Podcast
Questions and Answers
What hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the secretion of testosterone in males?
What hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the secretion of testosterone in males?
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone
- Luteinizing Hormone (correct)
Which of the following changes is associated with estrogen during puberty in females?
Which of the following changes is associated with estrogen during puberty in females?
- Widening of pelvis (correct)
- Increased aggression
- Increased hair growth on back
- Increased size of penis
What is the primary role of Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) in males?
What is the primary role of Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) in males?
- Blood sugar regulation
- Breast development
- Sperm development (correct)
- Muscle growth
Which condition is characterized by the pancreas' failure to produce insulin due to autoimmune destruction?
Which condition is characterized by the pancreas' failure to produce insulin due to autoimmune destruction?
Which of the following is not a function of testosterone in males?
Which of the following is not a function of testosterone in males?
What is the role of glucagon in blood sugar regulation?
What is the role of glucagon in blood sugar regulation?
What hormone is primarily responsible for the thickening of the uterus in preparation for potential pregnancy?
What hormone is primarily responsible for the thickening of the uterus in preparation for potential pregnancy?
Which hormone is secreted by the ovaries and is essential for facilitating ovulation?
Which hormone is secreted by the ovaries and is essential for facilitating ovulation?
What type of hormones can easily cross the cell membrane?
What type of hormones can easily cross the cell membrane?
What triggers the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland?
What triggers the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for uterine contractions during labor?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for uterine contractions during labor?
What is the primary effect of non-steroid hormones on target cells?
What is the primary effect of non-steroid hormones on target cells?
What is the primary function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in relation to the kidneys?
What is the primary function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in relation to the kidneys?
Which hormone stimulates milk production in the breasts after childbirth?
Which hormone stimulates milk production in the breasts after childbirth?
How do steroid hormones elicit a response in target cells?
How do steroid hormones elicit a response in target cells?
What condition is caused by hypersecretion of growth hormone during childhood?
What condition is caused by hypersecretion of growth hormone during childhood?
What is the main function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
What is the main function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Which type of hormones act faster in the body?
Which type of hormones act faster in the body?
What usually causes acromegaly in adults?
What usually causes acromegaly in adults?
What role does oxytocin play in the breastfeeding process?
What role does oxytocin play in the breastfeeding process?
Which hormone's release is inhibited by high levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy?
Which hormone's release is inhibited by high levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy?
What is the source of steroid hormones in the body?
What is the source of steroid hormones in the body?
What is the main physiological role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in relation to blood pressure?
What is the main physiological role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in relation to blood pressure?
What is a consequence of hyposecretion of growth hormone in children?
What is a consequence of hyposecretion of growth hormone in children?
What effect does obesity have on the risk of type II diabetes?
What effect does obesity have on the risk of type II diabetes?
What happens to cells in uncontrolled diabetes when they lack glucose?
What happens to cells in uncontrolled diabetes when they lack glucose?
Which of the following can be a severe consequence of metabolic acidosis caused by uncontrolled diabetes?
Which of the following can be a severe consequence of metabolic acidosis caused by uncontrolled diabetes?
Which of the following health problems is NOT associated with uncontrolled diabetes?
Which of the following health problems is NOT associated with uncontrolled diabetes?
What can happen if too much insulin is injected or injected when blood sugar is low?
What can happen if too much insulin is injected or injected when blood sugar is low?
What role does parathyroid hormone (PTH) play in the body?
What role does parathyroid hormone (PTH) play in the body?
What does the secretion of calcitonin from the thyroid gland indicate?
What does the secretion of calcitonin from the thyroid gland indicate?
Which of the following is a recommended practice for managing diabetes?
Which of the following is a recommended practice for managing diabetes?
Which hormone secreted by the ovaries is primarily involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle?
Which hormone secreted by the ovaries is primarily involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary consequence of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) in males?
What is the primary consequence of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) in males?
What effect does Estrogen have on the body during puberty in females?
What effect does Estrogen have on the body during puberty in females?
Which of the following is the primary function of the hormone insulin?
Which of the following is the primary function of the hormone insulin?
