Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a good safety principle to follow when using a lathe?
What is a good safety principle to follow when using a lathe?
- Not tying back long hair
- Wearing CSA-certified safety glasses (correct)
- Not wearing jewellery
- Wearing loose clothing
Why is it important to centre-drill work deeply enough on a lathe?
Why is it important to centre-drill work deeply enough on a lathe?
- To make the piece lighter
- To provide support for the piece while it is turning (correct)
- To make the piece heavier
- To make the piece more compact
What should you do with the chuck wrench after adjusting the chuck on a lathe?
What should you do with the chuck wrench after adjusting the chuck on a lathe?
- Leave it on the chuck
- Place it on the saddle
- Use it to measure the workpiece
- Remove it immediately (correct)
Why is it important to keep the floor around a lathe clean and free of oil and grease?
Why is it important to keep the floor around a lathe clean and free of oil and grease?
What should you do before taking measurements of any kind on a lathe?
What should you do before taking measurements of any kind on a lathe?
Why is it important to use a lifting device to handle heavy chucks or work on a lathe?
Why is it important to use a lifting device to handle heavy chucks or work on a lathe?
What is a safety requirement when using a lathe?
What is a safety requirement when using a lathe?
Why is it important to keep all lathe cutting tools sharp?
Why is it important to keep all lathe cutting tools sharp?
What is the main method of sizing a lathe based on the diameter of the workpiece?
What is the main method of sizing a lathe based on the diameter of the workpiece?
What is the primary function of the headstock in a lathe?
What is the primary function of the headstock in a lathe?
Which type of lathe is commonly used for production work and is easier to program?
Which type of lathe is commonly used for production work and is easier to program?
What is the length of bed primarily used for?
What is the length of bed primarily used for?
Which type of lathe is often used for one-off productions and requires more skill?
Which type of lathe is often used for one-off productions and requires more skill?
What is the primary function of the rack gear in a lathe?
What is the primary function of the rack gear in a lathe?
What is the distance between centers primarily used for?
What is the distance between centers primarily used for?
What is the main advantage of using a CNC lathe over other types of lathes?
What is the main advantage of using a CNC lathe over other types of lathes?
What type of center is mounted in the headstock?
What type of center is mounted in the headstock?
What is the name of the center that is mounted in the tailstock?
What is the name of the center that is mounted in the tailstock?
What is the purpose of a lathe drive dog?
What is the purpose of a lathe drive dog?
How are chucks typically sized?
How are chucks typically sized?
What is the name of the type of chuck that has four jaws that can be adjusted independently?
What is the name of the type of chuck that has four jaws that can be adjusted independently?
What type of center is shown in Figure 25?
What type of center is shown in Figure 25?
What should you never do when using a lathe?
What should you never do when using a lathe?
What type of center is required to use high-pressure lubricant?
What type of center is required to use high-pressure lubricant?
What is the outside diameter of an 8-inch three jaw universal chuck?
What is the outside diameter of an 8-inch three jaw universal chuck?
How do the jaws move in a three jaw universal chuck?
How do the jaws move in a three jaw universal chuck?
What is the advantage of using a four jaw independent chuck over a three jaw universal chuck?
What is the advantage of using a four jaw independent chuck over a three jaw universal chuck?
What type of workpiece is a collet chuck best suited for?
What type of workpiece is a collet chuck best suited for?
What is the purpose of a faceplate?
What is the purpose of a faceplate?
What is the main purpose of a mandrel?
What is the main purpose of a mandrel?
What type of mandrel has a taper per foot of 0.006 - 0.008?
What type of mandrel has a taper per foot of 0.006 - 0.008?
What is the purpose of a magnetic chuck?
What is the purpose of a magnetic chuck?
What is the purpose of using a carriage lock?
What is the purpose of using a carriage lock?
What are the three main parts of the carriage?
What are the three main parts of the carriage?
What type of dial reading is used on a direct reading dial?
What type of dial reading is used on a direct reading dial?
What is the purpose of the compound rest?
What is the purpose of the compound rest?
How does the graduated dial on the compound rest work?
How does the graduated dial on the compound rest work?
What is the purpose of the apron assembly?
What is the purpose of the apron assembly?
What type of dial reading is used on an indirect reading dial?
