Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of collagen in muscle?
What is the primary function of collagen in muscle?
- To store fat for energy
- To provide energy for muscle contraction
- To provide support to muscle and prevent over-stretching (correct)
- To aid in the metabolism of carbohydrates
What is marbling in the context of meat?
What is marbling in the context of meat?
- A type of bone structure
- Fat deposited in the muscle that can be seen as little white streaks or drops (correct)
- The process of tenderizing meat
- A type of muscle fiber
What gives meat its texture?
What gives meat its texture?
- The combination of muscle, connective tissue, and adipose tissue (correct)
- The proportion of water and bone
- The type of muscle fiber present
- The amount of ATP present
What is the main component of connective tissue?
What is the main component of connective tissue?
What is the role of ATP in meat?
What is the role of ATP in meat?
What is the primary source of energy for ATP?
What is the primary source of energy for ATP?
What is the primary factor that affects natural meat tenderness?
What is the primary factor that affects natural meat tenderness?
What is the term for the temporary stiff state of muscles after death?
What is the term for the temporary stiff state of muscles after death?
What is marbling, in the context of meat?
What is marbling, in the context of meat?
What is the purpose of aging in the meat industry?
What is the purpose of aging in the meat industry?
What is the main difference between wholesale and retail cuts of meat?
What is the main difference between wholesale and retail cuts of meat?
Which of the following factors can affect meat tenderness?
Which of the following factors can affect meat tenderness?
What is the primary purpose of searing in meat preparation?
What is the primary purpose of searing in meat preparation?
What is the term for inserting strips of bacon or fat into slits in the meat?
What is the term for inserting strips of bacon or fat into slits in the meat?
What is the primary purpose of barding in meat preparation?
What is the primary purpose of barding in meat preparation?
What is the term for the smaller cuts of meat obtained from wholesale cuts and sold to the consumer?
What is the term for the smaller cuts of meat obtained from wholesale cuts and sold to the consumer?
Before the advent of refrigeration, what was the primary method of meat preservation?
Before the advent of refrigeration, what was the primary method of meat preservation?
What is the primary function of the sheets of fat used in barding?
What is the primary function of the sheets of fat used in barding?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
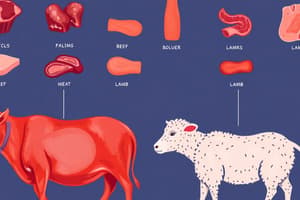
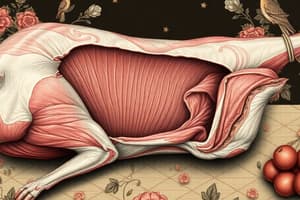
Composition of Meats
- Meats are composed of a combination of water, muscle, connective tissue, adipose (fatty) tissue, and bone.
- The proportions of these elements vary according to the animal and the part of its anatomy represented by the cut of meat.
ATP and Connective Tissue
- ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) is a universal energy compound in cells obtained from the metabolism of carbohydrate, fat, or protein.
- Connective tissue is a protein structure that surrounds living cells, giving them structure and adhesiveness within themselves and to adjacent tissues.
- Collagen is a pearly white, tough, and fibrous protein that provides support to muscle and prevents it from over-stretching.
Marbling and Tenderness
- Marbling is fat deposited in the muscle that can be seen as little white streaks or drops.
- Tenderness of meats is due to factors such as the cut, age, and fat content.
- Meats can be treated to make them more tender, and preparation temperatures and times also have an influence on tenderness.
Natural Tenderizing Factors
- Natural tenderizing factors include the cut of the meat, age at slaughter, heredity, diet, marbling, and slaughtering conditions.
- Aging, or ripening, occurs when carcasses are hung in refrigeration units for longer periods than that required for the reversal of rigor mortis.
Purchasing Meats
- Meats are divided into two major types: wholesale and retail cuts.
- Wholesale cuts are large cuts of an animal carcass, which are further divided into retail cuts.
- Retail cuts are smaller cuts of meat obtained from wholesale cuts and sold to the consumer.
Meat Preservation and Preparation
- Before refrigeration, meat was preserved by processing methods such as curing, smoking, canning, and drying.
- Larding involves inserting strips of bacon or fat into slits in the meat.
- Barding involves tying thin sheets of fat or bacon over lean meat to keep it moist during roasting.
- Searing involves cooking meat at high initial temperatures to "seal the pores," increase flavor, and enhance color by browning.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.