Podcast
Questions and Answers
What two primary structures are affected by an iliac crest contusion?
What two primary structures are affected by an iliac crest contusion?
The musculature in the area (especially the abdominal wall and gluteus medius) and the iliac crest.
What is meralgia paraesthetica and how is it related to an iliac crest contusion?
What is meralgia paraesthetica and how is it related to an iliac crest contusion?
Meralgia paraesthetica is the compression of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, which can occur secondary to an iliac crest contusion.
In which sports is an iliac crest contusion most frequently seen?
In which sports is an iliac crest contusion most frequently seen?
Iliac crest contusions are most frequently seen in sports such as volleyball and diving.
What symptom would lead you to suspect an iliac crest fracture rather than a contusion?
What symptom would lead you to suspect an iliac crest fracture rather than a contusion?
What factors may aggravate the pain associated with an iliac crest contusion?
What factors may aggravate the pain associated with an iliac crest contusion?
What are the potential complications one might encounter due to a hip pointer injury?
What are the potential complications one might encounter due to a hip pointer injury?
In what specific movements might a person with an iliac crest contusion experience enhanced pain?
In what specific movements might a person with an iliac crest contusion experience enhanced pain?
Why might someone suspect an iliac crest fracture instead of a contusion when symptoms are similar?
Why might someone suspect an iliac crest fracture instead of a contusion when symptoms are similar?
What is the impact of an iliac crest contusion on an athlete’s ability to perform in sports like volleyball?
What is the impact of an iliac crest contusion on an athlete’s ability to perform in sports like volleyball?
Identify the primary impact on musculature due to an iliac crest contusion.
Identify the primary impact on musculature due to an iliac crest contusion.
Which condition is commonly associated with an iliac crest contusion?
Which condition is commonly associated with an iliac crest contusion?
Pain referred from meralgia paraesthetica is localized to the medial thigh.
Pain referred from meralgia paraesthetica is localized to the medial thigh.
Name one muscle that would be most affected by an iliac crest contusion.
Name one muscle that would be most affected by an iliac crest contusion.
An iliac crest contusion is primarily seen in the sport of __________.
An iliac crest contusion is primarily seen in the sport of __________.
Match the following symptoms with their respective conditions:
Match the following symptoms with their respective conditions:
What is the most common region of the body for avulsion fractures?
What is the most common region of the body for avulsion fractures?
Name three specific locations where avulsion fractures can occur.
Name three specific locations where avulsion fractures can occur.
What is the primary mechanism of injury (MOI) for avulsion fractures in skeletally immature individuals?
What is the primary mechanism of injury (MOI) for avulsion fractures in skeletally immature individuals?
What other injury mechanism is synonymous with an avulsion fracture?
What other injury mechanism is synonymous with an avulsion fracture?
In which population are avulsion fractures most frequently seen and why?
In which population are avulsion fractures most frequently seen and why?
What are the common symptoms experienced with an avulsion fracture?
What are the common symptoms experienced with an avulsion fracture?
When is strength and function most diminished after an avulsion fracture?
When is strength and function most diminished after an avulsion fracture?
How would you describe the gait of a person with an avulsion fracture?
How would you describe the gait of a person with an avulsion fracture?
Are avulsion fractures ruled out in older populations?
Are avulsion fractures ruled out in older populations?
How are avulsion fractures and muscle ruptures treated?
How are avulsion fractures and muscle ruptures treated?
What are the 7 potential sites in the body where avulsion fractures can occur?
What are the 7 potential sites in the body where avulsion fractures can occur?
Explain why skeletally immature individuals are more prone to avulsion fractures.
Explain why skeletally immature individuals are more prone to avulsion fractures.
Describe the mechanism of injury (MOI) leading to an avulsion fracture.
Describe the mechanism of injury (MOI) leading to an avulsion fracture.
What are the common symptoms associated with avulsion fractures?
What are the common symptoms associated with avulsion fractures?
Why is palpation not very useful in diagnosing an avulsion fracture?
Why is palpation not very useful in diagnosing an avulsion fracture?
How does the gait change in individuals with avulsion fractures?
How does the gait change in individuals with avulsion fractures?
In what way are avulsion fractures and muscle ruptures treated?
In what way are avulsion fractures and muscle ruptures treated?
What role does nighttime play in the pain characteristics of avulsion fractures?
What role does nighttime play in the pain characteristics of avulsion fractures?
What is an apophysis?
What is an apophysis?
Is it possible to find avulsion fractures in older populations, and why?
Is it possible to find avulsion fractures in older populations, and why?
What is the most common region of the body where avulsion fractures occur?
What is the most common region of the body where avulsion fractures occur?
Avulsion fractures can only occur in skeletally mature individuals.
Avulsion fractures can only occur in skeletally mature individuals.
Name two common symptoms associated with avulsion fractures.
Name two common symptoms associated with avulsion fractures.
An avulsion fracture is described as the _______ away of the bony attachment of a ligament or tendon.
An avulsion fracture is described as the _______ away of the bony attachment of a ligament or tendon.
