Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is another name for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
What is another name for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
- Vascular malformation disorder
- Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome (correct)
- Angiodysplasia condition
- Autosomal recessive syndrome
What type of inheritance pattern is associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
What type of inheritance pattern is associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
- Autosomal dominant (correct)
- Mitochondrial inheritance
- Autosomal recessive
- X-linked recessive
Which of the following is a common clinical feature of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
Which of the following is a common clinical feature of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
- Frequent headaches
- Joint pain
- Skin rashes
- Nosebleeds (correct)
Where can telangiectasia develop in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
Where can telangiectasia develop in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
What rare complication can arise from hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
What rare complication can arise from hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
What is the primary cause of appendicitis in adults?
What is the primary cause of appendicitis in adults?
Which anatomical structure does the appendix attach to?
Which anatomical structure does the appendix attach to?
How does the location of abdominal pain change as appendicitis progresses?
How does the location of abdominal pain change as appendicitis progresses?
What are fecaliths in relation to appendicitis?
What are fecaliths in relation to appendicitis?
What characterizes the pain from appendicitis initially?
What characterizes the pain from appendicitis initially?
What is the term used to describe the worm-like appearance of the appendix?
What is the term used to describe the worm-like appearance of the appendix?
What happens when the outlet of the appendix becomes obstructed?
What happens when the outlet of the appendix becomes obstructed?
What role does the somatic nervous system play in appendicitis pain perception?
What role does the somatic nervous system play in appendicitis pain perception?
What does diverticulitis commonly present with?
What does diverticulitis commonly present with?
Which complication is associated with diverticulitis when an abscess forms?
Which complication is associated with diverticulitis when an abscess forms?
Which of the following is a characteristic symptom of a colovesical fistula?
Which of the following is a characteristic symptom of a colovesical fistula?
What is a common cause of small bowel obstruction related to previous surgeries?
What is a common cause of small bowel obstruction related to previous surgeries?
The symptom classically described as 'currant jelly' stool is associated with which condition?
The symptom classically described as 'currant jelly' stool is associated with which condition?
What is the purpose of a hema occult test?
What is the purpose of a hema occult test?
Which type of imaging is commonly used to diagnose diverticulitis?
Which type of imaging is commonly used to diagnose diverticulitis?
What complication can diverticulitis evolve into involving the intestinal lumen?
What complication can diverticulitis evolve into involving the intestinal lumen?
Which of the following best describes the treatment of diverticulitis?
Which of the following best describes the treatment of diverticulitis?
What can happen if inflammation from diverticulitis progresses significantly?
What can happen if inflammation from diverticulitis progresses significantly?
What condition is illustrated by the telescoping of the intestine?
What condition is illustrated by the telescoping of the intestine?
In children, what is a potential 'lead point' that can trigger intussusception?
In children, what is a potential 'lead point' that can trigger intussusception?
Which symptom indicates potential obstruction due to diverticulitis?
Which symptom indicates potential obstruction due to diverticulitis?
What is McBurney's point used to identify?
What is McBurney's point used to identify?
How is rebound tenderness identified during a physical exam?
How is rebound tenderness identified during a physical exam?
Which of the following is NOT a cause of an acute abdomen that may require surgical intervention?
Which of the following is NOT a cause of an acute abdomen that may require surgical intervention?
What characterizes a false diverticulum?
What characterizes a false diverticulum?
What condition is referred to when many diverticuli are present in the GI tract?
What condition is referred to when many diverticuli are present in the GI tract?
Which imaging technique can be performed to gain detailed information about the abdomen when appendicitis is suspected?
Which imaging technique can be performed to gain detailed information about the abdomen when appendicitis is suspected?
What is the main risk associated with a missed diagnosis of an acute abdomen?
What is the main risk associated with a missed diagnosis of an acute abdomen?
What dietary factor is commonly linked to the development of diverticulosis?
What dietary factor is commonly linked to the development of diverticulosis?
