Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which type of lipids can be converted into smaller molecules by hydrolysis?
Which type of lipids can be converted into smaller molecules by hydrolysis?
- Hydrolyzable lipids (correct)
- Saturated lipids
- Nonhydrolyzable lipids
- Trans fats
What characteristic defines fatty acids?
What characteristic defines fatty acids?
- They are nonpolar molecules.
- They always have an even number of carbon atoms.
- They are cyclic structures.
- They are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. (correct)
Which type of fatty acid contains only one double bond?
Which type of fatty acid contains only one double bond?
- Monounsaturated fatty acid (correct)
- Saturated fatty acid
- Polyunsaturated fatty acid
- Hydrolyzable fatty acid
How does the melting point of fatty acids change with the number of double bonds?
How does the melting point of fatty acids change with the number of double bonds?
What distinguishes linoleic acid as an omega-6 acid?
What distinguishes linoleic acid as an omega-6 acid?
What are waxes formed from?
What are waxes formed from?
What products are formed when wax is hydrolyzed in the presence of acid or base?
What products are formed when wax is hydrolyzed in the presence of acid or base?
Which fatty acid has multiple double bonds and is known as omega-3?
Which fatty acid has multiple double bonds and is known as omega-3?
What are triglycerides primarily composed of?
What are triglycerides primarily composed of?
Which type of triglyceride has three identical fatty acid side chains?
Which type of triglyceride has three identical fatty acid side chains?
What is the primary function of lipase in relation to triacylglycerols?
What is the primary function of lipase in relation to triacylglycerols?
Which type of phospholipid resembles a triacylglycerol but has an alcohol replacing the third fatty acid?
Which type of phospholipid resembles a triacylglycerol but has an alcohol replacing the third fatty acid?
What distinguishes sphingomyelins from phosphoacylglycerols?
What distinguishes sphingomyelins from phosphoacylglycerols?
Which of the following is a common type of phosphoacylglycerol?
Which of the following is a common type of phosphoacylglycerol?
What part of a phosphoacylglycerol is charged or polar?
What part of a phosphoacylglycerol is charged or polar?
What is a key structural difference between phosphoacylglycerols and triglycerides?
What is a key structural difference between phosphoacylglycerols and triglycerides?
What triggers the increase of LDL levels in the plasma?
What triggers the increase of LDL levels in the plasma?
Which vitamin is synthesized from cholesterol?
Which vitamin is synthesized from cholesterol?
What is the primary function of HDL cholesterol?
What is the primary function of HDL cholesterol?
What condition is caused by a deficiency of Vitamin D?
What condition is caused by a deficiency of Vitamin D?
Which vitamin regulates the synthesis of clotting proteins such as prothrombin?
Which vitamin regulates the synthesis of clotting proteins such as prothrombin?
Which antioxidant vitamin prevents the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids?
Which antioxidant vitamin prevents the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids?
What is a common outcome of high LDL cholesterol in the blood?
What is a common outcome of high LDL cholesterol in the blood?
What happens to cholesterol synthesis in the liver when serum cholesterol levels are low?
What happens to cholesterol synthesis in the liver when serum cholesterol levels are low?
What are sphingomyelins primarily categorized as?
What are sphingomyelins primarily categorized as?
Which of the following components is NOT a part of the cell membrane structure?
Which of the following components is NOT a part of the cell membrane structure?
What type of transport is required for larger polar molecules to efficiently cross the cell membrane?
What type of transport is required for larger polar molecules to efficiently cross the cell membrane?
Which lipoprotein is often referred to as 'good cholesterol'?
Which lipoprotein is often referred to as 'good cholesterol'?
What is the main function of low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)?
What is the main function of low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)?
What mechanism controls the number of LDL receptors on the surface of cells?
What mechanism controls the number of LDL receptors on the surface of cells?
Which statement about cholesterol is true?
Which statement about cholesterol is true?
Which of the following statements about the cell membrane is accurate?
Which of the following statements about the cell membrane is accurate?
What fatty acid is primarily used in the synthesis of prostaglandins?
What fatty acid is primarily used in the synthesis of prostaglandins?
What physiological effect does Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) have on blood vessels?
What physiological effect does Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) have on blood vessels?
Which enzyme is responsible for synthesizing prostaglandins from arachidonic acid?
Which enzyme is responsible for synthesizing prostaglandins from arachidonic acid?
Which COX enzyme is mainly involved in inflammation-induced prostaglandin production?
Which COX enzyme is mainly involved in inflammation-induced prostaglandin production?
What is a common effect of leukotrienes on the body?
What is a common effect of leukotrienes on the body?
Which of the following statements about NSAIDs is true?
Which of the following statements about NSAIDs is true?
What role does Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) play in childbirth?
What role does Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) play in childbirth?
Leukotrienes mainly occur in which type of cells?
Leukotrienes mainly occur in which type of cells?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Lipids
- Lipids are a diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are generally insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents like chloroform and ether.
- They can be categorized into hydrolyzable and non-hydrolyzable lipids.
- Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis, while non-hydrolyzable lipids cannot.
- Hydrolyzable lipids are derived from fatty acids.