Match the following structures with their location related to avulsion fractures:
Match the following structures with their location related to avulsion fractures:
What is a primary reason why avulsion fractures are more common in younger individuals?
What is a primary reason why avulsion fractures are more common in younger individuals?
Palpation is a highly effective method to diagnose an avulsion fracture.
Palpation is a highly effective method to diagnose an avulsion fracture.
What type of pain characteristics do patients with avulsion fractures typically report?
What type of pain characteristics do patients with avulsion fractures typically report?
The mechanism of injury for avulsion fractures can involve a sudden change of _______.
The mechanism of injury for avulsion fractures can involve a sudden change of _______.
Which of the following best describes the treatment for avulsion fractures?
Which of the following best describes the treatment for avulsion fractures?
What is apophysitis and which age group is it most commonly associated with?
What is apophysitis and which age group is it most commonly associated with?
List two specific locations where apophysitis is frequently found.
List two specific locations where apophysitis is frequently found.
What pain characteristics are typically described by individuals suffering from apophysitis?
What pain characteristics are typically described by individuals suffering from apophysitis?
How can apophysitis occasionally be asymptomatic, and in what context does this occur?
How can apophysitis occasionally be asymptomatic, and in what context does this occur?
Which well-known type of apophysitis is not associated with the hip region?
Which well-known type of apophysitis is not associated with the hip region?
What role does muscle tightness play in the development of apophysitis during growth spurts?
What role does muscle tightness play in the development of apophysitis during growth spurts?
What two key factors differentiate apophysitis from avulsion fractures?
What two key factors differentiate apophysitis from avulsion fractures?
In what manner can the deformity associated with apophysitis manifest in individuals?
In what manner can the deformity associated with apophysitis manifest in individuals?
What is the primary factor that limits the level of function (LOF) in individuals with apophysitis?
What is the primary factor that limits the level of function (LOF) in individuals with apophysitis?
What distinguishes the mechanism of injury (MOI) for apophysitis from that of an avulsion fracture?
What distinguishes the mechanism of injury (MOI) for apophysitis from that of an avulsion fracture?
Why is apophysitis exclusively observed in skeletally immature athletes?
Why is apophysitis exclusively observed in skeletally immature athletes?
How does muscle tightness contribute to the development of apophysitis during growth spurts?
How does muscle tightness contribute to the development of apophysitis during growth spurts?
What are the two key characteristics differentiating apophysitis symptoms from symptoms of an avulsion fracture?
What are the two key characteristics differentiating apophysitis symptoms from symptoms of an avulsion fracture?
In what way can apophysitis be asymptomatic in certain individuals?
In what way can apophysitis be asymptomatic in certain individuals?
What condition is considered the most well-known type of apophysitis outside the hip region?
What condition is considered the most well-known type of apophysitis outside the hip region?
What role does pain play in the limitation of function (LOF) in individuals with apophysitis?
What role does pain play in the limitation of function (LOF) in individuals with apophysitis?
How does the bony development from apophysitis manifest over time?
How does the bony development from apophysitis manifest over time?
What types of activities are likely to aggravate the pain associated with apophysitis?
What types of activities are likely to aggravate the pain associated with apophysitis?
Which of the following locations is NOT commonly associated with apophysitis?
Which of the following locations is NOT commonly associated with apophysitis?
Apophysitis can only occur in skeletally mature individuals.
Apophysitis can only occur in skeletally mature individuals.
What is the primary characteristic of pain experienced with apophysitis?
What is the primary characteristic of pain experienced with apophysitis?
The most well-known type of apophysitis, which is not located in the hip, is called __________.
The most well-known type of apophysitis, which is not located in the hip, is called __________.
Match the following locations with their relation to apophysitis:
Match the following locations with their relation to apophysitis:
It is not possible for apophysitis to be asymptomatic.
It is not possible for apophysitis to be asymptomatic.
What is the primary cause of apophysitis in athletes?
What is the primary cause of apophysitis in athletes?
Pain in apophysitis is commonly aggravated by __________.
Pain in apophysitis is commonly aggravated by __________.
What activity is most commonly associated with osteitis pubis in females?
What activity is most commonly associated with osteitis pubis in females?
What is one key characteristic that helps differentiate osteitis pubis from adductor strain and pubic symphysis sprain?
What is one key characteristic that helps differentiate osteitis pubis from adductor strain and pubic symphysis sprain?
Which populations are most affected by osteitis pubis?
Which populations are most affected by osteitis pubis?
Name two sports that commonly involve osteitis pubis due to the nature of their physical demands.
Name two sports that commonly involve osteitis pubis due to the nature of their physical demands.
What specific symptoms can indicate osteitis pubis related to mobility limitations?
What specific symptoms can indicate osteitis pubis related to mobility limitations?
What activity is osteitis pubis commonly associated with in females?
What activity is osteitis pubis commonly associated with in females?
Name two conditions that osteitis pubis closely mimics.
Name two conditions that osteitis pubis closely mimics.
