Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term for the process of urination?
What is the term for the process of urination?
- Micturition (correct)
- Urination
- Dehydration
- Diuresis
Where does the urine first collect from the collecting tubules?
Where does the urine first collect from the collecting tubules?
- Nephrons
- Renal calyx (correct)
- Renal medulla
- Renal cortex
What is the function of the valves in the ureters?
What is the function of the valves in the ureters?
- To enhance kidney function
- To prevent backflow of urine (correct)
- To regulate blood pressure
- To increase urine concentration
What is the direction of urine flow in the ureters?
What is the direction of urine flow in the ureters?
What is the name of the tube that connects the kidney to the bladder?
What is the name of the tube that connects the kidney to the bladder?
What is the term for the muscular tube that allows urine to exit the body?
What is the term for the muscular tube that allows urine to exit the body?
What is the name of the part of the kidney where the renal calyces coalesce?
What is the name of the part of the kidney where the renal calyces coalesce?
What happens if urine flows backwards in the ureters?
What happens if urine flows backwards in the ureters?
What type of epithelium lines the bladder?
What type of epithelium lines the bladder?
What is the function of the internal urethral sphincter?
What is the function of the internal urethral sphincter?
What is the term for the urine stream flowing from the ureters into the bladder?
What is the term for the urine stream flowing from the ureters into the bladder?
How much urine can the bladder hold?
How much urine can the bladder hold?
What type of muscle is the internal urethral sphincter?
What type of muscle is the internal urethral sphincter?
What is the name of the structure that conducts urine from the bladder to the outside world?
What is the name of the structure that conducts urine from the bladder to the outside world?
What is the main difference in the path from the bladder to the bathroom between men and women?
What is the main difference in the path from the bladder to the bathroom between men and women?
Where do the ureters conduct urine?
Where do the ureters conduct urine?
What does the transitional epithelium allow the bladder to do?
What does the transitional epithelium allow the bladder to do?
What is the name of the muscle that controls the flow of urine from the bladder?
What is the name of the muscle that controls the flow of urine from the bladder?
What is the name of the part of the urethra that passes through a membrane or sheet that circles the urethra?
What is the name of the part of the urethra that passes through a membrane or sheet that circles the urethra?
Which of the following is NOT under voluntary control?
Which of the following is NOT under voluntary control?
What is the name of the organ that the urethra passes through in males?
What is the name of the organ that the urethra passes through in males?
Why do women tend to have more urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
Why do women tend to have more urinary tract infections (UTIs)?
What is the name of the part of the urethra that is present in the penis?
What is the name of the part of the urethra that is present in the penis?
What is the term for urine hanging out in the kidney or ureter for a long period of time?
What is the term for urine hanging out in the kidney or ureter for a long period of time?
What is the function of urinating that helps prevent infection?
What is the function of urinating that helps prevent infection?
What type of muscle makes up the external urethral sphincter?
What type of muscle makes up the external urethral sphincter?
What is the term for the valves that ensure urine flows in one direction, from the kidney to the bladder?
What is the term for the valves that ensure urine flows in one direction, from the kidney to the bladder?
Why is backflow problematic?
Why is backflow problematic?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
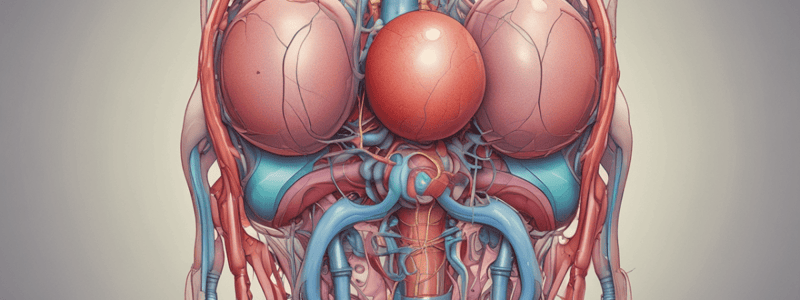
Micturition Process
- Micturition is a fancy phrase for "to pee" or "to urinate."
- The process of micturition begins in the kidney, where urine is concentrated in the nephrons.
Renal Calyx and Renal Pelvis
- The renal calyx collects urine from the collecting tubules.
- Several renal calyces coalesce together to form the renal pelvis.
- The renal pelvis leaves the kidney through the ureter.
Ureter
- The ureter conducts urine inferiorly (towards the feet) and connects to the bladder.
- The ureter has valves that prevent backflow of urine, making it a one-way street.
Bladder
- The bladder is lined with transitional epithelium, which allows it to expand and hold 300-500 milliliters of urine.
- The bladder has an internal urethral sphincter, a circle of muscle that prevents urine from leaking out unless it's really full.
- The internal urethral sphincter is not under our control and is made up of smooth muscle.
Urethra
- The urethra conducts urine to the outside world and is the organ used to pee.
- The path from the bladder to the bathroom is different for men and women.
Female Urethra
- The female urethra leads out of the body and has an internal urethral sphincter.
- It then passes through a membrane, or sheet, that circles the urethra, called the external urethral sphincter.
- The external urethral sphincter is under voluntary control and is made up of skeletal muscle.
Male Urethra
- The male urethra passes through the prostate gland, then through the membranous urethra.
- After the membranous urethra, it leads into the spongy urethra, which is in the penis.
Importance of Valves and Urine Flow
- Valves in the ureter ensure urine flows in one direction, preventing backflow and stasis.
- Backflow can lead to a greater risk of infection, especially in women who have a shorter urethra.
- Urinating helps to dispel bacteria that may have made it up the urethra from contact with the external environment.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.