Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the reproductive system?
- Facilitating childbirth
- Regulating body temperature
- Production of hormones
- Production of gametes (correct)
Which of the following correctly identifies male gametes?
Which of the following correctly identifies male gametes?
- Sperm cells (correct)
- Oocytes
- Zygotes
- Egg cells
What is the process called through which gametes are produced?
What is the process called through which gametes are produced?
- Meiosis (correct)
- Spermatogenesis
- Mitosis
- Fertilization
What does the zygote represent?
What does the zygote represent?
What is the function of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
Which structure produces enzymes to liquefy semen?
Which structure produces enzymes to liquefy semen?
Which muscle controls the temperature of the scrotum?
Which muscle controls the temperature of the scrotum?
What type of cells undergo meiosis during spermatogenesis?
What type of cells undergo meiosis during spermatogenesis?
What is contained within the head of a sperm cell?
What is contained within the head of a sperm cell?
Which gland secretes mucus that neutralizes vaginal pH?
Which gland secretes mucus that neutralizes vaginal pH?
What is the primary function of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the epididymis in the male reproductive system?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating testosterone production in the testes?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating testosterone production in the testes?
What is the role of seminal vesicles in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of seminal vesicles in the male reproductive system?
Which part of the female reproductive system is primarily responsible for the receiving and nourishing of a fertilized egg?
Which part of the female reproductive system is primarily responsible for the receiving and nourishing of a fertilized egg?
What process begins before birth in females?
What process begins before birth in females?
What is the primary sex hormone produced by the testes?
What is the primary sex hormone produced by the testes?
What is the term for the shedding of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
What is the term for the shedding of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
Which structure connects the ovaries to the uterus in the female reproductive system?
Which structure connects the ovaries to the uterus in the female reproductive system?
What gland secretes mucus to neutralize vaginal acidity?
What gland secretes mucus to neutralize vaginal acidity?
Which hormone is responsible for triggering ovulation in females?
Which hormone is responsible for triggering ovulation in females?
What role does prolactin play in the female body?
What role does prolactin play in the female body?
During which stage of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium rebuild?
During which stage of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium rebuild?
What hormone triggers the release of the egg from the ovary?
What hormone triggers the release of the egg from the ovary?
What marks the beginning of puberty in females?
What marks the beginning of puberty in females?
Which gland produces LH and FSH?
Which gland produces LH and FSH?
What is the average duration of the menstrual cycle?
What is the average duration of the menstrual cycle?
What happens to estrogen and progesterone levels during menstruation?
What happens to estrogen and progesterone levels during menstruation?
Which of the following is NOT a method of contraception?
Which of the following is NOT a method of contraception?
What is the role of progesterone during the menstrual cycle?
What is the role of progesterone during the menstrual cycle?
What occurs during the secretory stage of the menstrual cycle?
What occurs during the secretory stage of the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary role of interstitial cells in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary role of interstitial cells in the male reproductive system?
At which temperature does sperm development most effectively occur?
At which temperature does sperm development most effectively occur?
Which phase in spermatogenesis directly follows the secondary spermatocyte?
Which phase in spermatogenesis directly follows the secondary spermatocyte?
What is the purpose of the acrosome in a sperm cell?
What is the purpose of the acrosome in a sperm cell?
What structure connects the epididymis to the seminal vesicles?
What structure connects the epididymis to the seminal vesicles?
Which of the following best describes the function of sustentacular cells?
Which of the following best describes the function of sustentacular cells?
What typically occurs during the menses phase of the menstrual cycle?
What typically occurs during the menses phase of the menstrual cycle?
Which component of sperm is primarily responsible for locomotion?
Which component of sperm is primarily responsible for locomotion?
Which hormone levels are high during ovulation?
Which hormone levels are high during ovulation?
What is the term for the formation of sperm cells?
What is the term for the formation of sperm cells?
What is the purpose of contraception?
What is the purpose of contraception?
What is the initial cell type that develops into sperm cells during spermatogenesis?
What is the initial cell type that develops into sperm cells during spermatogenesis?
During which phase do estrogen levels remain high while progesterone levels are elevated?
During which phase do estrogen levels remain high while progesterone levels are elevated?
What structure serves as the site for sperm production?
What structure serves as the site for sperm production?
What triggers the release of an egg from the ovary?
What triggers the release of an egg from the ovary?
Which method is classified under hormonal contraception?
Which method is classified under hormonal contraception?
What happens to the menstrual cycle during menopause?
What happens to the menstrual cycle during menopause?
Which stage includes days 6 to 13 of the menstrual cycle?
Which stage includes days 6 to 13 of the menstrual cycle?
What characteristic defines long-acting reversible contraception?
What characteristic defines long-acting reversible contraception?
What occurs if fertilization does not happen by the end of the secretory stage?
What occurs if fertilization does not happen by the end of the secretory stage?
What is the primary function of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the prostate gland in the male reproductive system?
What hormones are released by the anterior pituitary gland in response to GnRH?
What hormones are released by the anterior pituitary gland in response to GnRH?
During which reproductive phase is a mature oocyte released from the ovary?
During which reproductive phase is a mature oocyte released from the ovary?
What is the main function of the seminal vesicles?
What is the main function of the seminal vesicles?
What role does estrogen play during puberty in females?
What role does estrogen play during puberty in females?
Which structure serves as the passageway for both urine and semen in males?
Which structure serves as the passageway for both urine and semen in males?
What triggers the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) in both males and females?
What triggers the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) in both males and females?
What structure in females is responsible for guiding the oocyte into the uterine tube?
What structure in females is responsible for guiding the oocyte into the uterine tube?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating milk production after childbirth?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating milk production after childbirth?
What is the function of the bulbourethral gland?
What is the function of the bulbourethral gland?
What is the role of the dartos muscle in the male reproductive system?
What is the role of the dartos muscle in the male reproductive system?
Which structure is primarily responsible for sperm production in males?
Which structure is primarily responsible for sperm production in males?
How many chromosomes are present in a sperm or egg cell?