How can you differentiate osteitis pubis from an adductor strain or pubic symphysis sprain?
How can you differentiate osteitis pubis from an adductor strain or pubic symphysis sprain?
Which sports are notably linked with the occurrence of osteitis pubis?
Which sports are notably linked with the occurrence of osteitis pubis?
What specific symptoms are typically observed in a person with osteitis pubis?
What specific symptoms are typically observed in a person with osteitis pubis?
Which of the following conditions does osteitis pubis mimic?
Which of the following conditions does osteitis pubis mimic?
Osteitis pubis is most commonly associated with high-impact sports like basketball and football.
Osteitis pubis is most commonly associated with high-impact sports like basketball and football.
What is the primary population affected by osteitis pubis?
What is the primary population affected by osteitis pubis?
Osteitis pubis is characterized by chronic __________ in nature.
Osteitis pubis is characterized by chronic __________ in nature.
Match the symptoms of osteitis pubis with their descriptions:
Match the symptoms of osteitis pubis with their descriptions:
Which population is most commonly affected by femoral neck stress fractures?
Which population is most commonly affected by femoral neck stress fractures?
Femoral neck stress fractures are often easy to locate due to their superficial position.
Femoral neck stress fractures are often easy to locate due to their superficial position.
What is the primary pain quality experienced with femoral neck stress fractures?
What is the primary pain quality experienced with femoral neck stress fractures?
Femoral neck stress fractures tend to aggravate during _________________.
Femoral neck stress fractures tend to aggravate during _________________.
Match the following characteristics with their relevance to femoral neck stress fractures:
Match the following characteristics with their relevance to femoral neck stress fractures:
At what time of day are stress fractures typically most bothersome?
At what time of day are stress fractures typically most bothersome?
All movements will be painful for someone with a femoral neck stress fracture.
All movements will be painful for someone with a femoral neck stress fracture.
What are the three key factors that contribute to the diagnosis of a stress fracture?
What are the three key factors that contribute to the diagnosis of a stress fracture?
The symptom of pain from a femoral neck stress fracture is exacerbated after ___________ ceases.
The symptom of pain from a femoral neck stress fracture is exacerbated after ___________ ceases.
Why do femoral neck stress fractures often present with deep aching pain?
Why do femoral neck stress fractures often present with deep aching pain?
At what time of day are stress fractures most bothersome, and why?
At what time of day are stress fractures most bothersome, and why?
What are the three key factors associated with the risk of developing a stress fracture?
What are the three key factors associated with the risk of developing a stress fracture?
How is range of motion (ROM) affected by a femoral neck stress fracture?
How is range of motion (ROM) affected by a femoral neck stress fracture?
Why are femoral neck stress fractures challenging to diagnose?
Why are femoral neck stress fractures challenging to diagnose?
Which specific movements most exacerbate the pain associated with a femoral neck stress fracture?
Which specific movements most exacerbate the pain associated with a femoral neck stress fracture?
In assessing a potential stress fracture, what could a positive active straight leg raise indicate?
In assessing a potential stress fracture, what could a positive active straight leg raise indicate?
What role does increased training load have on the development of stress fractures?
What role does increased training load have on the development of stress fractures?
What population is particularly prone to femoral neck stress fractures and why?
What population is particularly prone to femoral neck stress fractures and why?
Why do femoral neck stress fractures often go unnoticed initially?
Why do femoral neck stress fractures often go unnoticed initially?
At what time of day are stress fractures most bothersome, and what is the reason for this?
At what time of day are stress fractures most bothersome, and what is the reason for this?
What are the main movements that may be limited or painful in a femoral neck stress fracture?
What are the main movements that may be limited or painful in a femoral neck stress fracture?
What are the three key factors to consider when assessing an athlete with a stress fracture?
What are the three key factors to consider when assessing an athlete with a stress fracture?
How does the active straight leg raise test relate to femoral neck stress fractures?
How does the active straight leg raise test relate to femoral neck stress fractures?
What type of pain is typically associated with femoral neck stress fractures?
What type of pain is typically associated with femoral neck stress fractures?
What factors contribute to the aggravation of pain in a femoral neck stress fracture?
What factors contribute to the aggravation of pain in a femoral neck stress fracture?
What role does the fulcrum test play in the assessment of femoral neck stress fractures?
What role does the fulcrum test play in the assessment of femoral neck stress fractures?
What are the three types of femoral acetabular impingement (FAI)?
What are the three types of femoral acetabular impingement (FAI)?
What is required to confirm the presence of FAI?
What is required to confirm the presence of FAI?
What movement pattern is a primary predictor for early presentations of FAI?
What movement pattern is a primary predictor for early presentations of FAI?
Can FAI be asymptomatic, and if so, to what extent?
Can FAI be asymptomatic, and if so, to what extent?
What are two factors associated with the developmental form of FAI?
What are two factors associated with the developmental form of FAI?
What type of FAI is considered extremely problematic?
What type of FAI is considered extremely problematic?