Which statement is true about Meckel's diverticulum?
Which statement is true about Meckel's diverticulum?
In which quadrant is McBurney's point located?
In which quadrant is McBurney's point located?
What happens to the abdominal muscles when rebound tenderness is present?
What happens to the abdominal muscles when rebound tenderness is present?
What is the primary symptom that may indicate appendicitis?
What is the primary symptom that may indicate appendicitis?
What typically causes a true diverticulum?
What typically causes a true diverticulum?
Why is the term 'acute abdomen' significant in medical practice?
Why is the term 'acute abdomen' significant in medical practice?
What condition is often associated with enteric adenovirus infection in children?
What condition is often associated with enteric adenovirus infection in children?
In which location does intestinal volvulus typically occur?
In which location does intestinal volvulus typically occur?
What imaging finding is classically associated with sigmoid volvulus?
What imaging finding is classically associated with sigmoid volvulus?
What is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction?
What is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction?
What is a key clinical feature of bowel obstruction?
What is a key clinical feature of bowel obstruction?
What is a characteristic finding in abdominal X-ray of a patient with bowel obstruction?
What is a characteristic finding in abdominal X-ray of a patient with bowel obstruction?
What causes Hirschsprung's disease?
What causes Hirschsprung's disease?
What is a common presentation in infants with Hirschsprung's disease?
What is a common presentation in infants with Hirschsprung's disease?
What does a barium X-ray typically reveal in a child with Hirschsprung's disease?
What does a barium X-ray typically reveal in a child with Hirschsprung's disease?
Which patient demographic is most likely to experience intestinal volvulus?
Which patient demographic is most likely to experience intestinal volvulus?
What is the underlying cause of peristalsis failure in Hirschsprung's disease?
What is the underlying cause of peristalsis failure in Hirschsprung's disease?
What symptom indicates a potential bowel obstruction?
What symptom indicates a potential bowel obstruction?
What complication can arise from intestinal volvulus?
What complication can arise from intestinal volvulus?
What is always involved in Hirschsprung's disease?
What is always involved in Hirschsprung's disease?
Which method is used to obtain a biopsy that includes the submucosa in Hirschsprung's diagnosis?
Which method is used to obtain a biopsy that includes the submucosa in Hirschsprung's diagnosis?
What condition is characterized by a lack of bowel peristalsis?
What condition is characterized by a lack of bowel peristalsis?
What is a common complication seen in Ogilvie syndrome?
What is a common complication seen in Ogilvie syndrome?
What are the diagnostic criteria for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
What are the diagnostic criteria for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
In which population is Necrotizing Enterocolitis most commonly found?
In which population is Necrotizing Enterocolitis most commonly found?
What classic X-ray finding is associated with Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
What classic X-ray finding is associated with Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
Which statement about Angiodysplasia is true?
Which statement about Angiodysplasia is true?
Which medication class is commonly associated with causing ileus?
Which medication class is commonly associated with causing ileus?
What is a primary treatment approach for Infantile Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
What is a primary treatment approach for Infantile Necrotizing Enterocolitis?
What condition can lead to obstruction without a physical lesion?
What condition can lead to obstruction without a physical lesion?
Which of the following statements about treatment for IBS is correct?
Which of the following statements about treatment for IBS is correct?
What aspect differentiates IBS from structural bowel disorders?
What aspect differentiates IBS from structural bowel disorders?
Appendicitis is acute inflammation of the ______.
Appendicitis is acute inflammation of the ______.
The appendix is often called the ______ appendix due to its shape.
The appendix is often called the ______ appendix due to its shape.
In children, appendicitis is more commonly associated with ______ hyperplasia.
In children, appendicitis is more commonly associated with ______ hyperplasia.
Patients with appendicitis may initially develop abdominal pain in the mid ______ region.
Patients with appendicitis may initially develop abdominal pain in the mid ______ region.
As appendicitis progresses, the pain typically moves to the right lower ______.