What type of dial reading is used on an indirect reading dial?
What is the purpose of the saddle?
What is the purpose of the saddle?
What is the primary function of the headstock in a lathe?
What is the primary function of the headstock in a lathe?
What is the main advantage of using a CNC lathe over other types of lathes?
What is the main advantage of using a CNC lathe over other types of lathes?
What is the 'swing' of a lathe?
What is the 'swing' of a lathe?
What type of lathe is commonly used for production work and is easier to program?
What type of lathe is commonly used for production work and is easier to program?
What is the 'length of bed' of a lathe primarily used for?
What is the 'length of bed' of a lathe primarily used for?
What type of lathe is often used for one-off productions and requires more skill?
What type of lathe is often used for one-off productions and requires more skill?
What is the primary function of the rack gear in a lathe?
What is the primary function of the rack gear in a lathe?
What is the 'distance between centers' of a lathe?
What is the 'distance between centers' of a lathe?
What is the primary purpose of the chip and coolant shields on a lathe?
What is the primary purpose of the chip and coolant shields on a lathe?
What is the main advantage of using a CNC lathe over other types of lathes?
What is the main advantage of using a CNC lathe over other types of lathes?
What is the primary function of the headstock on a lathe?
What is the primary function of the headstock on a lathe?
How are lathes typically sized based on the diameter of the workpiece?
How are lathes typically sized based on the diameter of the workpiece?
What is the function of the split-nut lever on the apron?
What is the function of the split-nut lever on the apron?
What is the primary function of the rack gear on a lathe?
What is the primary function of the rack gear on a lathe?
What is the purpose of the tailstock?
What is the purpose of the tailstock?
What type of lathe is commonly used for production work and is easier to program?
What type of lathe is commonly used for production work and is easier to program?
What is the main purpose of a faceplate on a lathe?
What is the main purpose of a faceplate on a lathe?
What type of clutch mechanisms are used in lathe operation?
What type of clutch mechanisms are used in lathe operation?
What is the primary function of the apron assembly on a lathe?
What is the primary function of the apron assembly on a lathe?
What is a characteristic of a solid dead center?
What is a characteristic of a solid dead center?
What is the primary function of work holding devices?
What is the primary function of work holding devices?
What is the purpose of the apron assembly?
What is the purpose of the apron assembly?
What is a feature of the tailstock?
What is a feature of the tailstock?
What is a consideration for work holding devices?
What is a consideration for work holding devices?
Study Notes
Lathes - Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate CSA-certified safety glasses when using a lathe.
- Remove entanglement hazards such as loose clothing, jewelry, and long hair.
- Keep the floor free from obstructions and slip hazards.
- Ensure the lathe has a start/stop button within easy reach of the operator.
- Centre-drill work deeply enough to provide support for the piece while it is turning.
- Secure and clamp the piece being worked.
- Use a lifting device to handle heavy chucks or work.
- Inspect chucks for wear or damage.
- Remove chuck wrench immediately after adjusting chuck.
- Remove all tools, measuring instruments, and other objects from the saddle or lathe bed before starting the machine.
- Keep all lathe cutting tools sharp.
- Ensure that the chip and coolant shields are in place.
- Shut off the power supply to the motor before mounting or removing accessories.
- Stop the lathe before taking measurements of any kind.
- Use a vacuum, brush, or rake to remove cuttings only after the lathe has stopped moving.
- Keep the working surface clean of scrap, tools, and materials.
- Keep the floor around the lathe clean and free of oil and grease.
