Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a potential advantage of informal structures?
Which of the following is NOT a potential advantage of informal structures?
- Facilitates making contacts
- Susceptibility to rumor (correct)
- Sources of emotional support and friendship
- Stimulates informal learning
In which environment do functional structures typically work best?
In which environment do functional structures typically work best?
- Stable environments with few products or services (correct)
- Non-profit organizations with diverse functions
- Large corporations with a variety of divisions
- Dynamic environments with numerous products
What is a potential disadvantage of functional structures?
What is a potential disadvantage of functional structures?
- Enhanced interdepartmental collaboration
- Neglect of broader organizational issues (correct)
- Improved communication among functions
- Focus primarily on overall organizational goals
What is a disadvantage of informal structures in organizations?
What is a disadvantage of informal structures in organizations?
Which of the following describes a characteristic of functional structures?
Which of the following describes a characteristic of functional structures?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of divisional structures?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of divisional structures?
What is a major advantage of divisional structures?
What is a major advantage of divisional structures?
One disadvantage of informal structures is the presence of 'in and out groups.' What does this imply?
One disadvantage of informal structures is the presence of 'in and out groups.' What does this imply?
Which of the following describes a potential disadvantage of divisional structures?
Which of the following describes a potential disadvantage of divisional structures?
What advantage do functional structures offer regarding career paths?
What advantage do functional structures offer regarding career paths?
Which of the following is a potential disadvantage of informal social networks within organizations?
Which of the following is a potential disadvantage of informal social networks within organizations?
What is a defining feature of matrix structures?
What is a defining feature of matrix structures?
In which type of organization structure might you find duplication of resources often occurring?
In which type of organization structure might you find duplication of resources often occurring?
What is a primary characteristic of traditional organizational structures?
What is a primary characteristic of traditional organizational structures?
Which aspect of divisional structures can be seen as a drawback?
Which aspect of divisional structures can be seen as a drawback?
Matrix structures are particularly beneficial in which of the following contexts?
Matrix structures are particularly beneficial in which of the following contexts?
What is a significant potential disadvantage of using team structures?
What is a significant potential disadvantage of using team structures?
Which advantage is associated with network structures?
Which advantage is associated with network structures?
What is a key characteristic of boundaryless organizations?
What is a key characteristic of boundaryless organizations?
Which design is most fitting for a rapidly changing and uncertain environment?
Which design is most fitting for a rapidly changing and uncertain environment?
What is a characteristic of mechanistic designs?
What is a characteristic of mechanistic designs?
What is a potential risk when using network structures?
What is a potential risk when using network structures?
Which option best describes a potential disadvantage of excessive outsourcing in network structures?
Which option best describes a potential disadvantage of excessive outsourcing in network structures?
Which of the following is NOT typically associated with organic designs?
Which of the following is NOT typically associated with organic designs?
What contemporary organizing trend focuses on improving managerial efficiency?
What contemporary organizing trend focuses on improving managerial efficiency?
How do teams in a boundaryless organization typically operate?
How do teams in a boundaryless organization typically operate?
Which of the following features is least likely to be found in adaptive organizations?
Which of the following features is least likely to be found in adaptive organizations?
What describes a drawback of team structures regarding time management?
What describes a drawback of team structures regarding time management?
What is a common advantage of network structures related to employment?
What is a common advantage of network structures related to employment?
What is a significant benefit of decentralized authority in organizational designs?
What is a significant benefit of decentralized authority in organizational designs?
What does a wide span of control imply in an organizational context?
What does a wide span of control imply in an organizational context?
Which statement best describes the characteristic of bureaucratic organizations?
Which statement best describes the characteristic of bureaucratic organizations?
What does organizing primarily arrange within an organization?
What does organizing primarily arrange within an organization?
Which component is included in an organization chart?
Which component is included in an organization chart?
What is a characteristic of informal organization structures?
What is a characteristic of informal organization structures?
Which of the following is a weakness of traditional organizational structures?
Which of the following is a weakness of traditional organizational structures?
What does social network analysis identify within an organization?
What does social network analysis identify within an organization?
Which element is NOT typically associated with organization structures?
Which element is NOT typically associated with organization structures?
What aspect of organizing involves connecting various resources?
What aspect of organizing involves connecting various resources?
How has organizational design changed in today's workplace?
How has organizational design changed in today's workplace?
What is a main reason organizations are streamlining by cutting unnecessary levels of management?
What is a main reason organizations are streamlining by cutting unnecessary levels of management?
Which of the following statements best describes the principle of delegation in management?
Which of the following statements best describes the principle of delegation in management?
What is the correct order of the steps in the delegation process?
What is the correct order of the steps in the delegation process?
What is meant by centralization in an organizational context?
What is meant by centralization in an organizational context?
