Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the process called when the epiblast and hypoblast form from the inner cell mass?
What is the process called when the epiblast and hypoblast form from the inner cell mass?
- Primitive steak formation
- Trilaminar germ disc formation
- Bilaminar germ disc formation (correct)
- Gastrulation
Which of the following is NOT a germ layer formed during trilaminar disc formation?
Which of the following is NOT a germ layer formed during trilaminar disc formation?
- Endoderm
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Hypoblast (correct)
What is the fate of the cells that ingress during trilaminar disc formation?
What is the fate of the cells that ingress during trilaminar disc formation?
- They form the embryonic endoderm and mesoderm (correct)
- They contribute to the formation of the placenta
- They differentiate into the notochordal process
- They give rise to the amniotic ectoderm
What is the name of the structure that forms in the epiblast and gives rise to the notochordal process?
What is the name of the structure that forms in the epiblast and gives rise to the notochordal process?
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the epiblast?
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the epiblast?
What is the fate of the amniotic ectoderm and the rest of the hypoblast and trophoblast?
What is the fate of the amniotic ectoderm and the rest of the hypoblast and trophoblast?
What is the primary function of the notochordal process in gastrulation?
What is the primary function of the notochordal process in gastrulation?
What is the outcome of neural induction?
What is the outcome of neural induction?
What is the characteristic of presumptive neural plate cells?
What is the characteristic of presumptive neural plate cells?
What is the role of CAMs (cell adhesion molecules) in neural plate formation?
What is the role of CAMs (cell adhesion molecules) in neural plate formation?
What is the outcome of the first phase of neurulation?
What is the outcome of the first phase of neurulation?
What is the characteristic of neural plate cells?
What is the characteristic of neural plate cells?
What is the role of the axial mesoderm in gastrulation?
What is the role of the axial mesoderm in gastrulation?
What is the process of transformation of low columnar cells into tall columnar cells?
What is the process of transformation of low columnar cells into tall columnar cells?
What is the outcome of neurulation?
What is the outcome of neurulation?
What is the characteristic of presumptive epidermal cells?
What is the characteristic of presumptive epidermal cells?
What is the result of different concentration gradients of signalling factors?
What is the result of different concentration gradients of signalling factors?
Where are motor neurons expressed?
Where are motor neurons expressed?
What happens to the notochord after sending signals?
What happens to the notochord after sending signals?
What is the name of the opening at the head end of the neural tube?
What is the name of the opening at the head end of the neural tube?
What forms the ventricles of the central nervous system?
What forms the ventricles of the central nervous system?
What is the result of the failure of the anterior neuropore to close?
What is the result of the failure of the anterior neuropore to close?
What is the mild form of Spina Bifida?
What is the mild form of Spina Bifida?
What induces the formation of the neural tube?
What induces the formation of the neural tube?
Where does secondary neurulation occur?
Where does secondary neurulation occur?
What is the result of epithelialization in secondary neurulation?
What is the result of epithelialization in secondary neurulation?
What is the primary difference between the neural plate cells and the epidermal cells during the neural plate stage?
What is the primary difference between the neural plate cells and the epidermal cells during the neural plate stage?
What is the result of the neural plate deepening and the neural folds converging towards the midline?
What is the result of the neural plate deepening and the neural folds converging towards the midline?
What type of movement do the neural crest cells undergo during mesenchymal migration?
What type of movement do the neural crest cells undergo during mesenchymal migration?
What is the primary function of the dorsal mesoderm?
What is the primary function of the dorsal mesoderm?
What is the primary signaling molecule produced by the notochordal cells?
What is the primary signaling molecule produced by the notochordal cells?
What is the outcome of the convergence of the neural folds towards the midline?
What is the outcome of the convergence of the neural folds towards the midline?
What is the characteristic of neural crest cells that distinguishes them from epidermal cells and neural plate cells?
What is the characteristic of neural crest cells that distinguishes them from epidermal cells and neural plate cells?
What is the primary function of the ectodermal cells of the epidermis?
What is the primary function of the ectodermal cells of the epidermis?
What is the result of the exposure of the floor plate to Sonic hedgehog protein?
What is the result of the exposure of the floor plate to Sonic hedgehog protein?
What is the outcome of the migration of neural crest cells?
What is the outcome of the migration of neural crest cells?
What is the primary function of the neural crest cells in the development of the human brain?
What is the primary function of the neural crest cells in the development of the human brain?
What is the outcome of the fusion of the neural folds in the cervical region?
What is the outcome of the fusion of the neural folds in the cervical region?
What is the characteristic of the rhombencephalon at a later stage of development?
What is the characteristic of the rhombencephalon at a later stage of development?
What is the role of the neural plate in the development of the human brain?
What is the role of the neural plate in the development of the human brain?
What is the characteristic of the 20D embryo?
What is the characteristic of the 20D embryo?
What is the function of the neural crest cells in determining the position of the cranial nerves?
