Podcast
Questions and Answers
How does the pleural fluid reduce friction during ventilation?
How does the pleural fluid reduce friction during ventilation?
- It actively contracts and expands to aid lung movement.
- It provides a cushion between the ribs and the lungs.
- It acts as a lubricant between the lungs and the inner wall of the thorax. (correct)
- It creates a vacuum between the lungs and the diaphragm.
What is the primary role of the diaphragm during ventilation?
What is the primary role of the diaphragm during ventilation?
- To separate the thorax from the abdomen and aid in changing the volume of the thoracic cavity. (correct)
- To provide structural support to the trachea and bronchi.
- To facilitate gas exchange in the alveoli.
- To protect the lungs from external impact.
Why is the trachea structurally reinforced with semi-circles of cartilage?
Why is the trachea structurally reinforced with semi-circles of cartilage?
- To facilitate the contraction and expansion of the intercostal muscles.
- To provide flexibility while preventing collapse during pressure changes. (correct)
- To enable the trachea to secrete mucus efficiently.
- To allow the trachea to expand in length during deep inhalation.
How does the contraction of the external intercostal muscles contribute to inhalation?
How does the contraction of the external intercostal muscles contribute to inhalation?
What is the relationship between lung pressure and atmospheric pressure during inhalation?
What is the relationship between lung pressure and atmospheric pressure during inhalation?
Which of the following events occurs during inhalation?
Which of the following events occurs during inhalation?
What facilitates the expansion of the lungs during inhalation, according to the text?
What facilitates the expansion of the lungs during inhalation, according to the text?
Which of the following best describes 'negative pressure breathing' as it relates to mammalian ventilation?
Which of the following best describes 'negative pressure breathing' as it relates to mammalian ventilation?
What is the function of the bronchioles?
What is the function of the bronchioles?
How do the internal and external intercostal muscles work together during breathing?
How do the internal and external intercostal muscles work together during breathing?
Flashcards
What is the thorax?
What is the thorax?
An airtight compartment that encloses the lungs.
What are pleural membranes?
What are pleural membranes?
Membranes that surround each lung and line the thorax, containing pleural fluid.
What is the diaphragm?
What is the diaphragm?
A dome-shaped muscle at the base of the thorax that separates it from the abdomen.
What is the trachea?
What is the trachea?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the bronchi?
What are the bronchi?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are bronchioles?
What are bronchioles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are alveoli?
What are alveoli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is inspiration (inhalation)?
What is inspiration (inhalation)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to the ribs and intercostal muscles during inhalation?
What happens to the ribs and intercostal muscles during inhalation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to the diaphragm during inhalation?
What happens to the diaphragm during inhalation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
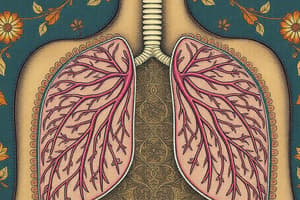
Structure of the Human Breathing System
- The lungs are enclosed in the thorax, an airtight compartment.
- Pleural membranes surround each lung and line the thorax.
- The pleural cavity sits between the pleural membranes and contains a few cm³ of pleural fluid, which acts as a lubricant.
- The pleural fluid prevents friction between the lungs and the inner wall of the thorax during ventilation.
- A dome-shaped sheet of muscle, the diaphragm, separates the thorax from the abdomen and sits at the base of the thorax.
- The ribs surround the thorax.
- Intercostal muscles are located between the ribs.
- The trachea is a flexible airway that brings air to the lungs.
- The two bronchi are branches of the trachea.
- The lungs consist of a branching network of tubes called bronchioles, which arise from the bronchi.
- Air sacs called alveoli sit at the ends of the bronchioles.
- Cartilage rings around the trachea are incomplete at the back to allow the oesophagus to bulge when swallowing a bolus of food.
Ventilation of the Lungs
- Mammals ventilate their lungs through negative pressure breathing, where the pressure inside the lungs must be below atmospheric pressure for air to enter.
- Breathing in(inspiration/inhalation): This is an active process because muscle contraction requires energy.
- The external intercostal muscles contract.
- The ribs are pulled upwards and outwards.
- The diaphragm muscles contract, so the diaphragm flattens at the same time as the above.
- The outer pleural membrane is attached to the thoracic cavity wall, so it is pulled up and out with the ribs and the lower part is pulled down with the diaphragm.
- The inner membrane follows, so the lungs expand, increasing the volume inside the alveoli.
- This reduces the pressure in the lungs.
- Atmospheric air pressure is now greater than the pressure in the lungs, so air is forced into the lungs.
- The internal intercostal muscles are antagonistic to the external intercostal muscles as they relax when the external intercostal muscles contract in inspiration and vice versa on expiration.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.