Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the simplest and effective contrasting method in microscopy?
What is the simplest and effective contrasting method in microscopy?
- Differential interference contrast
- Fluorescence
- Dark field (correct)
- Phase contrast
Who were the pioneers of histochemical staining of biological samples?
Who were the pioneers of histochemical staining of biological samples?
Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal
Frits Zernike was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
Frits Zernike was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
False (B)
What is the phenomenon exploited in polarization microscopy?
What is the phenomenon exploited in polarization microscopy?
What is the principal advantage of fluorescence microscopy?
What is the principal advantage of fluorescence microscopy?
In which year did Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie, and Robert Y. Tsien receive the Nobel Prize for their work on GFP?
In which year did Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie, and Robert Y. Tsien receive the Nobel Prize for their work on GFP?
Fluorescent dyes have limited stability and may _________ over time.
Fluorescent dyes have limited stability and may _________ over time.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Microscopy Techniques
- Dark-field microscopy improves contrast by exploiting light scattering on small particles.
- Staining with dyes that recognize specific structures enhances contrast and reveals tissue and cellular features.
- Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal pioneered histochemical staining techniques and were awarded the 1906 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
- Phase contrast microscopy, developed by Frits Zernike, utilizes changes in light polarization to visualize unstained specimens. Zernike received the 1953 Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery.
- Polarization microscopy observes changes in light polarization to study unstained specimens, finding applications in material science.
- Differential interference contrast microscopy, invented by Jerzy (Georges) Nomarski, uses two polarized light beams to create an illusion of 3D structure.
Fluorescence Microscopy
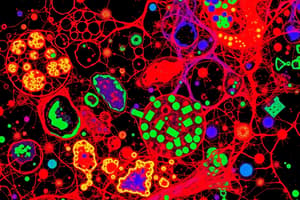
- Fluorescence microscopy utilizes fluorophores that absorb light at specific wavelengths and emit it at longer wavelengths.
- A wide variety of fluorophores are available, covering various wavelengths, and new ones are still being developed.
- Early fluorescent dyes were used for fabric dyeing before being adapted for biological research.
- The use of fluorescently stained antibodies and specially synthesized fluorescent probes revolutionized biological applications of fluorescence microscopy.
- Fluorescent proteins, like GFP, significantly influenced microscopy techniques and enabled advancements in cell biology.
- Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie, and Robert Y.Tsien received the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their work on GFP.
Benefits of Fluorescence Microscopy
- High contrast, sensitivity, specificity, and selectivity are key advantages of fluorescence microscopy.
Challenges of Fluorescence Microscopy
- Fluorescent dyes have limited stability, photobleaching over time, and may produce toxic substances, requiring careful handling and precautions.
Application of Fluorescence Microscopy
- Fluorescence microscopy effectively reveals intricate details in cells and tissues, providing insights into biological processes.
Key Figures
- Camillo Golgi
- Santiago Ramon y Cajal
- Frits Zernike
- Jerzy (Georges) Nomarski
- Osamu Shimomura
- Martin Chalfie
- Robert Y.Tsien
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.