Podcast
Questions and Answers
From which structure does the laryngotracheal diverticulum originate?
From which structure does the laryngotracheal diverticulum originate?
- Ventral wall of the foregut (correct)
- Dorsal wall of the hindgut
- Lateral wall of the hindgut
- Dorsal wall of the midgut
What anatomical structure forms from the undivided part of the laryngotracheal diverticulum?
What anatomical structure forms from the undivided part of the laryngotracheal diverticulum?
- Bronchioles
- Trachea (correct)
- Larynx
- Esophagus
Which structure is NOT part of the upper respiratory tract?
Which structure is NOT part of the upper respiratory tract?
- Larynx (correct)
- Nose
- Pharynx
- Nasal cavity
A tracheoesophageal fistula is most likely associated with which of the following conditions?
A tracheoesophageal fistula is most likely associated with which of the following conditions?
What do the right and left lung buds further develop into?
What do the right and left lung buds further develop into?
During which stage of lung development do respiratory bronchioles first appear?
During which stage of lung development do respiratory bronchioles first appear?
What is the primary structure formed during the terminal sac stage of lung development?
What is the primary structure formed during the terminal sac stage of lung development?
Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD) is associated with a deficiency in what substance?
Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD) is associated with a deficiency in what substance?
Which of the following is NOT a structure present in the pseudoglandular stage of lung development?
Which of the following is NOT a structure present in the pseudoglandular stage of lung development?
During the canalicular stage, what type of cell becomes closely associated with developing lung structures?
During the canalicular stage, what type of cell becomes closely associated with developing lung structures?
At what stage of lung development do true alveoli predominantly form?
At what stage of lung development do true alveoli predominantly form?
The formation of terminal sacs is a hallmark of which developmental stage?
The formation of terminal sacs is a hallmark of which developmental stage?
Which structures are directly adjacent to the terminal sacs at the end of the terminal sac stage?
Which structures are directly adjacent to the terminal sacs at the end of the terminal sac stage?
What occurs to circular DNA when it is cut and twisted at one end?
What occurs to circular DNA when it is cut and twisted at one end?
Which statement correctly describes positive supercoiling in DNA?
Which statement correctly describes positive supercoiling in DNA?
What effect does cutting one of the DNA strands have on supercoiling?
What effect does cutting one of the DNA strands have on supercoiling?
How does clockwise winding of DNA affect its conformation?
How does clockwise winding of DNA affect its conformation?
Which of the following describes the types of supercoiling in DNA?
Which of the following describes the types of supercoiling in DNA?
Which part of a nucleotide is responsible for its ability to store energy?
Which part of a nucleotide is responsible for its ability to store energy?
What distinguishes ribose from deoxyribose in nucleotide structure?
What distinguishes ribose from deoxyribose in nucleotide structure?
Which nitrogenous base is found in RNA but not in DNA?
Which nitrogenous base is found in RNA but not in DNA?
Which of the following correctly identifies the glycosidic bond in a nucleotide?
Which of the following correctly identifies the glycosidic bond in a nucleotide?
Which combination of nitrogenous bases correctly classifies the types of bases found in DNA?
Which combination of nitrogenous bases correctly classifies the types of bases found in DNA?
Which of the following statements about purines and pyrimidines is true?
Which of the following statements about purines and pyrimidines is true?
What is formed when a nucleoside is combined with a phosphate group?
What is formed when a nucleoside is combined with a phosphate group?
What percentage of nucleotides in tRNA are typically modified?
What percentage of nucleotides in tRNA are typically modified?
What is a characteristic of chemical modifications in RNA molecules?
What is a characteristic of chemical modifications in RNA molecules?
In phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers, what component replaces ribose or deoxyribose?
In phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers, what component replaces ribose or deoxyribose?
What is a significant function of the 2′ OH group in ribose?
What is a significant function of the 2′ OH group in ribose?
Which of the following statements about tRNA modifications is true?
Which of the following statements about tRNA modifications is true?
What is an effect of using phosphorodiamidate morpholino groups in RNA?
What is an effect of using phosphorodiamidate morpholino groups in RNA?
What role do modifications play in RNA molecules?
What role do modifications play in RNA molecules?
Which of the following is NOT a typical characteristic of modified RNAs?
Which of the following is NOT a typical characteristic of modified RNAs?
What happens to phosphodiester bonds in the presence of a 2′ OH group?
What happens to phosphodiester bonds in the presence of a 2′ OH group?
What role do Van der Waals interactions play in DNA structure?
What role do Van der Waals interactions play in DNA structure?
How far apart are base pairs in B-DNA?
How far apart are base pairs in B-DNA?