As appendicitis progresses, the pain typically moves to the right lower ______.
If the opening of the appendix becomes obstructed, bacteria can accumulate and lead to a small ______ in the appendix.
If the opening of the appendix becomes obstructed, bacteria can accumulate and lead to a small ______ in the appendix.
The visceral peritoneum is innervated by the ______ nervous system.
The visceral peritoneum is innervated by the ______ nervous system.
Fecaliths are hard fecal masses that can obstruct the outlet of the ______.
Fecaliths are hard fecal masses that can obstruct the outlet of the ______.
Hereditary hemorrhagic ______ is also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome.
Hereditary hemorrhagic ______ is also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome.
Patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia develop multiple dilated ______ beds in their GI tract.
Patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia develop multiple dilated ______ beds in their GI tract.
Common clinical features of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia include nosebleeds, GI bleeds, and iron deficiency ______.
Common clinical features of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia include nosebleeds, GI bleeds, and iron deficiency ______.
Telangiectasia can develop anywhere from the nasopharynx to the ______.
Telangiectasia can develop anywhere from the nasopharynx to the ______.
One rare complication of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is the formation of AVMs, which are arterial vascular ______.
One rare complication of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is the formation of AVMs, which are arterial vascular ______.
Diverticulitis is inflammation of a diverticulum that presents with ______ and elevated white blood cell count.
Diverticulitis is inflammation of a diverticulum that presents with ______ and elevated white blood cell count.
The first complication of diverticular disease is lower GI bleeding, also known as ______.
The first complication of diverticular disease is lower GI bleeding, also known as ______.
A positive test for ______ is commonly seen in diverticulitis.
A positive test for ______ is commonly seen in diverticulitis.
One serious complication of diverticulitis is the formation of an ______.
One serious complication of diverticulitis is the formation of an ______.
Diverticulitis can cause a bowel ______ due to narrowing of the intestinal lumen.
Diverticulitis can cause a bowel ______ due to narrowing of the intestinal lumen.
The term ______ refers to a connection that forms with another structure in the abdomen.
The term ______ refers to a connection that forms with another structure in the abdomen.
Symptoms of a colovesical fistula include ______ in the urine.
Symptoms of a colovesical fistula include ______ in the urine.
Intestinal ______ involves the folding of a segment of the intestine into another.
Intestinal ______ involves the folding of a segment of the intestine into another.
The stool characteristic of intussusception is described as ______ jelly.
The stool characteristic of intussusception is described as ______ jelly.
A ______ point can trigger intussusception by pinching the bowel.
A ______ point can trigger intussusception by pinching the bowel.
Presence of ______ is a classic cause of intussusception in children.
Presence of ______ is a classic cause of intussusception in children.
Adhesions are bands of ______ tissue that can form after surgery.
Adhesions are bands of ______ tissue that can form after surgery.
McBurney's point is located in the right ______ quadrant.
McBurney's point is located in the right ______ quadrant.
Surgery to remove adhesions is called ______ of adhesions.
Surgery to remove adhesions is called ______ of adhesions.
Rebound tenderness indicates ______ inflammation.
Rebound tenderness indicates ______ inflammation.
One complication resulting from adhesions is a small bowel ______.
One complication resulting from adhesions is a small bowel ______.
A condition marked by the acute onset of abdominal pain is referred to as an ______ abdomen.
A condition marked by the acute onset of abdominal pain is referred to as an ______ abdomen.
Diverticulosis usually occurs in the sigmoid ______.
Diverticulosis usually occurs in the sigmoid ______.
The presence of multiple diverticula in the GI tract is referred to as ______.
The presence of multiple diverticula in the GI tract is referred to as ______.
A ______ diverticulum contains all three layers of the GI tract.
A ______ diverticulum contains all three layers of the GI tract.
True diverticulum is exemplified by ______'s diverticulum.
True diverticulum is exemplified by ______'s diverticulum.