How many chromosomes are present in a sperm or egg cell?
What occurs during spermatogenesis?
What occurs during spermatogenesis?
Which type of cell develops into sperm cells during spermatogenesis?
Which type of cell develops into sperm cells during spermatogenesis?
What is a zygote?
What is a zygote?
Which muscle helps pull the testes closer to the body in cold temperatures?
Which muscle helps pull the testes closer to the body in cold temperatures?
What is the main function of sustentacular cells in the testes?
What is the main function of sustentacular cells in the testes?
When does spermatogenesis begin in males?
When does spermatogenesis begin in males?
What component of the sperm cell aids in fertilization?
What component of the sperm cell aids in fertilization?
What is the primary function of the midpiece of a sperm cell?
What is the primary function of the midpiece of a sperm cell?
Which hormone is responsible for inhibiting FSH production?
Which hormone is responsible for inhibiting FSH production?
Where does fertilization typically occur in the female reproductive system?
Where does fertilization typically occur in the female reproductive system?
What role do the seminal vesicles play in the male reproductive system?
What role do the seminal vesicles play in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the bulbourethral glands?
What is the function of the bulbourethral glands?
Which structure serves as the passageway for both urine and reproductive fluids in males?
Which structure serves as the passageway for both urine and reproductive fluids in males?
In which phase of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium thicken?
In which phase of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium thicken?
What process is initiated during puberty in females for the development of egg cells?
What process is initiated during puberty in females for the development of egg cells?
What happens during a vasectomy?
What happens during a vasectomy?
Which hormone triggers the release of oocytes from the ovaries?
Which hormone triggers the release of oocytes from the ovaries?
What is the key hormone responsible for the maintenance of pregnancy?
What is the key hormone responsible for the maintenance of pregnancy?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle do estrogen levels begin to significantly rise?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle do estrogen levels begin to significantly rise?
What process involves the attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterine wall?
What process involves the attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterine wall?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating breast tissue development during puberty?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating breast tissue development during puberty?
What happens during the secretory stage of the menstrual cycle?
What happens during the secretory stage of the menstrual cycle?
At what age does puberty in females typically commence?
At what age does puberty in females typically commence?
What process marks the first occurrence of menstrual bleeding in females?
What process marks the first occurrence of menstrual bleeding in females?
Which hormone is produced in the hypothalamus and stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH?
Which hormone is produced in the hypothalamus and stimulates the anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH?
What is the average length of the menstrual cycle?
What is the average length of the menstrual cycle?
During menopause, what occurs in relation to hormone production?
During menopause, what occurs in relation to hormone production?
What term did Casimir Funk coin in 1912 that refers to essential nutrients for life?
What term did Casimir Funk coin in 1912 that refers to essential nutrients for life?
Which vitamin deficiency is related to the disease known as scurvy?
Which vitamin deficiency is related to the disease known as scurvy?
What was one of the first actions taken by the U.S. government to prevent nutrient deficiencies?
What was one of the first actions taken by the U.S. government to prevent nutrient deficiencies?
Which biochemist is recognized as the father of vitamin therapy?
Which biochemist is recognized as the father of vitamin therapy?
In what decade did commercial vitamins and supplements become available?
In what decade did commercial vitamins and supplements become available?
Which deficiency is associated with the disease beri-beri?
Which deficiency is associated with the disease beri-beri?
Which vitamin was popularly marketed in cod liver oil as 'bottled sunshine'?
Which vitamin was popularly marketed in cod liver oil as 'bottled sunshine'?
Which nutrient was added to salt to help prevent goiter?
Which nutrient was added to salt to help prevent goiter?
By what year had the discovery of all vitamins been completed?
By what year had the discovery of all vitamins been completed?
What is the meaning of the prefix 'vita' in the word 'vitamin'?
What is the meaning of the prefix 'vita' in the word 'vitamin'?
Which type of vitamins can accumulate in the body?
Which type of vitamins can accumulate in the body?
What is the primary way water-soluble vitamins are lost from the body?
What is the primary way water-soluble vitamins are lost from the body?
Which organization develops Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) for vitamins and minerals?
Which organization develops Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) for vitamins and minerals?
What is a primary reason for the controversy surrounding vitamins and their requirements?
What is a primary reason for the controversy surrounding vitamins and their requirements?
Why might multivitamins be beneficial?
Why might multivitamins be beneficial?
Which of the following is an example of a trace mineral?
Which of the following is an example of a trace mineral?
What is the primary characteristic of water-soluble vitamins?
What is the primary characteristic of water-soluble vitamins?
What nutrients do the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) cover?
What nutrients do the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) cover?
Which of the following correctly identifies fat-soluble vitamins?
Which of the following correctly identifies fat-soluble vitamins?
What role did researchers play in understanding vitamins and minerals?
What role did researchers play in understanding vitamins and minerals?
Who coined the term 'vitamin'?
Who coined the term 'vitamin'?
What condition is caused by a deficiency of vitamin C?
What condition is caused by a deficiency of vitamin C?
In which decade did the commercial availability of vitamin supplements begin?
In which decade did the commercial availability of vitamin supplements begin?
Which vitamin deficiency was addressed by fortifying salt with iodine?
Which vitamin deficiency was addressed by fortifying salt with iodine?
What is considered the father of vitamin therapy?
What is considered the father of vitamin therapy?
Which vitamin was promoted as 'bottled sunshine' in the 1950s?
Which vitamin was promoted as 'bottled sunshine' in the 1950s?
By what year had all vitamins been discovered?
By what year had all vitamins been discovered?
What was the main reason for the U.S. government to begin fortifying foods?
What was the main reason for the U.S. government to begin fortifying foods?
Which was not a disease of deficiency identified by Casimir Funk?
Which was not a disease of deficiency identified by Casimir Funk?
What term describes the nutritional components missing in diseases of deficiency?
What term describes the nutritional components missing in diseases of deficiency?
What distinguishes fat-soluble vitamins from water-soluble vitamins?