What conditions might FAI present as?
What conditions might FAI present as?
What is often aggravated by activity or prolonged sitting in individuals with FAI?
What is often aggravated by activity or prolonged sitting in individuals with FAI?
What is a secondary predictor for presenting with FAI?
What is a secondary predictor for presenting with FAI?
In which individuals should FAI be evaluated?
In which individuals should FAI be evaluated?
Which type of FAI is considered extremely problematic and why?
Which type of FAI is considered extremely problematic and why?
What are the necessary steps to confirm the presence of FAI?
What are the necessary steps to confirm the presence of FAI?
How can FAI be asymptomatic and what should be considered in such cases?
How can FAI be asymptomatic and what should be considered in such cases?
What is the main predictor for early presentations of FAI?
What is the main predictor for early presentations of FAI?
What secondary factor can be associated with FAI, and how does it differ from the main predictor?
What secondary factor can be associated with FAI, and how does it differ from the main predictor?
Name two factors that can be associated with the developmental form of FAI.
Name two factors that can be associated with the developmental form of FAI.
What are the four conditions that may present alongside FAI?
What are the four conditions that may present alongside FAI?
What movements are painful with FAI determined by?
What movements are painful with FAI determined by?
Which of the following types of femoral acetabular impingement (FAI) is characterized by an abnormally shaped femoral head?
Which of the following types of femoral acetabular impingement (FAI) is characterized by an abnormally shaped femoral head?
FAI is solely a congenital condition.
FAI is solely a congenital condition.
What is the primary predictor for early presentations of femoral acetabular impingement?
What is the primary predictor for early presentations of femoral acetabular impingement?
Femoral acetabular impingement can be confirmed through __________.
Femoral acetabular impingement can be confirmed through __________.
Match the following conditions that may present with FAI:
Match the following conditions that may present with FAI:
Individuals with FAI can be asymptomatic.
Individuals with FAI can be asymptomatic.
List one factor that is associated with the developmental form of femoral acetabular impingement.
List one factor that is associated with the developmental form of femoral acetabular impingement.
Painful movements with FAI are determined by where the __________ is.
Painful movements with FAI are determined by where the __________ is.
Match the symptoms related to FAI with their descriptions:
Match the symptoms related to FAI with their descriptions:
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for osteoarthritis (OA)?
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for osteoarthritis (OA)?
Femoral acetabular impingement (FAI) typically presents with symptoms similar to those of osteoarthritis.
Femoral acetabular impingement (FAI) typically presents with symptoms similar to those of osteoarthritis.
What is a hallmark sign of hip osteoarthritis?
What is a hallmark sign of hip osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is characterized by degenerative changes at the acetabulum and/or ________ head.
Osteoarthritis is characterized by degenerative changes at the acetabulum and/or ________ head.
Match the hip conditions with their descriptions:
Match the hip conditions with their descriptions:
What is the typical pain characteristic associated with hip osteoarthritis?
What is the typical pain characteristic associated with hip osteoarthritis?
Early morning stiffness is commonly reported by individuals with osteoarthritis.
Early morning stiffness is commonly reported by individuals with osteoarthritis.
How many accessory movements would typically be reduced in an individual with osteoarthritis?
How many accessory movements would typically be reduced in an individual with osteoarthritis?
In osteoarthritis, the main difference compared to femoral acetabular impingement is that OA affects the ________ of the joint.
In osteoarthritis, the main difference compared to femoral acetabular impingement is that OA affects the ________ of the joint.
What phenomenon might individuals with femoral acetabular impingement experience?
What phenomenon might individuals with femoral acetabular impingement experience?
What are the five main risk factors associated with osteoarthritis (OA)?
What are the five main risk factors associated with osteoarthritis (OA)?
Name the four hip conditions that are risk factors for developing osteoarthritis.
Name the four hip conditions that are risk factors for developing osteoarthritis.
Identify another condition that could present with similar signs to hip OA, but to a lesser extent.
Identify another condition that could present with similar signs to hip OA, but to a lesser extent.
What abnormal sensations are commonly reported with femoral acetabular impingement?
What abnormal sensations are commonly reported with femoral acetabular impingement?
During which times of day is hip osteoarthritis typically most aggravating?
During which times of day is hip osteoarthritis typically most aggravating?
How does the main difference between OA and femoral acetabular impingement relate to pain sensation during motion restriction?
How does the main difference between OA and femoral acetabular impingement relate to pain sensation during motion restriction?
What imaging is ultimately necessary to determine whether an individual has osteoarthritis or femoral acetabular impingement?
What imaging is ultimately necessary to determine whether an individual has osteoarthritis or femoral acetabular impingement?
How many of the accessory movements would be reduced in an individual with osteoarthritis?
How many of the accessory movements would be reduced in an individual with osteoarthritis?
What is the underlying issue that commonalities between other forms of arthritis and spondylosis share?
What is the underlying issue that commonalities between other forms of arthritis and spondylosis share?
Name four hip conditions that act as risk factors for osteoarthritis.