Lathes - Identification: Types, Sizes, and Rated Capacity
- Three main methods of sizing a lathe:
- Swing (the greatest diameter of a workpiece that can be turned without hitting the ways)
- Distance between centers (the longest work that could be supported between centers on a lathe)
- Length of bed (the distance from one end of the lathe to the other)
- Common sizes of lathes:
- Small (10" swing, 30" between centers, 1/4 HP)
- Medium (20" swing, 60-72" between centers, 5-15 HP)
- Large (48" swing, 240" between centers, 20-60 HP)
Types of Lathes
- Engine Lathe
- Turret Lathe
- Automatic Lathe (Automatic Screw Machine)
- Tracer Lathe
- CNC Lathe (common for production work, requires more skill for programming and setup)
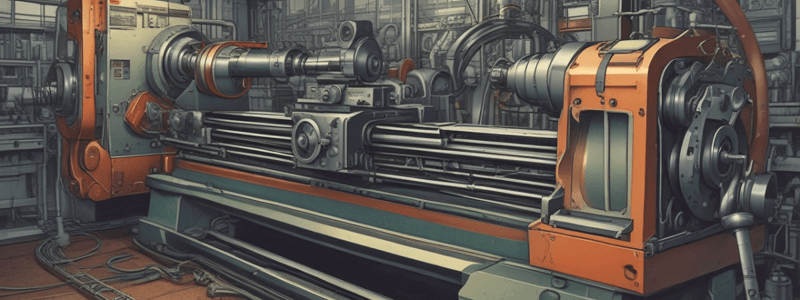
Major Parts of a Lathe and Their Function
- The Lathe Bed (flat side allows for thermal expansion, inverted prism ways)
- The Headstock (attached to the left side of the bed, houses the spindle, bearings, gears, and belts that drive the spindle)
- Carriage (made up of three main parts: saddle, cross-slide, and apron)
- Carriage Lock (used to face workpieces in an effort to eliminate convex or concave faces)
- Cross-slide (sits on top of the saddle, moves at right angles to the axis of the spindle)
- Apron (houses the drive gears, levers, and other devices that control the movements of the carriage)
- Compound Rest (can rotate 360 degrees, used for cutting external and internal tapers)
- Lathe Apron Assembly (often called the half-nut lever, used for threading)
- Headstock Center (rotates with the spindle, mounted within the spindle)
- Solid Centers (mounted in the headstock or tailstock, called "Live Centers" or "Dead Centers")
- Lathe Drive Dogs (companion equipment to the Dead and Live Center)
- Chucks (four main types: four jaw independent chuck, collet chuck, magnetic chuck, and three jaw universal chuck)
- Mandrels (used to grip a workpiece by the bore to permit the outside diameter to be machined, five types: solid mandrels, expansion mandrels, gang mandrels, threaded mandrels, and taper shank mandrels)
Lathes - Identification and Sizing
- Lathes are sized based on three main methods: swing (greatest diameter of workpiece that can be turned without hitting the ways), distance between centers (longest work that can be supported between centers), and length of bed (distance from one end of the lathe to the other).
- Common sizes of lathes include:
- Small: 10" (250mm) swing, 30" (750mm) length between centers, and 1/4 HP (0.2 kW) power.
- Medium: 20" (500mm) swing, 60-72" (1500-1800mm) length between centers, and 5-15 HP (3.7-11.2 kW) power.
- Large: 48" (1200mm) swing, 240" (6000mm) length between centers, and 20-60 HP (15-45 kW) power.
Lathes - Types
- Engine lathe: type of lathe.
- Turret lathe: type of lathe.
- Automatic lathe (Automatic Screw Machine): type of lathe.
- Tracer lathe: type of lathe.
- CNC lathe: type of lathe used for production work, requires more skill for programming and setup.
Lathes - Major Parts and Function
- The lathe bed: the main body of the lathe, allows for thermal expansion.
- Headstock: attached to the left side of the bed, houses the spindle, bearings, gears, and belts that drive the spindle.
- Headstock gears: control speed and feed selections.
- Levers: control speed and feed selections.
Lathe Components
- Apron: part of the lathe that houses controls.
- Apron controls: include split-nut lever, automatic feed lever, feed change lever, and carriage hand wheel.
- Lathe tailstock: allows for modification of the lathe axis for long taper machining.
- Tailstock spindle bore: manufactured with a Morse taper, holds tools such as drills, reamers, and revolving dead centers.
- Starting clutch: electronic or mechanical, used to start the lathe.
Workholding Devices
- Important features of workholding devices:
- Hold the work securely.
- Hold the work accurately.
- Be convenient and quick to use.
- Dead and live centers: used to hold workpieces.
- Solid dead center: made of hardened steel or carbide, more accurate than the revolving dead center.
- Half center: allows space for a facing tool.
- Drive plate: part of the workholding device.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers safety precautions, types, and major parts of a lathe, as well as workholding devices and tool posts. It is part of a machinist program's first period.