What distinguishes fat-soluble vitamins from water-soluble vitamins?
Which organization develops nutrient reference values for vitamins and minerals?
Which organization develops nutrient reference values for vitamins and minerals?
What are trace minerals needed for?
What are trace minerals needed for?
How are water-soluble vitamins primarily lost from the body?
How are water-soluble vitamins primarily lost from the body?
What role do multivitamins play in nutrition?
What role do multivitamins play in nutrition?
Which types of vitamins can accumulate in the body?
Which types of vitamins can accumulate in the body?
What historical misunderstanding about diseases was clarified by the study of vitamins?
What historical misunderstanding about diseases was clarified by the study of vitamins?
What is the primary function of the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)?
What is the primary function of the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)?
Which nutrients are considered micronutrients?
Which nutrients are considered micronutrients?
What impact do water-soluble vitamins have on the body when they are not used?
What impact do water-soluble vitamins have on the body when they are not used?
What is the primary role of vitamins in the body?
What is the primary role of vitamins in the body?
Which mineral is classified as a quantity element required by the body?
Which mineral is classified as a quantity element required by the body?
Which gene encodes the thiamine transporter responsible for intestinal uptake?
Which gene encodes the thiamine transporter responsible for intestinal uptake?
What condition is associated with mutations in the SLC19A2 gene?
What condition is associated with mutations in the SLC19A2 gene?
What is the form of vitamin B1 that is absorbed by the small intestine?
What is the form of vitamin B1 that is absorbed by the small intestine?
What triggers episodic encephalopathy in THMD2 patients?
What triggers episodic encephalopathy in THMD2 patients?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for converting thiamine to its active form?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for converting thiamine to its active form?
What is a common symptom of thiamine deficiency?
What is a common symptom of thiamine deficiency?
Which of the following best describes the condition known as Wernicke syndrome?
Which of the following best describes the condition known as Wernicke syndrome?
What is required for the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids?
What is required for the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids?
What is a symptom associated with riboflavin deficiency?
What is a symptom associated with riboflavin deficiency?
Which food is NOT a rich source of niacin?
Which food is NOT a rich source of niacin?
What is required for the synthesis of NAD from tryptophan?
What is required for the synthesis of NAD from tryptophan?
Which condition is associated with niacin deficiency?
Which condition is associated with niacin deficiency?
What is the main action of niacin in lowering cholesterol levels?
What is the main action of niacin in lowering cholesterol levels?
What is a primary characteristic of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS)?
What is a primary characteristic of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS)?
Which enzyme is responsible for the conversion of riboflavin to flavin mononucleotide (FMN)?
Which enzyme is responsible for the conversion of riboflavin to flavin mononucleotide (FMN)?
What role does the SLC19A3 gene play in Wernicke-like disorders?
What role does the SLC19A3 gene play in Wernicke-like disorders?
Which protein is significantly different from transketolase, lacking essential amino acids?
Which protein is significantly different from transketolase, lacking essential amino acids?
What is the daily requirement of riboflavin for normal adults?
What is the daily requirement of riboflavin for normal adults?
Which enzyme is exclusively localized to the mitochondria?
Which enzyme is exclusively localized to the mitochondria?
Which of the following genes produces the highest expression levels in skeletal muscle?
Which of the following genes produces the highest expression levels in skeletal muscle?
What role does pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) play in the metabolism of amino acids?
What role does pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) play in the metabolism of amino acids?
Which dietary sources are rich in pantothenic acid?
Which dietary sources are rich in pantothenic acid?
Which gene encodes the enzyme responsible for converting 4'-phosphopantetheine to coenzyme A?
Which gene encodes the enzyme responsible for converting 4'-phosphopantetheine to coenzyme A?
What is the main consequence of vitamin B6 deficiency related to heme biosynthesis?
What is the main consequence of vitamin B6 deficiency related to heme biosynthesis?
Which drugs are known to cause a deficiency in vitamin B6 by complexing with pyridoxal and PLP?
Which drugs are known to cause a deficiency in vitamin B6 by complexing with pyridoxal and PLP?
What enzyme is crucial for the recycling of biotin from biocytin in the body?
What enzyme is crucial for the recycling of biotin from biocytin in the body?
What role does pyruvate carboxylase serve in metabolism?
What role does pyruvate carboxylase serve in metabolism?
What happens to homocysteine levels in the presence of vitamin B6 deficiency?
What happens to homocysteine levels in the presence of vitamin B6 deficiency?
What is the role of haptocorrin in the absorption of vitamin B12?
What is the role of haptocorrin in the absorption of vitamin B12?
Which statement accurately describes intrinsic factor?
Which statement accurately describes intrinsic factor?
What is the function of cubilin in vitamin B12 absorption?
What is the function of cubilin in vitamin B12 absorption?
What is the primary role of transcobalamin II?
What is the primary role of transcobalamin II?
Which of the following accurately describes the TCN1 gene?
Which of the following accurately describes the TCN1 gene?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting propionyl-CoA into methylmalonyl-CoA?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting propionyl-CoA into methylmalonyl-CoA?
What is one of the key functions of the α-subunit in propionyl-CoA carboxylase?
What is one of the key functions of the α-subunit in propionyl-CoA carboxylase?
What condition is caused by mutations in the MCCC1 gene?
What condition is caused by mutations in the MCCC1 gene?
Which of the following foods is a rich source of biotin?
Which of the following foods is a rich source of biotin?
What best describes the nature of profound biotinidase deficiency?
What best describes the nature of profound biotinidase deficiency?
What is a main characteristic of thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 2 (THMD2)?
What is a main characteristic of thiamine metabolism dysfunction syndrome 2 (THMD2)?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting thiamine to its active form?
Which enzyme is responsible for converting thiamine to its active form?
What is a common symptom of thiamine deficiency?
What is a common symptom of thiamine deficiency?
What is the primary dietary source of thiamine?
What is the primary dietary source of thiamine?
Which cofactor is not required by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Which cofactor is not required by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
What is the main function of vitamins within the body?