Name four hip conditions that act as risk factors for osteoarthritis.
Which condition can present with the same hallmark sign as hip OA but to a lesser extent?
Which condition can present with the same hallmark sign as hip OA but to a lesser extent?
What are three abnormal sensations commonly associated with femoral acetabular impingement?
What are three abnormal sensations commonly associated with femoral acetabular impingement?
At what times of the day is osteoarthritis pain typically most aggravating?
At what times of the day is osteoarthritis pain typically most aggravating?
What is the main difference between osteoarthritis and femoral acetabular impingement?
What is the main difference between osteoarthritis and femoral acetabular impingement?
What diagnostic method is ultimately required to differentiate between osteoarthritis and femoral acetabular impingement?
What diagnostic method is ultimately required to differentiate between osteoarthritis and femoral acetabular impingement?
What is the earliest joint where osteoarthritis is likely to occur?
What is the earliest joint where osteoarthritis is likely to occur?
Which joint injury is similar to a hip labral tear?
Which joint injury is similar to a hip labral tear?
Between the shoulder and hip, which is more prone to dislocations?
Between the shoulder and hip, which is more prone to dislocations?
What are two acute mechanisms of injury (MOI) associated with labral tears?
What are two acute mechanisms of injury (MOI) associated with labral tears?
Is a labral tear more commonly due to acute or chronic mechanisms of injury?
Is a labral tear more commonly due to acute or chronic mechanisms of injury?
What are four common sensations experienced with a labral tear?
What are four common sensations experienced with a labral tear?
What two structural pathologies are associated with labral tears?
What two structural pathologies are associated with labral tears?
Which part of the labrum is most commonly injured in a labral tear?
Which part of the labrum is most commonly injured in a labral tear?
What is typically the most painful and restrictive movement associated with a labral tear?
What is typically the most painful and restrictive movement associated with a labral tear?
During a scouring test, what end feel would indicate a labral tear?
During a scouring test, what end feel would indicate a labral tear?
Why might a labral tear lead to a feeling of instability in the hip joint?
Why might a labral tear lead to a feeling of instability in the hip joint?
What type of joint injury has a similar mechanism of injury (MOI) to a hip labral tear?
What type of joint injury has a similar mechanism of injury (MOI) to a hip labral tear?
Are hip dislocations more common than shoulder dislocations?
Are hip dislocations more common than shoulder dislocations?
What two acute injuries share a similar mechanism of injury with a labral tear?
What two acute injuries share a similar mechanism of injury with a labral tear?
What is the primary likelihood of a labral tear occurring in terms of mechanism of injury?
What is the primary likelihood of a labral tear occurring in terms of mechanism of injury?
Name one structural pathology associated with a hip labral tear.
Name one structural pathology associated with a hip labral tear.
What sensation is typically experienced during a hip labral tear?
What sensation is typically experienced during a hip labral tear?
What is the most commonly injured aspect of the labrum in a labral tear?
What is the most commonly injured aspect of the labrum in a labral tear?
Which type of end feel characterizes a labral tear during joint assessments?
Which type of end feel characterizes a labral tear during joint assessments?
What typical movement is considered the most painful with a labral tear?
What typical movement is considered the most painful with a labral tear?
What is the effect of a labral tear on active range of motion (AROM) and passive range of motion (PROM)?
What is the effect of a labral tear on active range of motion (AROM) and passive range of motion (PROM)?
Which joint injuries have a similar mechanism of injury (MOI) to a hip labral tear?
Which joint injuries have a similar mechanism of injury (MOI) to a hip labral tear?
Chronic mechanisms of injury are more likely to cause a hip labral tear than acute mechanisms.
Chronic mechanisms of injury are more likely to cause a hip labral tear than acute mechanisms.
What are the four main sensations experienced with a labral tear of the hip?
What are the four main sensations experienced with a labral tear of the hip?
The aspect of the labrum that is most commonly injured is the _______.
The aspect of the labrum that is most commonly injured is the _______.
Which of these pathologies is NOT associated with a labral tear?
Which of these pathologies is NOT associated with a labral tear?
Match the following conditions with their respective characteristics:
Match the following conditions with their respective characteristics:
What factor can be key in differentiating a labral tear from osteoarthritis during an assessment?
What factor can be key in differentiating a labral tear from osteoarthritis during an assessment?
A labral tear will restrict both active range of motion (AROM) and passive range of motion (PROM) equally.
A labral tear will restrict both active range of motion (AROM) and passive range of motion (PROM) equally.
The four main risk factors for a labral tear include structural pathologies, degeneration, and _______.
The four main risk factors for a labral tear include structural pathologies, degeneration, and _______.
What is the most painful and restrictive movement associated with a labral tear?
What is the most painful and restrictive movement associated with a labral tear?
What are the two activities most aggravated with a hip sprain?
What are the two activities most aggravated with a hip sprain?
Hip sprains typically present with noticeable swelling that can easily be observed.
Hip sprains typically present with noticeable swelling that can easily be observed.
