Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary location where endochondral ossification occurs?
What is the primary location where endochondral ossification occurs?
- In a hyaline cartilage framework (correct)
- In sheet-like osteogenic membranes
- In cranial vault and facial bones
- In loose connective tissues
Which structure undergoes intramembranous ossification?
Which structure undergoes intramembranous ossification?
- Epiphyseal plates
- Cranial floor
- Cranial vault (correct)
- Long bones
What type of growth occurs in the cranial base during development?
What type of growth occurs in the cranial base during development?
- Appositional growth at sutures
- Hypertrophy of osteoblasts
- Growth at cranial sutures
- Endochondral growth at synchondroses (correct)
What is the role of fontanelles at birth in skull development?
What is the role of fontanelles at birth in skull development?
What characterizes the growth of the nasomaxillary complex?
What characterizes the growth of the nasomaxillary complex?
What condition is characterized by an exceptionally small mandible?
What condition is characterized by an exceptionally small mandible?
Which growth phenomenon can lead to mandibular overgrowth?
Which growth phenomenon can lead to mandibular overgrowth?
How does interstitial growth occur?
How does interstitial growth occur?
Which dimension of growth typically starts first during a growth spurt?
Which dimension of growth typically starts first during a growth spurt?
What type of bone growth occurs only through appositional mechanisms?
What type of bone growth occurs only through appositional mechanisms?
Which of the following methods is NOT used to study growth?
Which of the following methods is NOT used to study growth?
Which term describes the process of new mineralized bone formation?
Which term describes the process of new mineralized bone formation?
What is a common characteristic evident at birth for congenital hemifacial hypertrophy?
What is a common characteristic evident at birth for congenital hemifacial hypertrophy?
What is the primary component that controls the patterning of cranial neural crest cell derivatives?
What is the primary component that controls the patterning of cranial neural crest cell derivatives?
At what age does the head typically stop growing, according to normal craniofacial development?
At what age does the head typically stop growing, according to normal craniofacial development?
Which structure is formed from the fusion of the medial nasal processes?
Which structure is formed from the fusion of the medial nasal processes?
What is the likely outcome if there is a disturbance during the elevation of palatal shelves?
What is the likely outcome if there is a disturbance during the elevation of palatal shelves?
What is the term for the continuous change in a predetermined order during craniofacial development?
What is the term for the continuous change in a predetermined order during craniofacial development?
Which of the following statements best describes the growth of teeth after eruption?
Which of the following statements best describes the growth of teeth after eruption?
What percentage of neurocranium development is typically completed by 2 years of age?
What percentage of neurocranium development is typically completed by 2 years of age?
When do the nasal placodes appear on the frontonasal process?
When do the nasal placodes appear on the frontonasal process?
What type of bone formation is associated with the mandible?
What type of bone formation is associated with the mandible?
At what week of fetal development does the mandible begin to show membranous ossification sites?
At what week of fetal development does the mandible begin to show membranous ossification sites?
What is the primary reason for downward and forward growth of the mandible?
What is the primary reason for downward and forward growth of the mandible?
Which cartilage type does not exhibit an ordered columnar arrangement in the condylar cartilage?
Which cartilage type does not exhibit an ordered columnar arrangement in the condylar cartilage?
How does the size of the mandible compare to the maxilla initially during fetal life?
How does the size of the mandible compare to the maxilla initially during fetal life?
What is the fate of Meckel's cartilage during the development of the mandible?
What is the fate of Meckel's cartilage during the development of the mandible?
What does the articular surface of the mandibular condyle consist of?
What does the articular surface of the mandibular condyle consist of?
When does the mandible and maxilla reach equal size during fetal development?
When does the mandible and maxilla reach equal size during fetal development?
What mechanisms contribute to the downward growth of the maxillary arch?
What mechanisms contribute to the downward growth of the maxillary arch?
Which part of the maxilla experiences anterior bone deposition before the age of 5-6 years?
Which part of the maxilla experiences anterior bone deposition before the age of 5-6 years?
Which process is NOT part of the growth of the mandible?
Which process is NOT part of the growth of the mandible?
What factors contribute to the transverse growth of the maxilla?