What is the main function of vitamins within the body?
What is the consequence of destruction of the mammillary bodies in the brain associated with Korsakoff psychosis?
What is the consequence of destruction of the mammillary bodies in the brain associated with Korsakoff psychosis?
Which of the following is classified as a trace element?
Which of the following is classified as a trace element?
Which gene is linked to the cellular uptake of thiamine?
Which gene is linked to the cellular uptake of thiamine?
What role does the SLC19A2 gene play in thiamine uptake?
What role does the SLC19A2 gene play in thiamine uptake?
Which symptom is NOT associated with riboflavin deficiency?
Which symptom is NOT associated with riboflavin deficiency?
What are the potential outcomes of thiamine supplementation in individuals with Wernicke syndrome?
What are the potential outcomes of thiamine supplementation in individuals with Wernicke syndrome?
Which disorder is associated with mutations in the SLC19A2 gene?
Which disorder is associated with mutations in the SLC19A2 gene?
Which enzyme is NOT directly associated with riboflavin metabolism?
Which enzyme is NOT directly associated with riboflavin metabolism?
What substance is required to synthesize NAD from tryptophan?
What substance is required to synthesize NAD from tryptophan?
What are the two types of vitamins based on their solubility?
What are the two types of vitamins based on their solubility?
What disorder is associated with mutations in the SLC52A2 gene?
What disorder is associated with mutations in the SLC52A2 gene?
Which condition is associated with a diet deficient in niacin?
Which condition is associated with a diet deficient in niacin?
What is a known side effect of pharmacological doses of nicotinic acid?
What is a known side effect of pharmacological doses of nicotinic acid?
Which gene encodes the transporter for intestinal uptake of nicotinic acid?
Which gene encodes the transporter for intestinal uptake of nicotinic acid?
Which gene is responsible for the synthesis of coenzyme A?
Which gene is responsible for the synthesis of coenzyme A?
What is a known function of Pantothenic acid?
What is a known function of Pantothenic acid?
Which of the following symptoms is not associated with pantothenate deficiency?
Which of the following symptoms is not associated with pantothenate deficiency?
What is the highest expression level of the PANK3 gene found?
What is the highest expression level of the PANK3 gene found?
Which vitamin B6 form is transformed into its active form within intestinal enterocytes?
Which vitamin B6 form is transformed into its active form within intestinal enterocytes?
What is a common consequence of vitamin B6 deficiency in relation to heme biosynthesis?
What is a common consequence of vitamin B6 deficiency in relation to heme biosynthesis?
Which enzyme is primarily involved in the incorporation of biotin into biotin-requiring enzymes?
Which enzyme is primarily involved in the incorporation of biotin into biotin-requiring enzymes?
Which drug is known to cause vitamin B6 deficiency by complexing with pyridoxal and PLP?
Which drug is known to cause vitamin B6 deficiency by complexing with pyridoxal and PLP?
What is the primary role of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in human metabolism?
What is the primary role of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in human metabolism?
What common symptom can result from vitamin B6 deficiency?
What common symptom can result from vitamin B6 deficiency?
What is the primary function of propionyl-CoA carboxylase?
What is the primary function of propionyl-CoA carboxylase?
Which gene is responsible for encoding the α-subunit of 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase?
Which gene is responsible for encoding the α-subunit of 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase?
What condition can result from mutations in the BTD gene?
What condition can result from mutations in the BTD gene?
What is one of the classic symptoms of holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency?
What is one of the classic symptoms of holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency?
Which of the following compounds increases in urine organic acid analysis in patients with holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency?
Which of the following compounds increases in urine organic acid analysis in patients with holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency?
What is the primary role of intrinsic factor in vitamin B12 absorption?
What is the primary role of intrinsic factor in vitamin B12 absorption?
Which of the following foods is considered a rich source of biotin?
Which of the following foods is considered a rich source of biotin?
Which enzyme is responsible for hydrolyzing the haptocorrin-cobalamin complex in the small intestine?
Which enzyme is responsible for hydrolyzing the haptocorrin-cobalamin complex in the small intestine?
What is the consequence of the AMN protein in intestinal uptake of cobalamin?
What is the consequence of the AMN protein in intestinal uptake of cobalamin?
Where is the expression of the CBLIF gene primarily localized?
Where is the expression of the CBLIF gene primarily localized?
Flashcards
Gametes
Gametes
Reproductive cells (sperm and egg).
Fertilization
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg.
Zygote
Zygote
Fertilized egg cell.