What is the function of the neural crest cells in determining the position of the cranial nerves?
What is the characteristic of the 23D embryo?
What is the characteristic of the 23D embryo?
What is the role of the gray crescent region in neural induction?
What is the role of the gray crescent region in neural induction?
What is the characteristic of the 25D embryo?
What is the characteristic of the 25D embryo?
What is the outcome of the closure of the anterior neuropore?
What is the outcome of the closure of the anterior neuropore?
What is the primary location of neural tube formation in avians?
What is the primary location of neural tube formation in avians?
Which class of vertebrates exhibits exclusively secondary neurulation?
Which class of vertebrates exhibits exclusively secondary neurulation?
What is the function of hinge point cells in neural tube formation?
What is the function of hinge point cells in neural tube formation?
At which stage of avian primary neurulation do the neural folds converge?
At which stage of avian primary neurulation do the neural folds converge?
What is the characteristic of neural tube formation in the cephalic end of the embryo?
What is the characteristic of neural tube formation in the cephalic end of the embryo?
What is the fate of the neural crest cells during neural tube formation?
What is the fate of the neural crest cells during neural tube formation?
How many ways does differentiation of the neural tube occur simultaneously?
How many ways does differentiation of the neural tube occur simultaneously?
What is the level of the embryo where secondary neurulation takes place in humans?
What is the level of the embryo where secondary neurulation takes place in humans?
What is the role of the B-Catenin-Tcf-3 complex in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo?
What is the role of the B-Catenin-Tcf-3 complex in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo?
What is the function of the Goosecoid gene in the development of the embryo?
What is the function of the Goosecoid gene in the development of the embryo?
What is the role of the Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE) in embryonic development?
What is the role of the Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE) in embryonic development?
What is the outcome of the inactivation of the Goosecoid gene?
What is the outcome of the inactivation of the Goosecoid gene?
What is the role of the Beta-Catenin protein in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis?
What is the role of the Beta-Catenin protein in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis?
What is the function of the chordin and noggin genes in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis?
What is the function of the chordin and noggin genes in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis?
What is the role of the organizer in embryonic development?
What is the role of the organizer in embryonic development?
What is the outcome of the activation of the Goosecoid gene?
What is the outcome of the activation of the Goosecoid gene?
What is the role of the TGF-Beta signaling pathway in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis?
What is the role of the TGF-Beta signaling pathway in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis?
What is the outcome of the inhibition of BMP4 activity?
What is the outcome of the inhibition of BMP4 activity?
What is the primary function of the molecular cues or signals during embryonic development?
What is the primary function of the molecular cues or signals during embryonic development?
What is the result of the cytoplasmic rearrangement that occurs during fertilization?
What is the result of the cytoplasmic rearrangement that occurs during fertilization?
What is the role of VegT and Vg1 molecules during embryonic development?
What is the role of VegT and Vg1 molecules during embryonic development?
What is the characteristic of the gray crescent area formed during fertilization?
What is the characteristic of the gray crescent area formed during fertilization?
What is the outcome of the accumulation of beta catenin on the future dorsal side of the embryo?
What is the outcome of the accumulation of beta catenin on the future dorsal side of the embryo?
What is the role of cytoplasmic rearrangement during embryonic development?
What is the role of cytoplasmic rearrangement during embryonic development?
What is the function of the molecules dragged along with the cytoplasmic rearrangement during fertilization?
What is the function of the molecules dragged along with the cytoplasmic rearrangement during fertilization?
What is the significance of the region opposite to the site of sperm entry during fertilization?
What is the significance of the region opposite to the site of sperm entry during fertilization?
What is the role of the Goosecoid gene in the dorsal development of the embryo?
What is the role of the Goosecoid gene in the dorsal development of the embryo?
What is the outcome of the inhibition of BMP4 activity during gastrulation?
What is the outcome of the inhibition of BMP4 activity during gastrulation?
What is the characteristic of the embryonic cells after the midblastula transition?
What is the characteristic of the embryonic cells after the midblastula transition?
What is the role of the dorsal mesoderm during the formation of the body axes?
What is the role of the dorsal mesoderm during the formation of the body axes?
What is the name of the process that establishes the spatial information within the embryo?
What is the name of the process that establishes the spatial information within the embryo?
What is the relationship between the dorsal-ventral patterning of the neural tube and the BMP4 activity?
What is the relationship between the dorsal-ventral patterning of the neural tube and the BMP4 activity?
What is the nature of the inductive signal sent by the dorsal mesoderm during the formation of the body axes?
What is the nature of the inductive signal sent by the dorsal mesoderm during the formation of the body axes?
What is the role of the notochordal process during the formation of the body axes?
What is the role of the notochordal process during the formation of the body axes?
What is the outcome of the gastrulation process?
What is the outcome of the gastrulation process?
What is the characteristic of the neuroectoderm after receiving the inductive signal?
