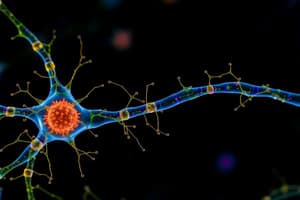
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of membrane receptors?
What is the main function of membrane receptors?
- To regulate cell division
- To provide structural support to the cell membrane
- To synthesize proteins
- To facilitate communication with the outside environment (correct)
What is the term used to describe signaling molecules that bind to membrane receptors?
What is the term used to describe signaling molecules that bind to membrane receptors?
- Hormones
- Neurotransmitters
- Receptors
- Ligands (correct)
What type of protein is a membrane receptor?
What type of protein is a membrane receptor?
- Cytoplasmic protein
- Integral protein (correct)
- Transmembrane protein
- Peripheral protein
What is the complex formed when a ligand binds to a membrane receptor?
What is the complex formed when a ligand binds to a membrane receptor?
What is the role of extra cellular signaling molecules?
What is the role of extra cellular signaling molecules?
What is the location of membrane receptors?
What is the location of membrane receptors?
What is the outcome when a ligand binds to a membrane receptor?
What is the outcome when a ligand binds to a membrane receptor?
What can extra cellular signaling molecules be?
What can extra cellular signaling molecules be?
What is the process called when an extracellular signal molecule binds to a membrane receptor, causing an intracellular response?
What is the process called when an extracellular signal molecule binds to a membrane receptor, causing an intracellular response?
What is the name of the model that describes the specific binding of a ligand to a receptor?
What is the name of the model that describes the specific binding of a ligand to a receptor?
What is the purpose of membrane receptors in cellular communication?
What is the purpose of membrane receptors in cellular communication?
What is the result of a ligand binding to a receptor protein?
What is the result of a ligand binding to a receptor protein?
Why do different cells have different receptors?
Why do different cells have different receptors?
What is the importance of membrane receptors in pharmaceutical drug design?
What is the importance of membrane receptors in pharmaceutical drug design?
What is the term for the process by which cells respond to signals from their environment?
What is the term for the process by which cells respond to signals from their environment?
What is the updated model of ligand-receptor binding?
What is the updated model of ligand-receptor binding?
What is the result of a signal being propagated throughout a cell?
What is the result of a signal being propagated throughout a cell?
Why is signal transduction important in cellular communication?
Why is signal transduction important in cellular communication?
What is the term used to describe the process of a ligand binding to a membrane receptor and triggering a response within the cell?
What is the term used to describe the process of a ligand binding to a membrane receptor and triggering a response within the cell?
What is the characteristic of the binding between ligands and membrane receptors?
What is the characteristic of the binding between ligands and membrane receptors?
How many major groups can membrane receptors be categorized into?
How many major groups can membrane receptors be categorized into?
What is the function of integral proteins in the cell membrane?
What is the function of integral proteins in the cell membrane?
What is the term used to describe the binding of a ligand to an enzyme-linked receptor?
What is the term used to describe the binding of a ligand to an enzyme-linked receptor?
Which of the following is NOT a type of membrane receptor?
Which of the following is NOT a type of membrane receptor?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Membrane Receptors
- Membrane receptors are integral proteins embedded in the cell membrane, allowing cells to communicate with the outside environment.
- Without membrane receptors, cells wouldn't be able to work together to form the human body.
- Membrane receptors are crucial for cells to respond to external signals, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and cell recognition molecules.
Signaling Molecules and Ligands
- Signaling molecules, also known as extracellular signaling molecules, are molecules outside the cell that bind to membrane receptors to trigger responses inside the cell.
- Ligands are signaling molecules that bind to membrane receptors, including ions, molecules, neurotransmitters, hormones, and cell recognition molecules.
How Membrane Receptors Work
- A ligand binds to a membrane receptor, forming a ligand-receptor complex.
- This complex triggers a response inside the cell, allowing the cell to respond to the external signal.
- This process is called signal transduction, which involves the binding of an extracellular signal molecule to a membrane receptor, leading to an intracellular response.
Signal Transduction
- Signal transduction is a process where an extracellular signal molecule binds to a membrane receptor, causing a response inside the cell.
- The receptor protein binds to the ligand, changing its conformation, which activates intracellular signaling proteins and triggers a response.
Specificity of Ligands and Membrane Receptors
- Membrane receptors have a highly specific preference for certain types of ligands, ensuring that only specific ligands can bind to specific receptors.
- The lock and key model describes this specificity, where the ligand acts as a key that fits into a specific lock (membrane receptor).
- The induced fit model is a more updated concept, suggesting that ligands and membrane receptors can change their conformation to fit each other, similar to how dough can be molded to fit a specific shape.
Classification of Membrane Receptors
- Membrane receptors can be grouped into three major categories: ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked receptors.
- Each category has distinct functions and mechanisms of action, but all play critical roles in cellular communication and response.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.