Testes
Testes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminiferous Tubules
Seminiferous Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Cell Structure
Sperm Cell Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scrotum
Scrotum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory Glands
Accessory Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Tail
Sperm Tail
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis Function
Epididymis Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Deferens
Ductus Deferens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicle Function
Seminal Vesicle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland Function
Prostate Gland Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
GnRH Function
GnRH Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH Function
LH Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH Function
FSH Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Tube Function
Uterine Tube Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Female Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammary Glands Function
Mammary Glands Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Puberty (Female)
Puberty (Female)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menarche
Menarche
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's Role
Estrogen's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone's Role
Progesterone's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause
Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contraception Methods
Contraception Methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasectomy Site
Vasectomy Site
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reproductive System's Role
Reproductive System's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicle Function
Seminal Vesicle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gamete Formation Process
Gamete Formation Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Male Reproductive Components
Male Reproductive Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland Role
Prostate Gland Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Gland Function
Bulbourethral Gland Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatogenesis Stages
Spermatogenesis Stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra's Role
Urethra's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Cell Parts
Sperm Cell Parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis Function
Epididymis Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis Function
Penis Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Follicles
Ovarian Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scrotum Function
Scrotum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization Definition
Fertilization Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH's Role (Female)
FSH's Role (Female)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes Role
Testes Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Tube Function
Uterine Tube Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Deferens Role
Ductus Deferens Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause
Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contraception
Contraception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menses
Menses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proliferative Stage
Proliferative Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretory Stage
Secretory Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormonal Methods (Contraception)
Hormonal Methods (Contraception)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sterilization (Contraception)
Sterilization (Contraception)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertility Awareness (Contraception)
Fertility Awareness (Contraception)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reproductive System's Role
Reproductive System's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gamete Formation
Gamete Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization
Fertilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygote
Zygote
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scrotum Function
Scrotum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes Function
Testes Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminiferous Tubules
Seminiferous Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Cell Structure
Sperm Cell Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interstitial Cells
Interstitial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midpiece Function
Midpiece Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tail's Role
Tail's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminiferous Tubules
Seminiferous Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis Function
Epididymis Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicles' Role
Seminal Vesicles' Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland's Role
Prostate Gland's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
GnRH's Role
GnRH's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovaries' Role
Ovaries' Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterine Tubes
Uterine Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstruation
Menstruation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovulation
Ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertilization
Fertilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation
Implantation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Puberty (Female)
Puberty (Female)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menarche
Menarche
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause
Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contraception
Contraception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal Fluctuations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micronutrients
Micronutrients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minerals
Minerals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multivitamins
Multivitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Discovery Timeline
Vitamin Discovery Timeline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Casimir Funk
Casimir Funk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Therapy
Vitamin Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Source (Early 20th Century)
Vitamin Source (Early 20th Century)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Food Fortification
Food Fortification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Commercial Vitamins
Commercial Vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Supplements Availability
Vitamin Supplements Availability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Marketing
Vitamin Marketing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micronutrients
Micronutrients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamins
Vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minerals
Minerals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multivitamins
Multivitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Discovery
Vitamin Discovery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Definition
Vitamin Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Discovery Timeline
Vitamin Discovery Timeline
Signup and view all the flashcards
Casimir Funk
Casimir Funk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Sources (Early 20th Century)
Vitamin Sources (Early 20th Century)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Therapy
Vitamin Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin Discovery
Vitamin Discovery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Early Vitamin Supplements Availability
Early Vitamin Supplements Availability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Government Fortification of Foods
Government Fortification of Foods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multivitamins
Multivitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamins
Vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minerals
Minerals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Transporter 1 (THTR1)
Thiamine Transporter 1 (THTR1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Responsive Megaloblastic Anemia Syndrome (TRMA)
Thiamine Responsive Megaloblastic Anemia Syndrome (TRMA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Metabolism Dysfunction Syndrome 2 (THMD2)
Thiamine Metabolism Dysfunction Syndrome 2 (THMD2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
SLC19A3 gene
SLC19A3 gene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Ganglia Disease, Biotin-responsive (BBGD)
Basal Ganglia Disease, Biotin-responsive (BBGD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wernicke encephalopathy
Wernicke encephalopathy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine
Thiamine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
TPK1 gene
TPK1 gene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc)
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc)
Signup and view all the flashcards
2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH)
2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKD)
Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine pyrophosphokinase 1 (TPK1)
Thiamine pyrophosphokinase 1 (TPK1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beriberi
Beriberi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wernicke Syndrome
Wernicke Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Sources of Thiamine
Dietary Sources of Thiamine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Korsakoff encephalopathy
Korsakoff encephalopathy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine deficiency
Thiamine deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammillary bodies
Mammillary bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retrograde amnesia
Retrograde amnesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transketolase
Transketolase
Signup and view all the flashcards
TKTL1 gene
TKTL1 gene
Signup and view all the flashcards
SLC19A3 gene
SLC19A3 gene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin
Riboflavin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flavoproteins
Flavoproteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin kinase
Riboflavin kinase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome 2
Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin Deficiency Symptoms
Riboflavin Deficiency Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin Decomposition
Riboflavin Decomposition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin Deficiency in Newborns
Riboflavin Deficiency in Newborns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin from Tryptophan
Niacin from Tryptophan
Signup and view all the flashcards
NAD+ and NADH
NAD+ and NADH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin Deficiency Symptoms
Niacin Deficiency Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pellagra
Pellagra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nicotinic Acid and Cholesterol
Nicotinic Acid and Cholesterol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coenzyme A Synthesis
Coenzyme A Synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenate Kinases
Pantothenate Kinases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC)
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin
Biotin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotinidase deficiency (BTD)
Biotinidase deficiency (BTD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK2 Enzyme Localization
PANK2 Enzyme Localization
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK2 Gene Location
PANK2 Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK2 mRNA Variants
PANK2 mRNA Variants
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK3 Gene Expression
PANK3 Gene Expression
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK4 Gene's Exons
PANK4 Gene's Exons
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK4 Mutation & Cataracts
PANK4 Mutation & Cataracts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phosphopantothenoylcysteine Synthetase
Phosphopantothenoylcysteine Synthetase
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPCS Gene Location