Peyer's patches can become enlarged and viral gastroenteritis, triggering ______.
Peyer's patches can become enlarged and viral gastroenteritis, triggering ______.
False diverticula form due to a breakdown in the ______ layer.
False diverticula form due to a breakdown in the ______ layer.
Intestinal volvulus is characterized by a twisting of the bowel around the ______.
Intestinal volvulus is characterized by a twisting of the bowel around the ______.
Increased ______ pressure can lead to the formation of diverticula.
Increased ______ pressure can lead to the formation of diverticula.
Bowel obstruction occurs most commonly in the ______, with about 75% of obstructions occurring here.
Bowel obstruction occurs most commonly in the ______, with about 75% of obstructions occurring here.
Surgical intervention is often necessary for conditions associated with an acute ______.
Surgical intervention is often necessary for conditions associated with an acute ______.
A classic imaging finding in sigmoid volvulus is a dilated ______.
A classic imaging finding in sigmoid volvulus is a dilated ______.
The ______ scan can be used for detailed imaging when appendicitis is suspected.
The ______ scan can be used for detailed imaging when appendicitis is suspected.
The common causes of small bowel obstruction are remembered by the mnemonic ______.
The common causes of small bowel obstruction are remembered by the mnemonic ______.
A ruptured appendix can lead to ______, which is life-threatening.
A ruptured appendix can lead to ______, which is life-threatening.
Acute abdomen symptoms may include rebound tenderness and exquisite ______.
Acute abdomen symptoms may include rebound tenderness and exquisite ______.
In cases of bowel obstruction, patients may experience ______, the inability to pass stool.
In cases of bowel obstruction, patients may experience ______, the inability to pass stool.
Hirschsprung's disease is associated with an absence of ______ cells in the intestines.
Hirschsprung's disease is associated with an absence of ______ cells in the intestines.
Diverticular disease is often caused by a ______ fiber diet.
Diverticular disease is often caused by a ______ fiber diet.
When pain moves away from the ______ region, it may indicate appendicitis.
When pain moves away from the ______ region, it may indicate appendicitis.
The diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease is usually made by a special type of ______.
The diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease is usually made by a special type of ______.
In children with Hirschsprung's disease, a classic finding on barium X-ray is the presence of a ______ zone.
In children with Hirschsprung's disease, a classic finding on barium X-ray is the presence of a ______ zone.
The vomiting in bowel obstruction occurs due to contents backing up into the ______.
The vomiting in bowel obstruction occurs due to contents backing up into the ______.
Children born with Hirschsprung's disease often present with a failure to pass ______.
Children born with Hirschsprung's disease often present with a failure to pass ______.
The mean age at which volvulus generally occurs is ______.
The mean age at which volvulus generally occurs is ______.
In bowel obstruction, patients may have a large distended abdomen from air-filled loops of ______.
In bowel obstruction, patients may have a large distended abdomen from air-filled loops of ______.
An airless rectum during imaging occurs because air cannot get beyond the ______.
An airless rectum during imaging occurs because air cannot get beyond the ______.
In Hirshsprung's disease, the ______________ is always involved.
In Hirshsprung's disease, the ______________ is always involved.
A standard biopsy of the rectal mucosa may only obtain the ______________.
A standard biopsy of the rectal mucosa may only obtain the ______________.
Ileus refers to the loss of bowel ______________.
Ileus refers to the loss of bowel ______________.
Post-op ileus commonly occurs after the administration of ______________.
Post-op ileus commonly occurs after the administration of ______________.
Ogilvie syndrome is described as a pseudo-______________.
Ogilvie syndrome is described as a pseudo-______________.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional bowel ______________.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional bowel ______________.
Symptoms of IBS must occur at least three days per ______________ for three months.
Symptoms of IBS must occur at least three days per ______________ for three months.
Patients with IBS may experience either _________________ or both.
Patients with IBS may experience either _________________ or both.