What two hip movements are most aggravated with a hip sprain?
What two hip movements are most aggravated with a hip sprain?
The most common mechanism of injury (MOI) for a hip sprain is trunk __________ of a fixed limb.
The most common mechanism of injury (MOI) for a hip sprain is trunk __________ of a fixed limb.
Match the symptoms of a hip sprain with their descriptions:
Match the symptoms of a hip sprain with their descriptions:
What are the two primary hip movements that are most aggravated during a hip sprain?
What are the two primary hip movements that are most aggravated during a hip sprain?
Describe why hip sprains are considered deeper injuries rather than superficial.
Describe why hip sprains are considered deeper injuries rather than superficial.
Identify two activities that are most likely to aggravate a hip sprain.
Identify two activities that are most likely to aggravate a hip sprain.
What is the most common mechanism of injury (MOI) leading to a hip sprain?
What is the most common mechanism of injury (MOI) leading to a hip sprain?
Discuss the typical presentation of swelling in a hip sprain.
Discuss the typical presentation of swelling in a hip sprain.
What are the primary activities and hip movements that are aggravated by a hip sprain?
What are the primary activities and hip movements that are aggravated by a hip sprain?
How common are hip sprains and what is the most common mechanism of injury associated with them?
How common are hip sprains and what is the most common mechanism of injury associated with them?
In terms of symptoms, would a hip sprain typically present with superficial or deep pain?
In terms of symptoms, would a hip sprain typically present with superficial or deep pain?
Is swelling a common symptom in hip sprains, and if so, how noticeable is it?
Is swelling a common symptom in hip sprains, and if so, how noticeable is it?
What are the potential challenges in assessing the presence of swelling in a hip sprain?
What are the potential challenges in assessing the presence of swelling in a hip sprain?
Flashcards
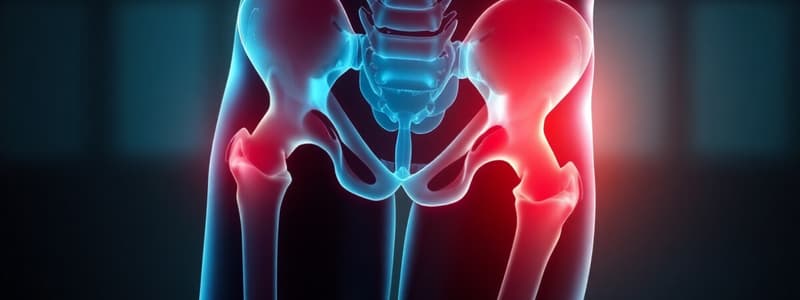
Iliac crest contusion (hip pointer)
Iliac crest contusion (hip pointer)
A bruise to the iliac crest (hip bone).
Affected structures in a hip pointer
Affected structures in a hip pointer
Muscles (like abdominal wall & gluteus medius) and the iliac crest itself can be affected.
Meralgia paraesthetica
Meralgia paraesthetica
Nerve compression causing pain in the outer thigh due to compression of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.
Pain referral in meralgia paraesthetica
Pain referral in meralgia paraesthetica
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iliac crest fracture vs. contusion
Iliac crest fracture vs. contusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pointer: Structures Affected
Hip Pointer: Structures Affected
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Muscle Affected in Hip Pointer
Common Muscle Affected in Hip Pointer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meralgia Paraesthetica: What Is It?
Meralgia Paraesthetica: What Is It?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pointer: What Aggravates Pain?
Hip Pointer: What Aggravates Pain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pointer vs. Fracture: How To Tell
Hip Pointer vs. Fracture: How To Tell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pointer: Where Does it Hurt?
Hip Pointer: Where Does it Hurt?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pointer: What Muscles are Affected?
Hip Pointer: What Muscles are Affected?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pointer: What Aggravates the Pain?
Hip Pointer: What Aggravates the Pain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture
Avulsion Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Avulsion Fracture Sites
Common Avulsion Fracture Sites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture in Children
Avulsion Fracture in Children
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture Mechanism of Injury
Avulsion Fracture Mechanism of Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture vs. Tendon Rupture
Avulsion Fracture vs. Tendon Rupture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture Pain
Avulsion Fracture Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture Diagnosis
Avulsion Fracture Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture Treatment
Avulsion Fracture Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis
Apophysitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis Significance
Apophysitis Significance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture in Young Athletes
Avulsion Fracture in Young Athletes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanism of Avulsion Fracture
Mechanism of Avulsion Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis and Sport
Apophysitis and Sport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment of Avulsion Fracture
Treatment of Avulsion Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture in Older Adults
Avulsion Fracture in Older Adults
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture Treatment vs. Muscle/Tendon Rupture Treatment
Avulsion Fracture Treatment vs. Muscle/Tendon Rupture Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is apophysitis?
What is apophysitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is apophysitis most common?
Where is apophysitis most common?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes apophysitis?
What causes apophysitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's a well-known type of apophysitis?
What's a well-known type of apophysitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who gets apophysitis?