PPCS Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
4'-Phospho-N-pantothenoylcysteine (PPC)
4'-Phospho-N-pantothenoylcysteine (PPC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coenzyme A Synthase (COASY) Role
Coenzyme A Synthase (COASY) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
COASY Gene Location
COASY Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenic Acid's Roles
Pantothenic Acid's Roles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenic Acid Deficiency Symptoms
Pantothenic Acid Deficiency Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 Forms
Vitamin B6 Forms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyridoxal Kinase Role
Pyridoxal Kinase Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
PLP's Role in Amino Acid Metabolism
PLP's Role in Amino Acid Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
PLP and Neurotransmitters
PLP and Neurotransmitters
Signup and view all the flashcards
PLP and Heme Synthesis
PLP and Heme Synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
O-(3-hydroxyvaleryl)-L-carnitine
O-(3-hydroxyvaleryl)-L-carnitine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elevated organic acids in urine
Elevated organic acids in urine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tigylglycine
Tigylglycine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalamin
Cobalamin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cob(I)alamin
Cob(I)alamin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Haptocorrin
Haptocorrin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transcobalamin II (TC)
Transcobalamin II (TC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubilin
Cubilin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubilin anchoring proteins
Cubilin anchoring proteins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 requirement during pregnancy and lactation
Vitamin B6 requirement during pregnancy and lactation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 deficiency causes
Vitamin B6 deficiency causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Role of pyridoxal kinase deficiency
Role of pyridoxal kinase deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 deficiency anemia
Vitamin B6 deficiency anemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cystathionine enzymes (CBS, cystathionase)
Cystathionine enzymes (CBS, cystathionase)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homocysteinemia/uria from B6 deficiency
Homocysteinemia/uria from B6 deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symptoms of Vitamin B6 deficiency
Symptoms of Vitamin B6 deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin (vitamin B7/H)
Biotin (vitamin B7/H)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biocytin
Biocytin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotinidase function
Biotinidase function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin absorption mechanism
Biotin absorption mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin-requiring enzymes
Biotin-requiring enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
ABC Enzymes
ABC Enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin-dependent carboxylating activities
Biotin-dependent carboxylating activities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS)
Holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Role
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Carboxylase (PC) Role
Pyruvate Carboxylase (PC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) Role
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase Role
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamins
Vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minerals
Minerals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
SLC19A2 gene
SLC19A2 gene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Responsive Megaloblastic Anemia (TRMA)/THMD1
Thiamine Responsive Megaloblastic Anemia (TRMA)/THMD1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water-soluble vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multivitamins
Multivitamins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Metabolism Dysfunction Syndrome 2 (THMD2)
Thiamine Metabolism Dysfunction Syndrome 2 (THMD2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
THMD2 symptoms
THMD2 symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin Treatment in THMD2
Biotin Treatment in THMD2
Signup and view all the flashcards
SLC19A3 gene mutation
SLC19A3 gene mutation
Signup and view all the flashcards
SLC25A19 gene mutation
SLC25A19 gene mutation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine Pyrophosphokinase 1 (TPK1)
Thiamine Pyrophosphokinase 1 (TPK1)
Signup and view all the flashcards
TPP's function in metabolic pathways
TPP's function in metabolic pathways
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine deficiency symptoms (early)
Thiamine deficiency symptoms (early)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine deficiency symptoms (advanced)
Thiamine deficiency symptoms (advanced)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertical nystagmus
Vertical nystagmus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beriberi (dry & wet)
Beriberi (dry & wet)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dietary Thiamine Sources
Dietary Thiamine Sources
Signup and view all the flashcards
High carbohydrate diet and thiamine
High carbohydrate diet and thiamine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Korsakoff encephalopathy
Korsakoff encephalopathy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS)
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (WKS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammillary bodies
Mammillary bodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Papez circuit
Papez circuit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiamine deficiency
Thiamine deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transketolase
Transketolase
Signup and view all the flashcards
TKTL1
TKTL1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin (B2)
Riboflavin (B2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin deficiency
Riboflavin deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin deficiency symptoms
Riboflavin deficiency symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin decomposition
Riboflavin decomposition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Riboflavin deficiency in newborns
Riboflavin deficiency in newborns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin
Niacin
Signup and view all the flashcards
NAD/NADP
NAD/NADP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin synthesis from tryptophan
Niacin synthesis from tryptophan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin deficiency symptoms
Niacin deficiency symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pellagra
Pellagra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Niacin and cholesterol
Niacin and cholesterol
Signup and view all the flashcards
HCA2 receptor
HCA2 receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenic acid
Pantothenic acid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coenzyme A (CoA)
Coenzyme A (CoA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenate kinase
Pantothenate kinase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Carboxylase (PC)
Pyruvate Carboxylase (PC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin
Biotin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotinidase Deficiency
Biotinidase Deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocarboxylase Synthetase Deficiency
Holocarboxylase Synthetase Deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
PC Gene Location
PC Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase Subunits
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase Subunits
Signup and view all the flashcards
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase subunits
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase subunits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 Requirement during Pregnancy/Lactation
Vitamin B6 Requirement during Pregnancy/Lactation
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK2 Enzyme Location
PANK2 Enzyme Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK2 Gene Location
PANK2 Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 Deficiency Causes
Vitamin B6 Deficiency Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK2 mRNA Splising
PANK2 mRNA Splising
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 Deficiency Impact on Heme
Vitamin B6 Deficiency Impact on Heme
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK3 Gene Expression
PANK3 Gene Expression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B6 Metabolism Role
Vitamin B6 Metabolism Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK3 Gene Chromosome
PANK3 Gene Chromosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin Roles for Enzymes
Biotin Roles for Enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin Transport from Intestines
Biotin Transport from Intestines
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK4 Gene Expression
PANK4 Gene Expression
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK4 Gene Chromosome
PANK4 Gene Chromosome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin-Dependent Carboxylating Enzymes
Biotin-Dependent Carboxylating Enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotin Incorporation into Enzymes
Biotin Incorporation into Enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
PANK4 Mutation Impact
PANK4 Mutation Impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPCS Gene Encoding
PPCS Gene Encoding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Role
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPCS Gene Location
PPCS Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate Carboxylase (PC) Role
Pyruvate Carboxylase (PC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) Role
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPC Product
PPC Product
Signup and view all the flashcards
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase (3MCC) Role
3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase (3MCC) Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPCDC Enzyme Function
PPCDC Enzyme Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
PPCDC Gene Location
PPCDC Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
4'-Phosphopantetheine to CoA
4'-Phosphopantetheine to CoA
Signup and view all the flashcards
COASY Gene Location
COASY Gene Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenic Acid in ACP
Pantothenic Acid in ACP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pantothenate Metabolism
Pantothenate Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine organic acid analysis (holocarboxylase synthetase deficient)
Urine organic acid analysis (holocarboxylase synthetase deficient)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tiglylglycine
Tiglylglycine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalamin
Cobalamin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalamin oxidation states
Cobalamin oxidation states
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalamin synthesis
Cobalamin synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cobalamin storage
Cobalamin storage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bioavailable vitamin B12 sources
Bioavailable vitamin B12 sources
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B12 activation
Vitamin B12 activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin B12 stomach release
Vitamin B12 stomach release
Signup and view all the flashcards
Haptocorrin (transcobalamin I)
Haptocorrin (transcobalamin I)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Haptocorrin's gene location
Haptocorrin's gene location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrinsic factor (IF)
Intrinsic factor (IF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transcobalamin II (TC)
Transcobalamin II (TC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubilin
Cubilin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubilin anchoring protein
Cubilin anchoring protein
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction
- The reproductive system is essential for the continuation of the human species.