Necrotizing enterocolitis occurs mainly in preterm or low birth weight ______________.
Necrotizing enterocolitis occurs mainly in preterm or low birth weight ______________.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is identified as air in the bowel ______________.
Pneumatosis intestinalis is identified as air in the bowel ______________.
Angiodysplasia is the presence of an ______________ blood vessel in the GI tract.
Angiodysplasia is the presence of an ______________ blood vessel in the GI tract.
Angiodysplasia is commonly seen in the cecum and the right-sided ______________.
Angiodysplasia is commonly seen in the cecum and the right-sided ______________.
Patients with angiodysplasia often present with lower GI __________________.
Patients with angiodysplasia often present with lower GI __________________.
The pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis is believed to involve the combination of food and ______________.
The pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis is believed to involve the combination of food and ______________.
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia is a _________________ syndrome.
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia is a _________________ syndrome.
Flashcards
Appendicitis
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix, a small, blind-ended tube attached to the cecum.
Appendix
Appendix
A small, blind-ended tube attached to the cecum, part of the large intestine.
Fecalith
Fecalith
Hard fecal mass that can obstruct the appendix.
Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral Peritoneum
Visceral Peritoneum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Peritoneum
Parietal Peritoneum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Location (Appendicitis)
Pain Location (Appendicitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
McBurney's Point
McBurney's Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Abdomen
Acute Abdomen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rebound Tenderness
Rebound Tenderness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diverticulum
Diverticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
False Diverticulum
False Diverticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
True Diverticulum
True Diverticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasa Recta
Vasa Recta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sigmoid Colon
Sigmoid Colon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intra-abdominal Pressure
Intra-abdominal Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appendicitis Pain Progression
Appendicitis Pain Progression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appendicitis Diagnosis
Appendicitis Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appendicitis Treatment
Appendicitis Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Abdomen Causes
Acute Abdomen Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peritonitis
Peritonitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hematochezia
Hematochezia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occult Blood
Occult Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diverticulitis Abscess
Diverticulitis Abscess
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diverticulitis Obstruction
Diverticulitis Obstruction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Colovesical Fistula
Colovesical Fistula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pneumaturia
Pneumaturia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fecaluria
Fecaluria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diverticulitis Perforation
Diverticulitis Perforation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adhesions
Adhesions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lysis of Adhesions
Lysis of Adhesions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intussusception
Intussusception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lead Point (Intussusception)
Lead Point (Intussusception)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Telangiectasia
Telangiectasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
AVMs (Arteriovenous Malformations)
AVMs (Arteriovenous Malformations)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Symptoms of HHT
Common Symptoms of HHT
Signup and view all the flashcards
HHT vs. Most Other Genetic Disorders
HHT vs. Most Other Genetic Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peyer's Patches
Peyer's Patches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intestinal Volvulus
Intestinal Volvulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hernia
Hernia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air-Fluid Levels
Air-Fluid Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hirschsprung's Disease
Hirschsprung's Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ganglion Cells
Ganglion Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Crest Cells
Neural Crest Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hirschsprung's Biopsy
Hirschsprung's Biopsy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ileus
Ileus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Op Ileus
Post-Op Ileus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ogilvie Syndrome
Ogilvie Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
IBS Symptoms
IBS Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
NEC X-Ray Finding
NEC X-Ray Finding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiodysplasia
Angiodysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiodysplasia Cause
Angiodysplasia Cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiodysplasia Symptoms
Angiodysplasia Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
HT Symptoms
HT Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes appendicitis pain to move?
What causes appendicitis pain to move?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the two main causes of appendicitis?
What are the two main causes of appendicitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the characteristic pain pattern in appendicitis?
What's the characteristic pain pattern in appendicitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the visceral peritoneum in appendicitis?
What is the role of the visceral peritoneum in appendicitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the parietal peritoneum in appendicitis?
What is the role of the parietal peritoneum in appendicitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the classic location of pain in appendicitis?