During which phase of diabetes mellitus does the immune system target and destroy beta cells in the pancreas?
During which phase of diabetes mellitus does the immune system target and destroy beta cells in the pancreas?
What role does Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) play in males?
What role does Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) play in males?
What physiological changes are associated with increased testosterone production during puberty in males?
What physiological changes are associated with increased testosterone production during puberty in males?
How does glucagon function in maintaining blood sugar levels?
How does glucagon function in maintaining blood sugar levels?
What triggers the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the neurons in the hypothalamus?
What triggers the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the neurons in the hypothalamus?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the kidneys to retain more water?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the kidneys to retain more water?
Which condition results from excess secretion of growth hormone during adulthood?
Which condition results from excess secretion of growth hormone during adulthood?
What physiological effect does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) have on blood pressure?
What physiological effect does antidiuretic hormone (ADH) have on blood pressure?
What role does prolactin play in postpartum lactation?
What role does prolactin play in postpartum lactation?
What is the primary consequence of hyposecretion of growth hormone in children?
What is the primary consequence of hyposecretion of growth hormone in children?
Which of the following hormones is produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
Which of the following hormones is produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
What primarily stimulates the release of prolactin after childbirth?
What primarily stimulates the release of prolactin after childbirth?
What is the primary effect of high blood glucose levels in diabetes?
What is the primary effect of high blood glucose levels in diabetes?
Which health problems can be caused by damage to blood vessels due to uncontrolled diabetes?
Which health problems can be caused by damage to blood vessels due to uncontrolled diabetes?
What complication arises from the production of ketones due to fat metabolism in uncontrolled diabetes?
What complication arises from the production of ketones due to fat metabolism in uncontrolled diabetes?
Which statement is true about insulin injection in diabetes management?
Which statement is true about insulin injection in diabetes management?
What role does parathyroid hormone (PTH) play in calcium regulation?
What role does parathyroid hormone (PTH) play in calcium regulation?
How does calcitonin affect blood calcium levels?
How does calcitonin affect blood calcium levels?
What should individuals with diabetes do to monitor their health?
What should individuals with diabetes do to monitor their health?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes steroid hormones from non-steroid hormones?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes steroid hormones from non-steroid hormones?
Which of the following statements about oxytocin is incorrect?
Which of the following statements about oxytocin is incorrect?
In the context of energy utilization in uncontrolled diabetes, what happens to cells lacking glucose?
In the context of energy utilization in uncontrolled diabetes, what happens to cells lacking glucose?
How do non-steroid hormones primarily exert their effects on target cells?
How do non-steroid hormones primarily exert their effects on target cells?
What type of response is typically associated with steroid hormones compared to non-steroid hormones?
What type of response is typically associated with steroid hormones compared to non-steroid hormones?
What role does the hypothalamus play in hormone release?
What role does the hypothalamus play in hormone release?
What physiological change does oxytocin induce in response to infant nursing?
What physiological change does oxytocin induce in response to infant nursing?
Which of the following best describes the release mechanism of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Which of the following best describes the release mechanism of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Which of the following hormones can be classified as a non-steroid hormone?
Which of the following hormones can be classified as a non-steroid hormone?
Flashcards
Hormones
Hormones
Chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream, influencing various bodily functions.
Steroid Hormones
Steroid Hormones
Lipid-soluble hormones (made from cholesterol) that can cross cell membranes and act on receptors within the cell.
Non-Steroid Hormones
Non-Steroid Hormones
Fat-insoluble hormones (made from amino acids) that act on cell membrane receptors, triggering intracellular responses.