- The reproductive system is responsible for physical and functional differences between males and females, and influences their behavior.
- The reproductive system is not essential for individual survival.
- The primary function of the reproductive system is the production of gametes.
Gamete Formation
- Gametes are reproductive cells.
- Sperm cells are male gametes.
- Oocytes or egg cells are female gametes.
- Gametes are produced through meiosis.
- Each sperm and egg cell has 23 chromosomes.
Terminology
- Fertilization: The union of sperm and egg cells.
- Zygote: A fertilized egg cell.
- Embryo: A fertilized egg that has developed for 3 to 14 days.
Male Reproductive System
- Components:
- Testes: Produce sperm cells.
- Epididymis: Where sperm cells mature and develop the ability to swim.
- Ductus Deferens: Connects the epididymis to the seminal vesicles.
- Urethra: Passageway for urine and reproductive fluids.
- Accessory Glands:
- Seminal Vesicles: Produce fructose and prostaglandins.
- Prostate Gland: Produces enzymes to liquefy semen and neutralizes vaginal pH.
- Bulbourethral Glands: Secrete mucus that neutralizes vaginal pH.
- Supporting Structures:
- Scrotum: Encloses the testes.
- Penis: Transfers sperm to the female.
- Scrotum:
- Contains the testes.
- Dartos Muscle: Controls the temperature of the scrotum to regulate sperm development.
- Cremaster Muscles: Extensions of the abdominal muscles that pull the testes closer to the body.
- Testes:
- Produce sperm cells.
- Seminiferous Tubules: Located within the testes, where sperm cells are produced.
- Interstitial Cells: Secrete testosterone.
- Germ Cells: Precursor cells to sperm cells.
- Sustentacular Cells: Nourish germ cells and produce hormones.
- Spermatogenesis:
- The process of sperm cell formation.
- Begins during puberty.
- Steps:
- Germ Cells: Undifferentiated male germ cells.
- Spermatogonia: Undifferentiated male germ cells.
- Primary Spermatocytes: Cells that undergo meiosis.
- Secondary Spermatocytes: Haploid cells.
- Spermatids: Mature sperm cells.
- Sperm Cells: Mature gametes.
- Sperm Cell Structure:
- Head: Contains the acrosome, nucleus, and centriole.
- Midpiece: Packed with mitochondria, providing energy for movement.
- Tail: Flagellum that propels the sperm cell.
- Epididymis:
- Thread-like tube connected to the seminiferous tubules.
- Site of sperm cell maturation and development of swimming ability.
- Ductus Deferens:
- A large tube that connects the epididymis to the seminal vesicles.
- Site of vasectomy, a form of male sterilization.
- Seminal Vesicles:
- Sack-shaped glands connected to the ductus deferens.
- Produce fructose (energy source for sperm) and prostaglandins (decrease mucus thickness in the cervix and uterine tubes).
- Prostate Gland:
- Surrounds the urethra.
- Secretes enzymes that liquefy semen and neutralize the acidic pH of the vagina.
- Bulbourethral Glands:
- Located near the base of the prostate gland.
- Secrete mucus that neutralizes the acidic pH of the vagina.
- Semen:
- A mixture of sperm cells and secretions from the accessory glands.
- Provides a transport medium, protection, and nutrients for the sperm cells.
Male Hormones
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH):
- Produced in the hypothalamus.
- Stimulates the release of Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH):
- Stimulates testosterone production in the testes.
- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH):
- Stimulates spermatogenesis (sperm cell production).
- Testosterone:
- The primary male sex hormone.
- Produced by the interstitial cells of the testes.
- Responsible for male sexual development and characteristics.
- Inhibin:
- Produced by sustentacular cells in the seminiferous tubules.
- Inhibits FSH production, regulating sperm cell production.
Female Reproductive System
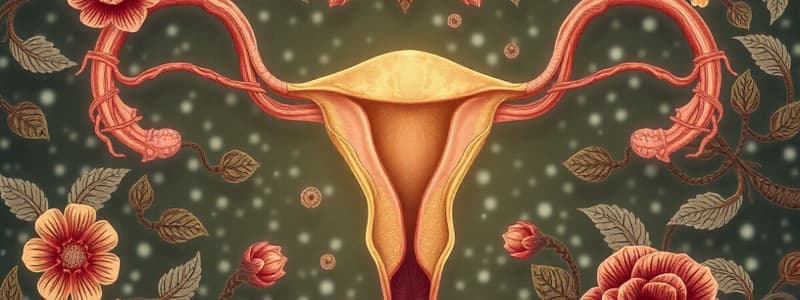
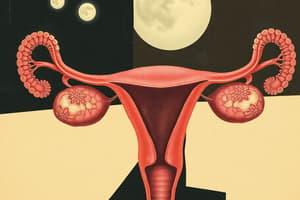
- Components:
- Ovaries: Produce oocytes and sex hormones.
- Uterine Tubes: Where fertilization occurs.
- Uterus: Receives and nourishes a fertilized egg.
- Vagina: Passageway for the penis during intercourse and for the baby during childbirth.
- Vulva: External female genitalia.
- Mammary Glands: Produce milk.
- Ovaries:
- Primary female reproductive organs.
- Located on either side of the uterus.
- Ovarian Follicles: Contain oocytes.
- Oogenesis:
- The production of oocytes.
- Begins before birth.
- Steps:
- Oogonia: Undifferentiated female germ cells.
- Primary Oocytes: Cells that undergo meiosis.
- Secondary Oocytes: Haploid cells.
- Oocytes: Mature egg cells.
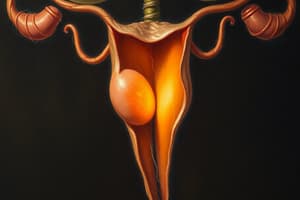
- Uterine Tubes:
- Also called fallopian tubes.
