to a year.
- Most cells in the human body can complete the cell cycle in about 24 hours.
- The fertilized zebrafish can divide into 256 cells in just 2.5 hours.
- Interphase is a period of cell growth and development.
- Interphase is followed by a shorter mitotic phase (also called mitosis).
- Most cells spend the majority of their life in interphase.
- Most cells go through three stages during interphase: G1, S, and G2.
- Interphase is followed by the mitotic phase, also called mitosis, a shorter phase.
Interphase Stages
- The G1 stage is the first stage of interphase and is a period of rapid growth.
- G1 is the longest stage of the cell cycle,during this stage the cell grows and carries out normal cell functions.
- The S phase is the second stage of interphase, during this stage a cell grows and copies its DNA
- The G2 stage is the third and final stage of interphase.
- The G2 phase is a period of growth and final preparation for mitosis.
- Cells use energy during the S phase to copy DNA.
- During G2, the cell stores energy that will be used during the mitotic phase of the cell cycle.
- To understand mitosis a cell must make a copy of organelles and DNA before dividing.
- During cell division, the organelles are distributed between the two new cells.
- Before a cell divides, it makes a copy of each organelle, these copies of organelles come from materials like proteins and lipids .
- Genetic information is in the form of DNA, located in the nucleus.
- Cells must organize DNA so it can copy itself and divide into new cells with identical DNA in both of them.
- DNA is organized into chromosomes, which are made up of DNA and proteins.
- Chromosomes are counted by the number of centromeres (circles in the center) that are present.
- Before a body cell divides, the genetic material in the nucleus copies itself.
- Mitosis is the dividing of the nucleus to create 2 cells from 1
- Each cell gets genetic material that is the same as the parent cell's.
- If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes, each daughter cell will also have 46 chromosomes.
- Before chromosomes can divide, they are duplicated; that's why chromosomes are technically 46, but each has 2 chromatids called sister chromatids.
- Cells contain 46 chromosomes (2 sets), which make up the diploid number of chromosomes.
- One set of 23 chromosomes comes from the father; the other set of 23 comes from the mother.
- Human cells have 46 chromosomes that get duplicated before the cell divides.
Mitotic Phase
- The mitotic phase of the cell cycle follows interphase.
- There are two stages of mitotic phase mitosis and cytokinesis.
- Cell division occurs in a series of stages or phases, ensuring that daughter cells are the same as the parent cell.
- As a cell prepares to divide, each chromosome in the nucleus makes an exact copy of itself for replication.The two copies are called sister chromatids.
- Mitosis makes 2 identical cells.
- Mitosis and cell division allow living things to grow bigger and replace old or injured cells.
- Mitosis occurs in body cells.
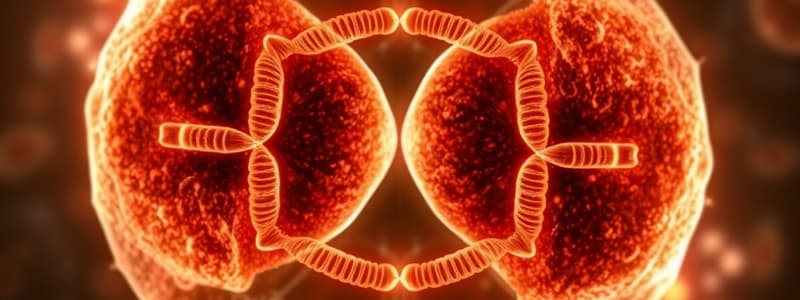
Stages of Mitosis
- The first stage is Prophase where the nucleus is still present and the chromosomes are condensing (becoming visible). "Pro" means "before".
- The second phase is metaphase, where the nucleus disassembles, remember “M” for “middle”
- The third stage is anaphase, where the chromatids separate and begin to move "away" from the middle, and move to the poles of the cell. Think of it like “A” for “ away”
- The final phase is Telophase where two new nuclei begin to form, think "T" for "two"
- Then during the last part of mitosis is cytokinesis, where the cytoplasm of a cell divides, creating 2 new identical daughter cells.
- Mitosis results in two new cells, daughter cells, that are genetically the same.
Cell cycle stages
-Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.