What is the classic location of pain in appendicitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the most common cause of appendicitis in adults?
What is the most common cause of appendicitis in adults?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the most common cause of appendicitis in children?
What is the most common cause of appendicitis in children?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common HHT Symptoms
Common HHT Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abscess (Diverticulitis)
Abscess (Diverticulitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowel Obstruction (Diverticulitis)
Bowel Obstruction (Diverticulitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perforation (Diverticulitis)
Perforation (Diverticulitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Currant Jelly Stools
Currant Jelly Stools
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ileal-Cecal Junction
Ileal-Cecal Junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intussusception Trigger in Kids
Intussusception Trigger in Kids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intussusception in Adults
Intussusception in Adults
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Intestinal Volvulus?
What is Intestinal Volvulus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volvulus Locations
Volvulus Locations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Volvulus Imaging Findings
Volvulus Imaging Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowel Obstruction Location
Bowel Obstruction Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowel Obstruction Symptoms
Bowel Obstruction Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mnemonics for Bowel Obstruction Causes
Mnemonics for Bowel Obstruction Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large Bowel Obstruction Causes
Large Bowel Obstruction Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowel Obstruction X-ray
Bowel Obstruction X-ray
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hirschsprung's Disease Cause
Hirschsprung's Disease Cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hirschsprung's Disease Presentation
Hirschsprung's Disease Presentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Barium X-ray in Hirschsprung's Disease
Barium X-ray in Hirschsprung's Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosis of Hirschsprung's Disease
Diagnosis of Hirschsprung's Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rectum Involvement in Hirschsprung's
Rectum Involvement in Hirschsprung's
Signup and view all the flashcards
IBS Diagnostic Criteria
IBS Diagnostic Criteria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiodysplasia vs HHT
Angiodysplasia vs HHT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Intestinal Disorders
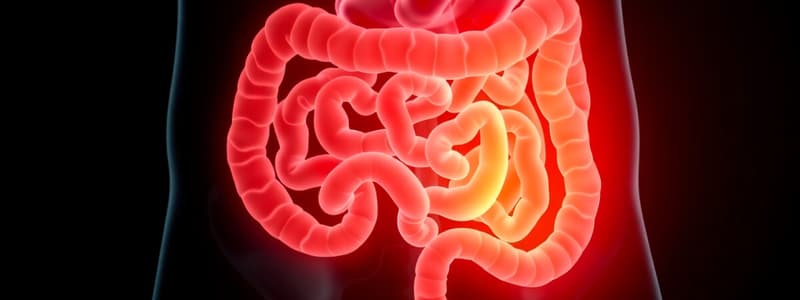
- Appendicitis: Acute inflammation of the appendix, a worm-like tube attached to the cecum.
- Occurs when the appendix's opening to the cecum becomes blocked, allowing bacteria to accumulate and form an abscess.
- Common causes include fecaliths (hard fecal masses) in adults and lymphoid hyperplasia (enlarged lymphoid tissue) in children (often triggered by viral infections).
- Initial pain is typically in the mid-epigastric region around the umbilicus due to irritation of the visceral peritoneum (poorly localized autonomic innervation).
- As inflammation progresses, pain moves to the right lower quadrant (RLQ), specifically to McBurney's point (one-third of the distance from the iliac crest to the umbilicus).
- Diagnosis can be made by history and physical exam. CT scan if unsure or more details are needed.
- Treatment involves surgical removal of the appendix.
- Acute abdomen: acute onset abdominal pain with rebound tenderness (pain when pressure is released from the abdomen); a serious diagnosis needing urgent intervention due to potential for perforation and peritonitis.
Diverticular Disease
- Diverticulum: A blind pouch or sac protruding from the GI tract wall—a "false" diverticulum lacks all three GI tract layers.
- Commonly occurs in the sigmoid colon.
- Caused by straining to pass stool (increased intra-abdominal pressure) and a low-fiber diet. Resulting in hard stool.