What is the characteristic of the neuroectoderm after receiving the inductive signal?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
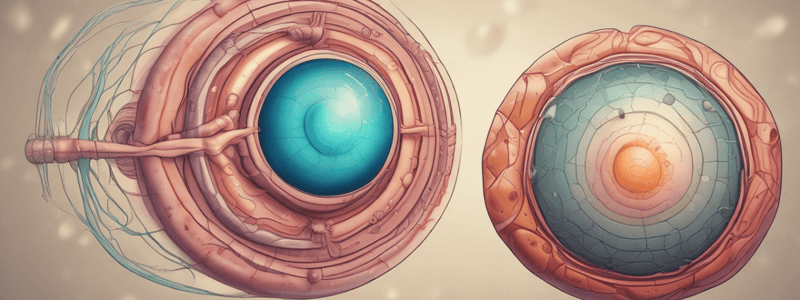
Mammalian Gastrulation
- Formation of primitive streak similar to avian embryo
- Inner cell mass undergoes delamination to form epiblast and hypoblast
- Epiblast forms amniotic ectoderm and embryonic epiblast, where the primitive streak will form
- Formation of epiblast and hypoblast is called bilaminar germ disc formation
Formation of Germ Layers
- Ingression of cells to form embryonic endoderm and mesoderm
- Left on top (outermost) will form embryonic ectoderm
- Formation of three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm (trilaminar disc formation)
Neural Induction
- Process where mesodermal cells (notochordal process) act on overlying ectoderm to transform dorsal ectoderm to neural plate
- Chordamesoderm/notochordal process has an inductive effect, enhancing neural induction
- Neural plate formation involves epithelial cell behaviors (bending, folding) and cellular activities (change in cell shape)
Neurulation
- Formation of neural plate, neural groove, and neural folds
- Neural groove deepens and neural folds converge towards the midline, forming a V-shaped cavity
- Neural tube formation through closure of the neuropore
- Two primary signaling centers: ectodermal cells of the epidermis produce BMP4 and BMP7, and notochordal cells produce Sonic hedgehog protein
- Secondary signaling centers established within the neural tube, determining dorsal-ventral specification
Development of the Neural Tube
- Open anterior and posterior neuropores
- Anterior neuropore closes around 24th-26th day, and posterior neuropore closes around 28th day
- Cavity of the neural tube forms the ventricles of the central nervous system
- Neurocoel (cavity of the neural tube) allows passage of anionic fluid
Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
- Failure of anterior neuropore closure: anencephaly
- Failure of posterior neuropore closure: spina bifida
- Spina bifida occulta: mild form, no pain, no neurological disorder
- Spina bifida cystica: more severe, spinal cord bulges out dorsally, with neurological disorder### Dorsal-Ventral Axis Establishment
- Dorsal development is allowed when Chordin and Noggin inhibit BMP4 activity
- Dorsal development leads to the establishment of dorsal mesoderm
- Dorsal mesoderm consists of notochordal process/axial mesoderm, paraxial mesoderm/somites, and lateral plate mesoderm
Body Axes Formation
- Body axes formation occurs after gastrulation
- Body axes formation involves the establishment of spatial information (positional information)
- Positional information is supplied by molecular cues or molecular signals
- Body axes include dorso-ventral axis, anterior-posterior axis (cranio-caudal axis), and left-right axis
Dorsal-Ventral Axis Establishment (Continued)
- In amphibian oocyte, cortical reaction occurs at fertilization, leading to cytoplasmic rearrangement
- Cytoplasmic rearrangement results in the movement of cytoplasm towards the point of sperm entry, creating a gray crescent area
- Molecules that specify dorsal fate, such as VegT and Vg1, are dragged towards the gray crescent region, marking the future dorsal side of the embryo
- Beta-catenin accumulates in the gray crescent region, participating in establishing the cordo-mesodermal cells
Molecular Mechanism
- Beta-catenin undergoes gradual accumulation in the gray crescent region
- Beta-catenin forms a complex with Tcf-3, which translocates into the nuclei of cells in the gray crescent region
- The complex regulates the expression of genes involved in establishing the ventral and dorsal sides of the embryo
- Siamois and twin genes are activated, which in turn activate the goosecoid gene
- Goosecoid gene codes for a transcription factor that regulates the chordamesodermal cells
- Chordin and Noggin, inhibitors of BMP4, are activated, allowing dorsal development to proceed
Neurulation
- Neurulation occurs when dorsal development is allowed
- Neurulation involves the formation of notochord (midline), paraxial mesoderm (lateral to the notochord), and dorsal ectoderm/epidermis (overlaying paraxial mesoderm)
Anterior-Posterior (A-P) Axis/Cranio-Caudal Axis
- In mammalian development, A-P polarity is specified by Hox genes during gastrulation
- Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE) is an organizing center for the embryo
- AVE expresses genes coding for transcription factors, such as OTX2, LIM1, and HESX1, and secreted factors, such as Cerberus and Lefty
- AVE specifies the neural pattern by inhibiting primitive streak formation anteriorly
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.