What is the diameter of the DNA helix approximately?
What is the diameter of the DNA helix approximately?
Which DNA conformation can be induced by DNA binding proteins?
Which DNA conformation can be induced by DNA binding proteins?
What is the characteristic feature of Z-DNA?
What is the characteristic feature of Z-DNA?
Which groove in B-DNA is wider, allowing for specific molecular interactions?
Which groove in B-DNA is wider, allowing for specific molecular interactions?
Which type of base pairing tends to make DNA regions more bendable?
Which type of base pairing tends to make DNA regions more bendable?
How often does the B-DNA helix repeat its structure?
How often does the B-DNA helix repeat its structure?
What effect does methylation of cytosine have on DNA structure?
What effect does methylation of cytosine have on DNA structure?
What is a major characteristic of A-DNA compared to B-DNA?
What is a major characteristic of A-DNA compared to B-DNA?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases in a DNA molecule?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the sugar-phosphate backbone and the bases in a DNA molecule?
What provides the structural stability to the DNA double helix, allowing it to maintain its unique shape?
What provides the structural stability to the DNA double helix, allowing it to maintain its unique shape?
What is the significance of the fact that the two strands of DNA are antiparallel?
What is the significance of the fact that the two strands of DNA are antiparallel?
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of Chargaff's rules?
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of Chargaff's rules?
Why are the bases stacked in the interior of the DNA helix while the sugar-phosphate backbone is on the exterior?
Why are the bases stacked in the interior of the DNA helix while the sugar-phosphate backbone is on the exterior?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the structure of a single nucleotide?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the structure of a single nucleotide?
What is the significance of the 5' and 3' ends of a DNA strand?
What is the significance of the 5' and 3' ends of a DNA strand?
What is the primary function of the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs in DNA?
What is the primary function of the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs in DNA?
Which of the following scientists is NOT credited with the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA?
Which of the following scientists is NOT credited with the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA?
Which of the following base pairs is characterized by having the weakest hydrogen bonding interaction?
Which of the following base pairs is characterized by having the weakest hydrogen bonding interaction?
Flashcards
Laryngotracheal Diverticulum Formation
Laryngotracheal Diverticulum Formation
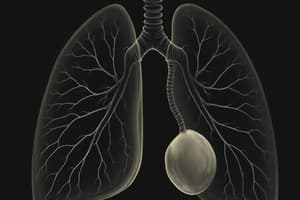
The ventral wall of the foregut forms a groove, which then develops into a pouch called the laryngotracheal diverticulum. This diverticulum eventually gives rise to the larynx, trachea, and lung buds.
Lung Bud Development
Lung Bud Development
The laryngotracheal diverticulum divides into two parts. The distal end forms the right and left lung buds, which will develop into the bronchi and lungs. The undivided part becomes the trachea, and the opening of the diverticulum forms the larynx.
Tracheoesophageal Fistula/Atresia
Tracheoesophageal Fistula/Atresia
A condition where there is a connection between the trachea and esophagus, often accompanied by a blockage in the esophagus. This can occur due to incomplete separation of the trachea and esophagus during development.
Respiratory Tract Divisions
Respiratory Tract Divisions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lung Development Stages
Lung Development Stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudoglandular Stage
Pseudoglandular Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Canalicular Stage
Canalicular Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terminal Sac Stage
Terminal Sac Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Stage
Alveolar Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II Pneumocytes
Type II Pneumocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Hyaline Membrane Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surfactant
Surfactant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Bronchioles
Respiratory Bronchioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Nucleic Acids?
What are Nucleic Acids?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a nucleotide?
What is a nucleotide?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the sugars in nucleotides?
What are the sugars in nucleotides?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the nitrogenous bases in nucleotides?
What are the nitrogenous bases in nucleotides?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a glycosidic bond?
What is a glycosidic bond?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are nucleosides and nucleotides?
What are nucleosides and nucleotides?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some functions of nucleotides?
What are some functions of nucleotides?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-transcriptional modification
Post-transcriptional modification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers
Signup and view all the flashcards
2' OH in ribose
2' OH in ribose
Signup and view all the flashcards
2' OH and phosphodiester bonds
2' OH and phosphodiester bonds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Modified RNAs
Modified RNAs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conserved tRNA modifications
Conserved tRNA modifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
tRNA modifications percentage
tRNA modifications percentage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Permanent RNA modifications
Permanent RNA modifications
Signup and view all the flashcards
RNA modifications and function
RNA modifications and function
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is supercoiling?
What is supercoiling?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the types of supercoiling?
What are the types of supercoiling?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is negative supercoiling?
What is negative supercoiling?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is positive supercoiling?