How can organizations benefit from decentralization?
How can organizations benefit from decentralization?
Which of the following contrasts centralization and decentralization?
Which of the following contrasts centralization and decentralization?
What role does information technology play in modern organizational designs regarding decentralization?
What role does information technology play in modern organizational designs regarding decentralization?
Why is empowerment crucial in modern management practices?
Why is empowerment crucial in modern management practices?
Flashcards
Organizing as a Management Function
Organizing as a Management Function
Arranging, connecting, and integrating people and resources to achieve a goal.
Organization Structure
Organization Structure
The formal system of tasks, workflows, and relationships connecting work and activities.
Formal Organization Structure
Formal Organization Structure
The official, documented structure within a company, depicted in an organizational chart.
Informal Organization Structure
Informal Organization Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organizational Chart
Organizational Chart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Division of Work
Division of Work
Signup and view all the flashcards
Supervisory Relationships
Supervisory Relationships
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Network Analysis
Social Network Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Informal structures
Informal structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Informal structures benefits
Informal structures benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Informal structures drawbacks
Informal structures drawbacks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional structures
Functional structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional structures advantages
Functional structures advantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional structures - stable environments
Functional structures - stable environments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional structures - examples
Functional structures - examples
Signup and view all the flashcards
Traditional Org Structures
Traditional Org Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Team Structure Disadvantages
Team Structure Disadvantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Network Structures
Network Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Network Structure Advantages
Network Structure Advantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Network Structure Disadvantages
Network Structure Disadvantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Boundaryless Organizations
Boundaryless Organizations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Outsourcing
Outsourcing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Strategic Alliances
Strategic Alliances
Signup and view all the flashcards
Core Components
Core Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Structure Disadvantages
Functional Structure Disadvantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisional Structure Advantages
Divisional Structure Advantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisional Structure Disadvantages
Divisional Structure Disadvantages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matrix Structure
Matrix Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functional Chimneys Problem
Functional Chimneys Problem
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisional Structures Types
Divisional Structures Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Divisional structure benefits
Divisional structure benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matrix Structure Uses
Matrix Structure Uses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanistic Design
Mechanistic Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organic Design
Organic Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contingency Perspective
Contingency Perspective
Signup and view all the flashcards
Span of Control
Span of Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chain of Command
Chain of Command
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fewer Levels of Management
Fewer Levels of Management
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decentralization with Centralization
Decentralization with Centralization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adaptive Organizations
Adaptive Organizations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flatter Organization Structure
Flatter Organization Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Empowerment Through Delegation
Empowerment Through Delegation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Delegation Process
Delegation Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centralization vs. Decentralization
Centralization vs. Decentralization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centralized Control
Centralized Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decentralization Trend
Decentralization Trend
Signup and view all the flashcards
Information Technology's Role
Information Technology's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Structures
Horizontal Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Management Chapter 11: Organization Structures
- Organizing as a Management Function: Organizing is a management function that involves arranging, connecting, and integrating people and resources to achieve a goal. This includes creating an organization structure—the system of tasks, workflows, reporting relationships, and communication channels connecting work and activities.
Learning Objectives
- 11.1: Explain organizing as a management function and contrast formal and informal organization structures.
- 11.2: Identify the strengths and weaknesses of traditional organizational structures.
- 11.3: Identify the strengths and weaknesses of team, virtual, and network structures.
- 11.4: Discuss how and why organizational designs are changing in today's workplace.
Organizing as a Management Function (Detailed)
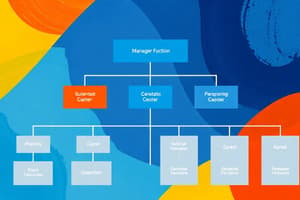
- Organization Chart: A diagram illustrating formal reporting relationships and work positions within an organization. It displays division of work, supervisory relationships, communication channels, major subunits, and levels of management.
- Informal Structures: Unofficial working relationships among organization members. Social network analysis (sociometrics) identifies informal structures and social relationships.
- Advantages of Informal Structures: Informal structures allow people to connect with others for assistance, stimulate learning, and provide emotional support/friendship.
- Disadvantages of Informal Structures: Potential disadvantages include susceptibility to rumor, inaccurate information, resistance to change, diversion of work efforts, creation of "in-groups/out-groups," and feelings of alienation by "outsiders".
- Organizing function's relationship to other management functions: Organizing is related to planning (setting the direction), leading (inspiring effort), and controlling (ensuring results).
Traditional Organizational Structures
-
Functional Structures: Group people with similar skills and tasks into formal work units. Members specialize in functional areas of expertise. They work well in stable environments and for organizations with few products/services.
-
Advantages of Functional Structures: Economies of scale, task assignments aligned with expertise, high-quality technical problem-solving, in-depth training, clear career paths.
