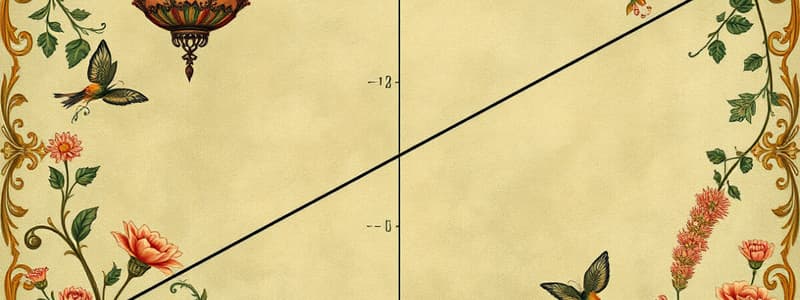Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the y-intercept in the equation of a straight line?
What is the y-intercept in the equation of a straight line?
- The x-coordinate of the line at y = 0
- The value of y at the point where the line crosses the y-axis (correct)
- The slope of the line
- The point where the line crosses the x-axis
What are x-intercepts?
What are x-intercepts?
Points on the graph where y is zero.
Define domain in the context of a function.
Define domain in the context of a function.
The set of values of the independent variable(s) for which a function or relation is defined.
What does range refer to in a set of values?
What does range refer to in a set of values?
What characterizes a linear equation?
What characterizes a linear equation?
Give a brief description of a non-linear system.
Give a brief description of a non-linear system.
What is a linear function?
What is a linear function?
What does a constant rate of change imply in mathematics?
What does a constant rate of change imply in mathematics?
What is the slope of a line?
What is the slope of a line?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Slope Intercept Key Terms
-
Y-Intercept: Part of the linear equation represented as y = mx + b, where 'b' signifies the y-value at the point where the line intersects the y-axis.
-
X-Intercept: Represents points where the graph crosses the x-axis (y = 0). These points occur when the value of y is zero.
-
Domain: Refers to the set of valid values for the independent variable(s) that result in real outputs (y-values) for a function. Typically includes all x-values that yield real y-values.
-
Range: Defined as the difference between the maximum and minimum values in a dataset. It can also encompass all output values of a function, representing the span of values a function can produce.
-
Linear Equation: An algebraic expression where each term consists of a constant or the product of a constant and the first power of a single variable. Linear equations are foundational in mathematics and often appear in various mathematical disciplines.
-
Non-linear Function: Characterized by equations where the unknowns are part of a polynomial of degree greater than one. Non-linear functions do not produce straight-line graphs.
-
Linear Function: A specific type of function whose graph is a straight line. Algebraically, it is defined as a polynomial of degree one or a constant horizontal line (y = c).
-
Constant Rate of Change: Indicates no acceleration; a function exhibiting this trait has a second derivative of zero. Graphically, it appears as a straight line, with a uniform change in y corresponding to changes in x.
-
Slope: Represents the steepness of a line defined by the rise over run between two points. Various formulas exist to calculate slope, illustrating its significance in determining line steepness in geometry and algebra.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.