- Connect the ovaries to the uterus.
- Site of fertilization.
- Fimbria: Finger-like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes that sweep the oocyte into the tube.
- Ampulla: Widest part of the fallopian tube, where fertilization usually occurs.
- Uterus:
- Pear-shaped organ located in the pelvic cavity.
- Site of implantation and development of the embryo.
- Fundus: Rounded top portion of the uterus.
- Body: Largest portion of the uterus.
- Cervix: Narrow neck of the uterus that connects to the vagina.
- Uterine Wall Layers:
- Perimetrium: Outermost layer.
- Myometrium: Middle layer composed of smooth muscle.
- Endometrium: Innermost layer; discarded each cycle during menstruation.
- Vagina:
- Muscular tube extending from the cervix to the outside of the body.
- Passageway for the penis during intercourse and for the baby during childbirth.
- Vulva: External female genitalia.
- Mons Pubis: Fatty layer of skin over the pubic bone.
- Labia Majora: Outer fleshy folds around the vaginal opening.
- Labia Minora: Inner folds of skin that surround the vaginal opening.
- Clitoris: Small, sensitive, erectile organ located at the top of the vulva.
- Hymen: Thin membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening.
- Mammary Glands:
- Located in the breasts.
- Produce milk after childbirth.
- Menstrual Cycle:
- Monthly cycle of hormonal changes that prepares the uterus for a potential pregnancy.
- Stages:
- Menstruation: Shedding of the endometrium.
- Follicular Phase: Maturation of an ovarian follicle.
- Ovulation: Release of a mature egg from the ovary.
- Luteal Phase: Formation and degradation of the corpus luteum.
- Female Hormones:
- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH): Stimulates follicle development and the production of estrogen.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH): Triggers ovulation and the production of progesterone.
- Estrogen: Responsible for female sexual development and characteristics.
- Progesterone: Prepares the uterus for implantation.
- Hormonal Regulation of the Menstrual Cycle:
- The hypothalamus secretes GnRH, which stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release FSH and LH.
- FSH stimulates follicle growth and the production of estrogen.
- Estrogen levels rise, causing a surge in LH release.
- LH triggers ovulation.
- The corpus luteum forms and produces progesterone, which prepares the uterus for implantation.
- If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degrades, progesterone levels drop, and menstruation occurs.
Comparison of Male and Female Reproductive Systems
| Characteristic | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Reproductive Organ | Testes | Ovaries |
| Gamete | Sperm | Oocyte |
| Gamete Production | Spermatogenesis | Oogenesis |
| Start of Gamete Production | Puberty | Before Birth |
| Site of Gamete Production | Seminiferous Tubules | Ovarian Follicles |
| Hormone Responsible for Gamete Production | FSH | FSH |
| Primary Sex Hormone | Testosterone | Estrogen |
| Secondary Sex Characteristics | Development of facial hair, deepening of voice, muscular growth | Development of breasts, widening of hips, menstrual cycles |
| Sterilization | Vasectomy (cutting the ductus deferens) | Tubal ligation (tying the fallopian tubes) |
External Genitalia
- The entrance to the vagina in females is analogous to the scrotum in males.
- The labia minora are thinner folds of skin located inside the labia majora, surrounding the vaginal opening.
- The clitoris, a small erectile structure in females, is equivalent to the penis in males.
Mammary Glands
- Mammary glands are located in the breasts and are responsible for milk production.
- Prolactin, a hormone produced by the endocrine system, stimulates milk production.
- Puberty in females begins between the ages of 11 and 13 and is typically complete by 16.
- Menarche refers to the first menstrual bleeding experienced during puberty.
Hormonal Changes During Puberty
- Increased levels of estrogen and progesterone are secreted by the ovaries during puberty.
- GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus stimulates the production of LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) in both males and females.
- LH and FSH are produced in the anterior pituitary gland.
Hormonal Functions in Females
- LH triggers ovulation, releasing the egg from the ovary.
- FSH helps the follicles in the ovaries develop.
- Estrogen is essential for the proliferation of endometrial cells, mammary gland development, and breast growth.
- Estrogen also controls the secretion of FSH and LH.
- Progesterone plays a crucial role in the enlargement of endometrial cells and maintaining pregnancy.
- Progesterone also contributes to mammary gland development, but compared to estrogen, its role is smaller.
- Progesterone can control FSH, LH, and estrogen secretion.
The Menstrual Cycle
- The menstrual cycle represents a series of changes occurring in sexually mature, non-pregnant females.
- Menstruation, the shedding of the endometrium from the uterus, is just one part of this cycle.
- The menstrual cycle typically lasts 28 days.
- Menstruation occurs on average between days 1 and 5 of the cycle, when the endometrium is shed, resulting in bleeding.
- During menstruation, both estrogen and progesterone levels are low.
Menstrual Cycle Stages
- Proliferative Stage (Days 6-13): The endometrium rebuilds, estrogen levels increase, and progesterone levels remain low.
- Ovulation Stage (Day 14): LH triggers the release of the egg (ovum) from the ovary. The egg travels to the fallopian tubes aided by the fimbriae. Estrogen levels are high, and progesterone levels begin to increase.
- Secretory Stage (Days 15-28): The endometrium prepares for implantation. Progesterone levels remain high, while estrogen levels decrease.
Menopause
- During menopause, the ovaries produce significantly fewer hormones, and the number of follicles decreases.
- This leads to irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation.
Contraception
- Contraception refers to methods used to prevent pregnancy.
- Six main types are categorized:
- Long-acting reversible contraception
- Barrier methods
- Sterilization (tubal ligation for females, vasectomy for males)
- Hormonal methods
- Fertility awareness
- Emergency contraception (Plan B or morning-after pills)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the key concepts of the human reproductive system, including gamete formation, terminology related to fertilization, and the male reproductive system components. Understand the physiological differences between males and females and their roles in reproduction.