What factors contribute to the transverse growth of the maxilla?
What is the primary area of bone deposition during the growth of the mandible?
What is the primary area of bone deposition during the growth of the mandible?
In what way does the mandible grow vertically and sagittally?
In what way does the mandible grow vertically and sagittally?
What changes occur in the ramus during mandibular growth?
What changes occur in the ramus during mandibular growth?
Which of the following best describes the growth processes of mandible?
Which of the following best describes the growth processes of mandible?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
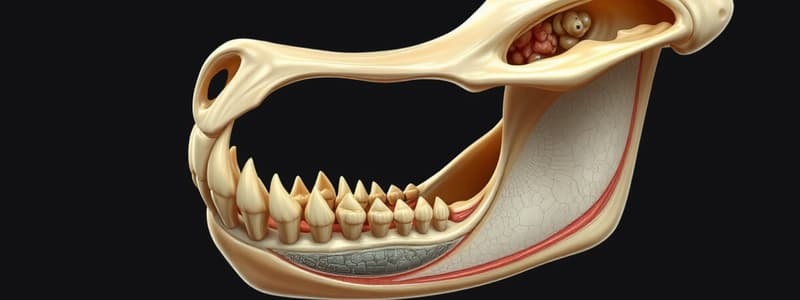
Mandible Formation and Growth
- Formation involves both endochondral and intramembranous processes.
- Mandible growth occurs at the condylar cartilage and through appositional growth.
- Condylar cartilage differs from epiphyseal plates and synchondroses.
- Growth primarily occurs in a downward and forward direction, particularly from the condyle.
Tissue Layers of Mandibular Condyle
- Condylar cartilage hyperplasia is unique to connective tissue cells.
- Hypertrophy only affects cartilage cells without showing an ordered columnar structure.
- The articular surface is covered by dense fibrous connective tissue.
Relationship with Meckel's Cartilage
- Mandible does not replace Meckel's cartilage; it forms through intramembranous ossification lateral to it.
- Remnants of Meckel’s cartilage contribute to certain bones of the middle ear.
- Perichondrium persists as the sphenomandibular ligament.
Development of Condylar Cartilage
- Condylar cartilage develops as an independent secondary cartilage structure.
Prenatal Growth of the Mandible
- Meckel’s cartilage appears by the fourth week of gestation.
- Membranous ossification starts around the fifth to sixth week, adjacent to Meckel's cartilage.
- Secondary cartilaginous sites, including the condyle, develop by the tenth week.
- Endochondral ossification initiates by the fourteenth week.
- Initially, the mandible is larger than the maxilla during early fetal life.
Growth Comparison with Maxilla
- By the eighth week, the maxilla begins to overlap the mandible.
- At the eleventh week, the sizes of the upper and lower jaws become equal.
- Between the thirteenth and twentieth weeks, mandible growth lags behind maxilla.
- At birth, the mandible is often retrognathic compared to the maxilla.
Craniofacial Growth Overview
- Facial growth is continuous and time-dependent with no independent developmental parts.
- Growth occurs from underneath the brain, with teeth remaining unchanged post-eruption.
- Orthodontic interventions can correct discrepancies resulting from growth patterns.
Craniofacial Structural Corners
- Cranial vault, cranial base, nasomaxillary complex, and mandible are key components of the craniofacial complex.
Growth Mechanisms
- Vertical growth of the maxilla is facilitated by downward development of palatal shelves and maxillary arch displacement.
- Horizontal and transverse growth involve remodeling processes and are influenced by surrounding structures.
Mandibular Anatomy and Growth
- Features a basic arc (corpus) with three functional processes: coronoid, alveolar, and angular processes.
- The mandible has the longest growth duration among facial bones.
- Growth involves deposition at the posterior surface of the ramus and resorption at its anterior border.
- Significant growth occurs in the condylar cartilages, posterior border of the ramus, and alveolar ridges.
Mandibular Growth Characteristics
- Vertical and sagittal displacement occurs, moving the mandible away from the glenoid fossa.
- The condyle and ramus subsequently grow upward and backward into the space created by this displacement.
- The anterior part of the mandible experiences little change, emphasizing growth around its processes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.