Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of Cytochrome C in living organisms?
What is the primary function of Cytochrome C in living organisms?
- Aid in the production of ATP (correct)
- Facilitate oxygen transport
- Regulate body temperature
- Assist in muscle contraction
What characteristic indicates that two species are closely related?
What characteristic indicates that two species are closely related?
- Color of their fur
- Common habitat
- Similar body size
- Identical Cytochrome C sequence (correct)
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for fossil formation?
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for fossil formation?
- Presence of oxygen (correct)
- Quick burial by sediment
- Exclusion of scavengers
- Hard body parts present
What does the law of superposition state?
What does the law of superposition state?
What is the advantage of absolute dating compared to relative dating?
What is the advantage of absolute dating compared to relative dating?
Which method employs the use of index fossils?
Which method employs the use of index fossils?
Why is quick burial by sediment important in fossil formation?
Why is quick burial by sediment important in fossil formation?
What process is primarily responsible for determining the age of fossils through measuring radioactive atoms?
What process is primarily responsible for determining the age of fossils through measuring radioactive atoms?
What is the main function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
What is the main function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
Which organ in the male reproductive system is responsible for producing sperm?
Which organ in the male reproductive system is responsible for producing sperm?
Which organ transports mature sperm to the urethra in the male reproductive system?
Which organ transports mature sperm to the urethra in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary role of the uterus in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary role of the uterus in the female reproductive system?
What crucial role does the scrotum play in male reproduction?
What crucial role does the scrotum play in male reproduction?
What function does the cervix serve in the female reproductive system?
What function does the cervix serve in the female reproductive system?
Which of these hormones are primarily secreted by the ovaries?
Which of these hormones are primarily secreted by the ovaries?
What is the role of the prostate gland in male reproduction?
What is the role of the prostate gland in male reproduction?
What is the maximum age for fossils that can be dated using Carbon-14?
What is the maximum age for fossils that can be dated using Carbon-14?
What is the half-life of Carbon-14?
What is the half-life of Carbon-14?
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for natural selection to occur?
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for natural selection to occur?
Which process describes the survival and reproduction of organisms with favorable traits?
Which process describes the survival and reproduction of organisms with favorable traits?
How does isolation contribute to natural selection?
How does isolation contribute to natural selection?
What change allows for evolution through natural selection?
What change allows for evolution through natural selection?
What is a benefit of the jelly bean model in demonstrating natural selection?
What is a benefit of the jelly bean model in demonstrating natural selection?
What happens to the traits of organisms that survive through natural selection?
What happens to the traits of organisms that survive through natural selection?
What effect did the selection pressure have on the jelly bean population?
What effect did the selection pressure have on the jelly bean population?
Which color of toothpick was at a disadvantage due to selection pressure in the toothpick model?
Which color of toothpick was at a disadvantage due to selection pressure in the toothpick model?
How does the process of reproduction in the toothpick model affect allele frequency?
How does the process of reproduction in the toothpick model affect allele frequency?
Which environmental change allowed dark peppered moths to survive better during the Industrial Revolution?
Which environmental change allowed dark peppered moths to survive better during the Industrial Revolution?
What happens to bacterial populations treated with antibiotics?
What happens to bacterial populations treated with antibiotics?
What is the result of the dark color allele being passed on in peppered moths?
What is the result of the dark color allele being passed on in peppered moths?
What limitation is identified regarding the models discussed?
What limitation is identified regarding the models discussed?
What does the term 'selection pressure' refer to in the context of evolution?
What does the term 'selection pressure' refer to in the context of evolution?
What physical adaptation helps Queensland koalas survive the heat?
What physical adaptation helps Queensland koalas survive the heat?
Which statement correctly describes the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration?
Which statement correctly describes the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration?
What is the key difference between distance and displacement?
What is the key difference between distance and displacement?
What is the force required to accelerate a 400 kg rock at 8 m/s²?
What is the force required to accelerate a 400 kg rock at 8 m/s²?
Why have horses evolved larger sizes and fused bones?
Why have horses evolved larger sizes and fused bones?
What is the primary weather condition difference between Southern and Northern Australia?
What is the primary weather condition difference between Southern and Northern Australia?
How do koalas in Southern Australia adapt to the environment?
How do koalas in Southern Australia adapt to the environment?
What happens to displacement when the direction is not considered?