- Diverticulosis: Presence of multiple diverticula.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation of a diverticulum often presenting with left lower quadrant pain, rebound tenderness, and elevated white blood cell count. Potential for bleeding (hematochezia) or occult blood (detected with a fecal occult blood test).
- Complication possibilities include abscess formation, bowel obstruction, fistula formation (connection to another structure, e.g., colovesical fistula—air or fecal matter in urine), and perforation.
- Treatment can include antibiotics and sometimes surgery.
Adhesions
- Adhesions: Bands of scar tissue in the peritoneal cavity, often forming after abdominal surgery.
- Can cause small bowel obstruction, infertility, chronic abdominal/pelvic pain.
- Treatment is lysis of adhesions (surgical cutting of the adhesions), though this can sometimes result in more adhesions.
Intussusception
- Intussusception: Telescoping of one portion of the intestine into another, often triggered by a "lead point" (e.g., Meckel's diverticulum, lymphoid hyperplasia, viral gastroenteritis).
- Often happens near the ileocecal junction in children under one year old.
- Can lead to compromised blood supply, necrosis, bleeding, and presenting with "currant jelly" stool (thick, red stool).
- Medical emergency requiring treatment.
Intestinal Volvulus
- Intestinal volvulus: Twisting of the bowel around its mesentery.
- Common locations are the sigmoid colon and the cecum.
- Can lead to bowel obstruction and infarction.
- Imaging in sigmoid volvulus often show dilated sigmoid colon and an airless rectum.
- Typically occurs in elderly individuals (mean age ~70).
Bowel Obstruction
- Bowel obstruction: Often in small intestine (75%).
- Presents with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting (vomiting of stomach contents due to obstruction), abdominal distension, and obstipation (inability to pass stool or gas).
- Common causes include adhesions, hernias, and tumors (colon).
- Diagnosis can include abdominal x-ray (dilated loops of bowel, air-fluid levels).
Hirschsprung's Disease
- Hirschsprung's disease: Congenital motor disorder of the intestine due to absence of ganglion cells in the bowel (neural crest cells do not migrate properly)
- Results in lack of peristalsis leading to bowel obstruction.
- Presents in newborns with failure to pass meconium, abdominal distension, and bilious vomiting. Rectum is always involved.
- Diagnosis often made via rectal suction biopsy to look for ganglion cells.
- Treatment involves surgical resection of affected portion.
- Rectum is always involved in diagnosis.
Ileus
- Ileus: Loss of bowel peristalsis.
- Common causes include medications (especially narcotics), post-operative states (post-op ileus), and Ogilvie syndrome.
- Ogilvie syndrome: Pseudo-obstruction (dilated colon without an obstructing lesion). Often seen in sedentary, hospitalized, elderly patients.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- IBS: Functional bowel disorder (problem with bowel function, not structure).
- Characterized by recurrent abdominal pain, at least 3 days/month for 3 months.
- Associated with bowel changes—frequency, appearance—and defecation relieves pain.
- Primarily presents in women. No reliable cure available, treatment is often symptomatic.
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
- NEC: Neonatal disorder (first month of life), commonly in preterm/low birth weight infants.
- Intestinal necrosis, obstruction, and possible perforation.
- Signs include abdominal distension, nausea, vomiting, and air in the bowel wall (pneumatosis intestinalis).
- Treatment involves bowel rest, antibiotics, and often surgery.
Angiodysplasia
- Angiodysplasia: Aberrant blood vessels in the GI tract, often in the cecum/right colon.
- Common cause of lower GI bleeding (hematochezia) in older adults.
- Thought to develop from high wall stress and compression over time.
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
- HHT (Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome): Inherited vascular disorder.
- Multiple dilated capillary beds (telangiectasia) throughout the GI tract (similar to angiodysplasia).
- Risk of GI bleeds, nosebleeds, and iron deficiency anemia.
- Often leads to formation of arterial vascular malformations (AVMs).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.