Oxytocin
Oxytocin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Target Cells
Target Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormone Receptors
Hormone Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH Function 1
ADH Function 1
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH Function 2
ADH Function 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prolactin
Prolactin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prolactin Regulation
Prolactin Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth Hormone (GH)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gigantism
Gigantism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH & FSH in Puberty
LH & FSH in Puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH & LH in Females
FSH & LH in Females
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH & LH in Males
FSH & LH in Males
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone's Role
Testosterone's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's Role
Estrogen's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone's Role
Progesterone's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon's Function
Glucagon's Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin's Function
Insulin's Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II Diabetes Risk
Type II Diabetes Risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Symptom: Frequent Urination
Diabetes Symptom: Frequent Urination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Symptom: Fatigue
Diabetes Symptom: Fatigue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Symptom: Weight Loss
Diabetes Symptom: Weight Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uncontrolled Diabetes: Acidosis
Uncontrolled Diabetes: Acidosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uncontrolled Diabetes: Blood Vessel Damage
Uncontrolled Diabetes: Blood Vessel Damage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin Injection Complications: Hypoglycemia
Insulin Injection Complications: Hypoglycemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Managing Diabetes: Exercise
Managing Diabetes: Exercise
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are hormones?
What are hormones?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steroid hormone action
Steroid hormone action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-steroid hormone action
Non-steroid hormone action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxytocin: Function 1
Oxytocin: Function 1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxytocin: Function 2
Oxytocin: Function 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxytocin: Function 3
Oxytocin: Function 3
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH function: Water balance
ADH function: Water balance
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH function: Blood pressure
ADH function: Blood pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH and Blood Pressure
ADH and Blood Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prolactin's Role
Prolactin's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growth Hormone: What it Does
Growth Hormone: What it Does
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gigantism: Too Much Growth Hormone
Gigantism: Too Much Growth Hormone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly: Growth Hormone Excess in Adults
Acromegaly: Growth Hormone Excess in Adults
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pituitary Dwarfism
Pituitary Dwarfism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Puberty Trigger
Puberty Trigger
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH/FSH in Females
LH/FSH in Females
Signup and view all the flashcards
LH/FSH in Males
LH/FSH in Males
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone's Effects
Testosterone's Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's Effects
Estrogen's Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucagon's Role
Glucagon's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin's Role
Insulin's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Types
Diabetes Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes and Blood Glucose
Diabetes and Blood Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes and Fatigue
Diabetes and Fatigue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes and Weight Loss
Diabetes and Weight Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Management: Exercise
Diabetes Management: Exercise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parathyroid Hormone Function
Parathyroid Hormone Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Endocrine System
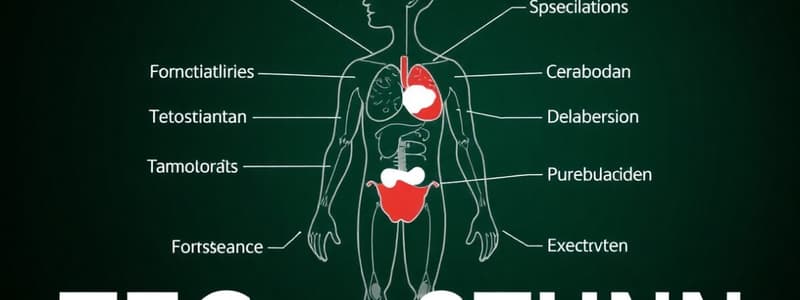
- Hormones are molecules acting as messages between body parts.
- Hormones are produced in endocrine glands.
- Hormones circulate in the blood, reaching all cells.
- Hormones only affect target cells with specific protein receptors.
Steroid Hormones
- Lipid soluble, derived from cholesterol.
- Cross cell membranes easily.
- Bind to receptors within target cells.
- Action is slower, requiring new protein synthesis.
- Examples: estrogen, progesterone, testosterone.
Steroid Hormone Action
- Steroid hormone diffuses into target cell.
- Binds to receptor protein inside target cell.
- Hormone-receptor complex enters nucleus.
- Hormone-receptor complex activates genes.
- Activation leads to protein synthesis.
- New protein alters cell activity.
Non-Steroid Hormones
- Fat insoluble, derived from amino acids.
- Cannot cross cell membranes.
- Bind to receptors on cell membranes of target cells.
- Trigger second messengers within target cells.
- Second messengers activate enzymes within cells.
- Action is quicker than steroid hormones.
- Examples: glucagon, epinephrine, norepinephrine.
Non-Steroid Hormone Action
- Non-steroid hormone binds to receptor on target cell membrane.
- Binding activates a second messenger, often cyclic AMP (cAMP).