-
Disadvantages of Functional Structures: Focus on departmental concerns, potential neglect of "big picture" issues, communication barriers between functions, "functional chimneys problem", narrow view of performance goals.
-
Divisional Structures: Group people based on product, geography, customer, or process. These structures are common in complex organizations and help avoid problems associated with functional structures.
-
Types of Divisional Structures: Product, geographical, customer, and process structures.
-
Advantages of Divisional Structures: Increased flexibility in responding to environmental changes, improved coordination across functional areas, clear responsibility for product/service delivery, expertise focused on specific customers/products/regions, ease in restructuring.
-
Disadvantages of Divisional Structures: Duplication of resources/efforts across divisions, competition and poor coordination between divisions, emphasis on divisional goals over organizational goals.
-
Matrix Structures: Combine functional and divisional structures to combine advantages and minimize disadvantages. Cross-functional teams are created to achieve goals. This structure is used in manufacturing, service industries, and professional fields.
-
Advantages of Matrix Structures: Better communication/cooperation across functions, improved decision making/problem-solving, increased flexibility, better customer service, better performance accountability, and improved strategic management.
-
Disadvantages of Matrix Structures: Increased costs due to team leaders, potential for power struggles (two-boss system), task confusion/conflict, time-consuming meetings, "groupitis".
Horizontal Organizational Structures
-
Team Structures: Use permanent and temporary teams to handle problems, projects, and day-to-day tasks. Often cross-functional with members from various departments. Project teams are convened for specific tasks/projects and disbanded afterwards.
-
Advantages of Team Structures: Barriers to collaboration reduced, talents from various areas combined, improved morale, involvement/identification with tasks, higher enthusiasm, increased quality/speed of decision making.
-
Disadvantages of Team Structures: Conflicting member loyalties, excessive time spent in meetings, effective use of time dependent on interpersonal relations, group dynamics, and team management.
-
Network Structures: Use information technologies to connect with a network of outside suppliers/service contractors. This approach involves only core components and uses strategic alliances/outsourcing for other components.
-
Advantages of Network Structures: Operates with fewer full-time employees (reduced overhead). Flexible internal systems. Permit use of outsourcing. Increased operating efficiency.
-
Disadvantages of Network Structures: Control and coordination difficulties. Breakdown in one part of the network can affect the entire system. Potential loss of control over outsourced activities. Loyalty issues with contractors . Excessively aggressive outsourcing can be problematic.
Boundaryless Organizations
- Boundaryless Organizations: Remove internal/external boundaries among subsystems/external environment. Combination of team and network structures with a focus on "temporariness" and use of spontaneous teamwork/communication to replace formal lines of authority.
- Key Requirements: Little hierarchy, team member empowerment., technology utilization, acceptance of impermanence.
- Features: Encourages creativity, quality, flexibility and efficiency, and makes knowledge sharing an essential component.
- Virtual Organization: Special form of boundaryless organization. Operates via a shifting network of external alliances, using IT and the Internet, as required.
- Latent Organization: Project-based structure; based on willing people for flexible environments, tasks completed, and key groups may continue later.
Organizational Designs
-
Organizational Design: The process of creating structures to achieve mission and objectives It aims to align structures with situational contingencies. Alternatives include mechanistic/bureaucratic (stable environment) and organic/adaptive (rapidly changing environment).
-
Bureaucracy: Organization based on logic, order, and legitimate use of formal authority. Features include clearly defined labor division, strict hierarchy, formal rules/procedures, and promotion based on job performance.
-
Contingency Perspective: Questions the suitability of bureaucracy in certain situations and the alternatives available.
-
Environment & Design: Environment dictates most suitable design. Mechanistic designs are most effective in stable environments. Organic designs better serve rapidly changing/uncertain ones; adaptive designs seek a balance that minimizes bureaucracy and promotes empowerment/teamwork.
-
Mechanistic Designs: Predictable goals, centralized authority, numerous rules/procedures, narrow spans of control, specialized tasks, few teams, formal/impersonal coordination
-
Organic Designs: Adaptable goals, decentralized authority, few rules/procedures, wide spans of control, shared tasks, many teams, informal/personal coordination.
Contemporary Organizing Trends
- Fewer Levels of Management, Shorter Chains of Command, Less Unity of Command: Streamlining, reducing levels of management, and flatter organizational structures are competitive advantages.
- Wider Spans of Control Supervisors managing more people.
- More Delegation & Empowerment: Distributing responsibilities, granting authority to act, and providing accountability.
- Decentralization with Centralization: Some decisions remain top-level while others are delegated to lower levels. This remains dynamic, not static.
- Reduced Use of Staff: Organizations reducing staff and embracing outsourcing to increase efficiency.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.