Who gets apophysitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the symptoms of apophysitis?
What are the symptoms of apophysitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can apophysitis be asymptomatic?
How can apophysitis be asymptomatic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is apophysitis different from an avulsion fracture?
How is apophysitis different from an avulsion fracture?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What aggravates apophysitis?
What aggravates apophysitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Apophysitis Locations
Common Apophysitis Locations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis Cause
Apophysitis Cause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osgood-Schlatter's Disease
Osgood-Schlatter's Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis Symptoms
Apophysitis Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asymptomatic Apophysitis
Asymptomatic Apophysitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis vs. Avulsion Fracture
Apophysitis vs. Avulsion Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis Aggravating Factors
Apophysitis Aggravating Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Description in Apophysitis
Pain Description in Apophysitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apophysitis in Athletes
Apophysitis in Athletes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteitis Pubis
Osteitis Pubis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteitis Pubis in Females
Osteitis Pubis in Females
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteitis Pubis vs. Adductor Strain
Osteitis Pubis vs. Adductor Strain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteitis Pubis vs. Pubic Symphysis Sprain
Osteitis Pubis vs. Pubic Symphysis Sprain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteitis Pubis: Limited Mobility
Osteitis Pubis: Limited Mobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Osteitis Pubis?
What is Osteitis Pubis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who gets Osteitis Pubis?
Who gets Osteitis Pubis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the symptoms of Osteitis Pubis?
What are the symptoms of Osteitis Pubis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is Osteitis Pubis different from Adductor Strain?
How is Osteitis Pubis different from Adductor Strain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is Osteitis Pubis different from Pubic Symphysis Sprain?
How is Osteitis Pubis different from Pubic Symphysis Sprain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Osteitis Pubis
Symptoms of Osteitis Pubis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Who?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Who?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Pain?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Pain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Why Night Pain?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Why Night Pain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Hard to Locate?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Hard to Locate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: ROM Impact?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: ROM Impact?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Key Factors
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Key Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stress Fracture: Active Straight Leg Raise
Stress Fracture: Active Straight Leg Raise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fulcrum: Definition
Fulcrum: Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Joint Play: Superior Glide
Joint Play: Superior Glide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: What's the Pain Like?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: What's the Pain Like?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Why Worse at Night?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Why Worse at Night?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Why Hard to Find?
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Why Hard to Find?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Key Factors to Consider
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture: Key Factors to Consider
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stress Fracture: Active Straight Leg Raise Test
Stress Fracture: Active Straight Leg Raise Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fulcrum: What is it?
Fulcrum: What is it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain in Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Pain in Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Night Pain in Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Night Pain in Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Hard to Find?
Why are Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Hard to Find?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What Limits Range of Motion (ROM) with Femoral Neck Stress Fracture?
What Limits Range of Motion (ROM) with Femoral Neck Stress Fracture?
Signup and view all the flashcards
3 Key Factors to Diagnose Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
3 Key Factors to Diagnose Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Active Straight Leg Raise Test
Positive Active Straight Leg Raise Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fulcrum
Fulcrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Acetabular Impingement (FAI)
Femoral Acetabular Impingement (FAI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of FAI
Types of FAI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Most Problematic FAI Type
Most Problematic FAI Type
Signup and view all the flashcards
FAI: Congenital or Developmental?
FAI: Congenital or Developmental?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When to Evaluate for FAI
When to Evaluate for FAI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Confirming FAI
Confirming FAI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of FAI
Symptoms of FAI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Painful Movements in FAI
Painful Movements in FAI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Other Conditions FAI Can Mimic
Other Conditions FAI Can Mimic
Signup and view all the flashcards
FAI: Pelvic Tilt Impact
FAI: Pelvic Tilt Impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
What makes Mixed FAI problematic?
What makes Mixed FAI problematic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Is FAI congenital or developmental?
Is FAI congenital or developmental?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Who should be evaluated for FAI?
Who should be evaluated for FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is FAI confirmed?
How is FAI confirmed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some common symptoms of FAI?
What are some common symptoms of FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What other conditions can FAI mimic?
What other conditions can FAI mimic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does pelvic tilt affect FAI?
How does pelvic tilt affect FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Can FAI be asymptomatic?
Can FAI be asymptomatic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pelvic Tilt and FAI
Pelvic Tilt and FAI
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
What is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are 5 risk factors for OA?
What are 5 risk factors for OA?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What 4 hip conditions can increase OA risk?
What 4 hip conditions can increase OA risk?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the hallmark sign of hip OA?
What is the hallmark sign of hip OA?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Femoral Acetabular Impingement (FAI)?
What is Femoral Acetabular Impingement (FAI)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are 3 abnormal sensations common with FAI?
What are 3 abnormal sensations common with FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main difference between OA and FAI?
What is the main difference between OA and FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is common between OA, FAI, and other arthritis?
What is common between OA, FAI, and other arthritis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Does OA occur earlier at the hip compared to other joints?
Does OA occur earlier at the hip compared to other joints?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is needed to distinguish between OA and FAI?