- cAMP activates enzymes.
- Enzymes cause changes within target cell, inducing cell activity.
Hypothalamus and Posterior Pituitary Gland
- The hypothalamus releases hormones into the posterior pituitary.
- Oxytocin: causes uterus contractions during childbirth; triggers affection and milk ejection during breastfeeding.
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (vasopressin): causes kidneys to retain more water; raises blood pressure.
Anterior Pituitary Gland
- Hypothalamus triggers the anterior pituitary to produce several hormones.
- Prolactin: stimulates milk production.
- Growth hormone: promotes protein synthesis and cell division.
- Affects bone and muscle growth through chondroblasts.
- Pituitary dwarfism: insufficient growth hormone.
- Gigantism: excess growth hormone causing excess growth during childhood.
- Acromegaly: excess growth hormone during adulthood causing enlarged bones and soft tissues.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) / Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Maturation of neurons in hypothalamus triggers LH and FSH production.
- LH and FSH trigger puberty.
- FSH/LH in females stimulate estrogen/progesterone secretion by ovaries.
- FSH/LH in males stimulate testosterone secretion in testes.
- FSH is essential for sperm development.
- LH plays a role in testosterone production.
Testosterone and Puberty
- Testosterone, a steroid hormone, causes: increased sperm production, penis/testis growth, bone lengthening, muscle growth, hairiness, enlarged larynx, increased male sex drive and aggression.
Estrogen, Progesterone and Puberty
- Estrogen, a steroid hormone, causes: long bone growth, widening pelvis, redistribution of fat to hips and breasts.
- Progesterone, a steroid hormone, is crucial for the menstrual cycle, including ovulation, and maintaining a thickened uterus during pregnancy.
- Minute amounts of testosterone-like hormones are secreted by adrenal glands in women. These hormones have limited effects on women as men already have significant testosterone levels.
Pancreas: Endocrine Homeostasis
- Alpha cells in the pancreas produce glucagon.
- Glucagon raises blood sugar levels by converting glycogen to glucose, converting amino acids to glucose, and releasing fatty acids from triglycerides.
- Beta cells in the pancreas produce insulin to decrease blood sugar.
- Insulin allows glucose to enter liver, muscles and adipose tissues and to turn it to glycogen and fat.
Diabetes Mellitus
- Type I Diabetes: insufficient insulin production, autoimmune disease.
- Type II Diabetes: insulin resistant cells, often related to obesity.
- Signs of Diabetes: high blood sugar, frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision; glucose in the urine.
Uncontrolled Diabetes: Health Problems
- Uncontrolled diabetes causes ketone production.
- Metabolic acidosis can occur (low blood pH)
- Can lead to confusion, tiredness, or death.
- Can damage blood vessels, leading to conditions like blindness, stroke, heart attack, kidney failure, reduced circulation, gangrene, and amputation.
- Poor blood circulation can lead to lack of feeling in the extremities and cause wounds that do not heal properly.
Controlling Diabetes
- Monitoring blood sugar regularly to ensure levels are neither too high nor too low.
- Type I diabetics require daily insulin injections, while some Type II diabetics may also need insulin.
- Avoiding sugar-heavy foods is crucial for effective blood sugar control.
- Exercise can help control blood sugar without requiring insulin.
- Checking toes regularly for any sign of abnormalities is important.
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
- Thyroid and parathyroid glands release calcitonin and parathyroid hormone.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
- Released to increase blood calcium levels.
- Removes calcium from bone (stimulates osteoclasts).
- Increases absorption in digestive tract (activates Vitamin D).
- Increases kidney retention of calcium.
Calcitonin
- Released to decrease blood calcium levels.
- Adds calcium to bone (stimulates osteoblasts).
- Decreases calcium absorption in digestive tract.
- Decreases calcium retention in kidneys.
Erythropoietin
- Stimulates red blood cell production in bone marrow.
Epinephrine/Norepinephrine
- Increased heart rate, respiratory rate, blood flow to skeletal muscles (fight or flight response).
- Released by adrenal medulla in response to sympathetic nervous system stimulation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.