What happens to displacement when the direction is not considered?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Human Reproduction
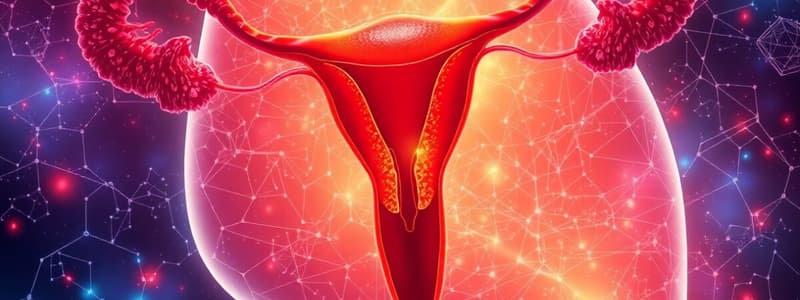
- Female Reproductive System:
- Ovaries: Produce eggs (ova) and hormones (estrogen and progesterone) that regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Fallopian Tubes: Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Uterus: Where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus.
- Cervix: Opens to allow menstrual flow and sperm entry during intercourse.
- Vagina: Receives the penis during intercourse and serves as a passage for menstrual flow.
- Male Reproductive System:
- Testes: Primary reproductive organs that produce and store sperm and testosterone.
- Scrotum: Contains the testes, providing temperature regulation.
- Vas Deferens: Transports sperm towards the urethra.
- Prostate Gland: Secretes prostate fluid, a component of semen.
- Seminal Vesicles: Produce seminal fluid, which provides energy and nourishment for sperm.
- Urethra: Carries urine and semen out of the body.
- Penis: Organ for sexual intercourse.
Fossil Record & Earth's Age
- Fossils: Remains or traces of once-living organisms.
- Fossil Formation:
- Requires quick burial by sediment to prevent scavenging and erosion.
- Oxygen exclusion is necessary to prevent decay.
- Hard body parts (bones, teeth, shells) are more likely to fossilize.
- Fossil Age Determination:
- Relative Dating: Comparing fossils to similar rocks and fossils of known ages.
- Law of Superposition: Older fossils are found in lower rock layers, younger in higher layers (in undisturbed rock formations).
- Index Fossils: Organisms with a short lifespan, useful for dating surrounding fossils.
- Absolute Dating (Radiometric Dating): Measuring the remaining radioactive atom proportions.
- Carbon-14: Dates fossils younger than 50,000 years.
- Uranium-238: Dates rocks older than 50,000 years.
- Relative Dating: Comparing fossils to similar rocks and fossils of known ages.
Natural Selection & Evolution
- Natural Selection: Mechanism for evolution where favorable alleles become more prevalent.
- Survival of the Fittest: Organisms with traits better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Isolation: Speeds up natural selection by preventing interbreeding.
- Requirements for Natural Selection:
- Overproduction: More offspring produced than can survive.
- Variation: Individuals possess unique combinations of traits.
- Competition: Organisms compete for limited resources.
- Selection: Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Isolation: Prevents interbreeding, contributing to speciation.
- Examples of Evolution by Natural Selection:
- Antibiotic Resistance: Bacteria with resistant genes survive antibiotic treatment and reproduce, increasing the resistance in the population.
- Peppered Moths: Industrial pollution darkened tree trunks, favoring darker moths that blended in better.
- Koalas: Variations in fur length and color are advantageous in different climates (longer darker fur in colder regions, shorter lighter fur in warmer regions).
- Horses: Deforestation led to changes in size, hoof development, and dentition, adapting them to open grasslands.
Force, Mass, and Acceleration
- Force: An interaction that can change the motion of an object.
- Mass: The amount of matter in an object.
- Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity.
- Relationship: Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration: F = ma.
- Greater mass requires greater force to produce the same acceleration.
- Lighter objects accelerate more quickly than heavier objects with the same force.
- Example Problem:
- A 400 kg rock is pushed with a force that causes it to accelerate at 8 m/s².
- To calculate the force, use: F = ma = (400 kg)(8 m/s²) = 3200 Newtons (N).
Distance, Speed, and Time
- Distance: Total length traveled between two points.
- Displacement: Distance and direction from the starting point to the final position.
- Scalar: Distance has magnitude only.
- Vector: Displacement has both magnitude and direction.
- Speed: The rate at which an object changes its position.
- Time: The duration of an event.
- Relationship: Speed is calculated by dividing distance by time.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.