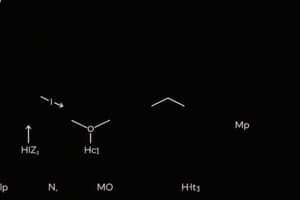
- Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains of 12 to 20 carbon atoms.
- Fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms.
- Saturated fatty acids have only single bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond.
- Naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids contain cis double bonds.
- Monounsaturated fatty acids have one double bond, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) have multiple double bonds.
- As the number of double bonds in a fatty acid increases, its melting point decreases.
Waxes
- Waxes are esters formed from a fatty acid and a high molecular weight alcohol.
- They are hydrolyzed in the presence of acid or base to reform the carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Triglycerides
- Triglycerides (also known as triacylglycerols) are esters formed from glycerol and three molecules of fatty acids.
- Simple triglycerides have three identical fatty acid side chains.
- Mixed triglycerides have two or three different fatty acids.
- Animal fats contain mainly saturated triglycerides, which are solid at room temperature.
- Vegetable oils contain mainly unsaturated triglycerides, which are liquid at room temperature.
- Triacylglycerols are hydrolyzed in the presence of acid, base, or enzymes (like lipase) to produce glycerol and fatty acids.
Phospholipids
- Phospholipids are lipids containing a phosphorus atom.
- They are the major components of cell membranes and are responsible for the selective permeability of the cell membrane.
- Two common types of phospholipids are phosphoacylglycerols and sphingomyelins.
- Phosphoacylglycerols structurally resemble a triacylglycerol with a phosphodiester bonded to an alcohol replacing the third fatty acid.
- Cephalin (or phosphatidylethanolamine) and lecithin (or phosphatidylcholine) are two main types of phosphoacylglycerols.
- Sphingomyelins do not contain a glycerol backbone; they have a sphingosine backbone instead.
- The myelin sheath, which surrounds nerve cells, is rich in sphingomyelins.
Steroids
- Steroids are lipids containing a carbon skeleton composed of several fused rings.
- Cholesterol is the most prominent steroid and is synthesized in the liver.
- Cholesterol is obtained in the diet from meat, cheese, butter, and eggs.
- Lipoproteins are carriers (transporters) of cholesterol.
- The four main types of lipoproteins are:
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
- Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
- Chylomicrons
- HDL ("good cholesterol") consists of about 33% protein and 30% cholesterol, while LDL ("bad cholesterol") contains about 25% protein and 50% cholesterol.
- LDL transports cholesterol from the liver to the tissues, while HDL transports cholesterol from tissues back to the liver.
- When LDL receptors are sufficient, LDL is removed from circulation, decreasing its concentration in blood plasma.
- The number of LDL receptors is controlled by a feedback mechanism.
- High levels of cholesterol in the cell suppress the synthesis of LDL receptors, resulting in increased LDL levels in blood plasma.
- Excess LDL cholesterol deposits on the walls of arteries, forming plaque that restricts blood flow.
- HDL reduces LDL levels in the bloodstream by transporting excess cholesterol back to the liver.
- HDL levels can be increased by exercise and weight loss.
- The synthesis of cholesterol in the liver is regulated by serum cholesterol levels.
- Statin drugs inhibit the synthesis of cholesterol by blocking HMG-CoA reductase, a key enzyme in cholesterol synthesis.
Vitamins
- Vitamins are organic compounds required in small quantities for normal metabolism.
- They are obtained from the diet and are either water-soluble or fat-soluble.
- The four fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) are found in fruits, vegetables, fish, liver, and dairy products.
- Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in adipose cells and used when needed.
- Vitamin A is found in liver, fish, and dairy products.
- Vitamin A deficiency causes night blindness and dry eyes and skin.
- Vitamin D is synthesized from cholesterol and can be obtained in the diet from many foods.
- Vitamin D deficiency causes rickets (bone malformation).
- Vitamin E is an antioxidant that protects the unsaturated side chains in fatty acids from oxidation.
- Vitamin E deficiency can cause neurological problems.
- Vitamin K regulates the synthesis of clotting proteins.
- Vitamin K deficiency leads to excessive or fatal bleeding.
Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes
- Prostaglandins are fatty-acid-like substances with a 20-carbon skeleton of prostanoic acid.
- They are not stored in tissues but are synthesized from membrane-bound 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids (like arachidonic acid) in response to physiological triggers.
- Prostaglandins are synthesized from arachidonic acid through ring closure at carbons 8 and 12 catalyzed by the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX).
- COX occurs in two forms:
- COX-1 catalyzes the normal production of prostaglandins.
- COX-2 is responsible for the production of prostaglandins in response to inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit both COX enzymes.
- Drugs like Vioxx, Bextra, and Celebrex specifically block the COX-2 enzyme.
Leukotrienes
- Leukotrienes are synthesized from arachidonic acid and are found mainly in white blood cells (leukocytes).
- They cause inflammation, fever, and muscle contractions, especially in the lungs, and can contribute to asthma-like attacks.
- Zileuton is a drug that inhibits the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase, which is involved in the synthesis of leukotrienes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.