What is positive supercoiling?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can supercoiling be released?
How can supercoiling be released?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the structure of nucleic acids?
What is the structure of nucleic acids?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the directionality of nucleic acid strands?
What is the directionality of nucleic acid strands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the backbone of DNA and RNA?
What is the backbone of DNA and RNA?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Chargaff's Rule?
What is Chargaff's Rule?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do the two DNA strands associate?
How do the two DNA strands associate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the relationship between the two DNA strands?
What is the relationship between the two DNA strands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Watson-Crick model of DNA?
What is the Watson-Crick model of DNA?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who contributed significantly to the understanding of DNA's structure?
Who contributed significantly to the understanding of DNA's structure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the significance of the Watson-Crick model?
What is the significance of the Watson-Crick model?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who received the Nobel Prize for the discovery of DNA's structure?
Who received the Nobel Prize for the discovery of DNA's structure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Base-stacking in DNA
Base-stacking in DNA
Signup and view all the flashcards
DNA Double Helix Structure
DNA Double Helix Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uniform DNA Helix Diameter
Uniform DNA Helix Diameter
Signup and view all the flashcards
B-DNA Structure
B-DNA Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major and Minor Grooves in DNA
Major and Minor Grooves in DNA
Signup and view all the flashcards
DNA Flexibility and A-T Rich Regions
DNA Flexibility and A-T Rich Regions
Signup and view all the flashcards
A-DNA Conformation
A-DNA Conformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Z-DNA Conformation
Z-DNA Conformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic DNA Structure
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic DNA Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
DNA Packaging in Eukaryotes
DNA Packaging in Eukaryotes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to the Respiratory System
- The respiratory system's primary function, gas exchange, begins after birth.
- Embryonic development involves the formation of the respiratory tract, diaphragm, and lungs.
- The respiratory tract is anatomically divided into upper and lower tracts.
- The upper respiratory tract comprises the nose, nasal cavity, and pharynx.
- The lower respiratory tract consists of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, alveoli, and diaphragm.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the development of the lung bud and surrounding structures within the pharyngeal foregut.
- Learn the four key developmental stages of lung formation and their distinguishing characteristics.
- Identify the lobes of the right and left lungs, along with their associated bronchopulmonary segments.
Development of Lower Respiratory Tract and Lungs
- The ventral wall of the foregut forms the laryngotracheal groove.
- This groove subsequently develops into the laryngotracheal diverticulum.
- The diverticulum further divides into the trachea and lung buds.
- The tracheoesophageal septum forms during respiratory system development, crucial for separating the trachea from the esophagus.
Tracheoesophageal Fistula/Atresia
- Hypoplasia of the tracheoesophageal septum is a potential issue.
- A fistula between the trachea and esophagus can occur.
- This condition often co-occurs with esophageal atresia.
Bronchial Development
- The distal end of the laryngotracheal diverticulum divides into right and left lung buds.
- This division establishes the bronchi and lungs.
- The undivided portion of the diverticulum becomes the trachea.
- The opening of the diverticulum ultimately forms the larynx.
Pseudoglandular and Canalicular Stages
- The Pseudoglandular stage (5-16 weeks) features branching of airways, presence of terminal sacs, and a noticeable presence of CT cells in the respiratory tract, as well as capillaries.
- The Canalicular stage (16-25 weeks) showcases developing respiratory bronchioles and terminal bronchioles.
Terminal Sac and Alveolar Stages
- The Terminal sac stage (26 weeks-birth) is characterized by the presence of terminal sacs, respiratory bronchioles, and the beginning of alveolar development.
- The Alveolar stage (birth-8 years) is marked by the formation of alveoli, smooth muscle cells, and the development of the alveolar capillary network.
Hyaline Membrane Disease
- Hyaline membrane disease (HMD) results from a deficiency in surfactant, a surface-active agent produced by type II pneumocytes.
- Adequate surfactant is essential for maintaining alveolar patency and preventing collapse.
- Infants born prematurely, those of diabetic mothers, and those experiencing fetal distress are at a higher risk for HMD.
- Clinical symptoms include dyspnea, tachypnea, inspiratory retractions, expiratory grunting, cyanosis, and nasal flaring.
- Treatment often involves administering corticosteroids like betamethasone.
Knowledge Check Quiz
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome (NRDS) stems from a lack of adequate surfactant, causing alveolar damage. This critical role of surfactant in maintaining lung function is a key feature of this condition.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the anatomy and development of the respiratory system, focusing on the upper and lower tracts. You'll explore the key stages of lung development, the lung bud formation, and the structural components of the lungs and airways. Gain a better understanding of how these systems function and interact.