What is needed to distinguish between OA and FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip OA Risk Factors
Hip OA Risk Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallmark Sign of Hip OA
Hallmark Sign of Hip OA
Signup and view all the flashcards
FAI Abnormal Sensations
FAI Abnormal Sensations
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA vs. FAI: Main Difference
OA vs. FAI: Main Difference
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA Commonality With Other Arthritis
OA Commonality With Other Arthritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA Earliest Joint
OA Earliest Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA vs. FAI: Motion Restriction
OA vs. FAI: Motion Restriction
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA vs. FAI: Diagnosis
OA vs. FAI: Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Conditions and OA Risk
Hip Conditions and OA Risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
FAI - Similar to OA
FAI - Similar to OA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Early Morning and Night Pain
Early Morning and Night Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common FAI Sensations
Common FAI Sensations
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA - Stiffness and Weakness
OA - Stiffness and Weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA and FAI - Imaging
OA and FAI - Imaging
Signup and view all the flashcards
OA - Reduced Accessory Movements
OA - Reduced Accessory Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a hip labral tear?
What is a hip labral tear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main sensations felt with a hip labral tear?
What are the main sensations felt with a hip labral tear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What movements are restricted with a labral tear?
What movements are restricted with a labral tear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the most painful and restrictive movement with a labral tear?
What is the most painful and restrictive movement with a labral tear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is a labral tear different from osteoarthritis?
How is a labral tear different from osteoarthritis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the 3 main risk factors for a labral tear?
What are the 3 main risk factors for a labral tear?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hip FAI (Femoral Acetabular Impingement)?
What is hip FAI (Femoral Acetabular Impingement)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the types of FAI?
What are the types of FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the most problematic type of FAI?
What is the most problematic type of FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the symptoms of FAI?
What are the symptoms of FAI?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Labral Tear: Similar Injury?
Hip Labral Tear: Similar Injury?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Dislocation: Common or Rare?
Hip Dislocation: Common or Rare?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Acute or Chronic Injury?
Labral Tear: Acute or Chronic Injury?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: What's the Pain?
Labral Tear: What's the Pain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Movement Limitation?
Labral Tear: Movement Limitation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: End Feel?
Labral Tear: End Feel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Commonly Injured Area?
Labral Tear: Commonly Injured Area?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Instability: Why?
Hip Instability: Why?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Pain: What Conditions Can Cause It?
Hip Pain: What Conditions Can Cause It?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structural Factors for Hip Labral Tears?
Structural Factors for Hip Labral Tears?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Acute vs. Chronic?
Labral Tear: Acute vs. Chronic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Dislocation: Associated Injuries
Hip Dislocation: Associated Injuries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Main Sensations
Labral Tear: Main Sensations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear Impact on Motion
Labral Tear Impact on Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Diagnostic Movements?
Labral Tear: Diagnostic Movements?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: End Feel Assessment
Labral Tear: End Feel Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Instability: Intra-articular Causes
Hip Instability: Intra-articular Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labral Tear: Most Affected Location
Labral Tear: Most Affected Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Common Mechanism
Hip Sprain: Common Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Aggravating Activities
Hip Sprain: Aggravating Activities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Aggravating Movements
Hip Sprain: Aggravating Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Location of Pain
Hip Sprain: Location of Pain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Joint Play
Hip Sprain: Joint Play
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the most common hip sprain MOIs?
What are the most common hip sprain MOIs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What activities are most aggravated by a hip sprain?
What activities are most aggravated by a hip sprain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What hip movements are most aggravated by a hip sprain?
What hip movements are most aggravated by a hip sprain?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Would a hip sprain be deep or superficial?
Would a hip sprain be deep or superficial?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Does a hip sprain present with swelling?
Does a hip sprain present with swelling?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Common MOI
Hip Sprain: Common MOI
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Most Aggravated Motions
Hip Sprain: Most Aggravated Motions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Sprain: Joint Play Assessment
Hip Sprain: Joint Play Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Iliac Crest Contusion (Hip Pointer)
-
Primary Affected Structures:
- Abdominal wall musculature
- Gluteus medius muscle
- Iliac crest
-
Most Affected Muscles:
- Abdominal wall
- Gluteus medius
-
Associated Condition: Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury (or lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh) - can be secondary to a hip pointer
-
Meralgia Paraesthetica:
- Condition describing compression of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- Results in pain in the proximal distribution of the nerve.
-
Mechanism of Injury:
- Direct blow or fall, like diving or landing
-
Pain Characteristics:
- Often disproportionate to the visible injury; bone is well-innervated
- Aggravated by coughing, sneezing, or bearing down
-
Other Symptoms:
- Swelling (possibly with ecchymosis)
- Discoloration (bruising)
- Loss of function (LOF)
-
Common Sports:
- Volleyball
- Diving
- Landing activities
-
Mimicking Condition: Iliac crest fracture
-
Distinguishing Factor (Iliac Crest Fracture vs. Contusion): Presence of crepitus (a grating sound or feeling) strongly suggests a fracture.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.