Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of these processes is NOT involved in mechanical digestion?
Which of these processes is NOT involved in mechanical digestion?
- Mixing food with saliva
- Breaking down starches into sugars (correct)
- Using teeth to grind food
- Chewing food
Which of the following is a function of the salivary amylase enzyme?
Which of the following is a function of the salivary amylase enzyme?
- Breaking down fats into fatty acids
- Breaking down proteins into amino acids
- Absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream
- Breaking down starches into sugars (correct)
Which of these body systems works directly with the digestive system to provide the body with energy?
Which of these body systems works directly with the digestive system to provide the body with energy?
- Respiratory system (correct)
- Circulatory system
- Excretory system
- Nervous system
Which organ is responsible for preventing food from entering the lungs during swallowing?
Which organ is responsible for preventing food from entering the lungs during swallowing?
What are the main types of molecules that the digestive system breaks down for the body to use as energy?
What are the main types of molecules that the digestive system breaks down for the body to use as energy?
Which of the following is the correct order of organs in the digestive system?
Which of the following is the correct order of organs in the digestive system?
What is the main function of the small intestine?
What is the main function of the small intestine?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the digestive system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the digestive system?
Which of these correctly describes the flow of air into the lungs?
Which of these correctly describes the flow of air into the lungs?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the excretory system?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the excretory system?
What is the primary function of bronchioles in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of bronchioles in the respiratory system?
Why does oxygen diffuse from the alveoli into the capillaries?
Why does oxygen diffuse from the alveoli into the capillaries?
What is the primary function of the bladder?
What is the primary function of the bladder?
What is the main role of the circulatory system in the body?
What is the main role of the circulatory system in the body?
What is the primary function of the skin in excretion?
What is the primary function of the skin in excretion?
How are arteries and veins different?
How are arteries and veins different?
What is the role of the renal arteries in the excretory system?
What is the role of the renal arteries in the excretory system?
Which of the following components is NOT part of the central nervous system?
Which of the following components is NOT part of the central nervous system?
Which muscle plays a crucial role in inhalation by contracting and pulling air into the lungs?
Which muscle plays a crucial role in inhalation by contracting and pulling air into the lungs?
What is the primary function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
What is the function of dendrites in a neuron?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems?
Which of the following best describes how the nervous system allows the body to react to changes in the environment?
Which of the following best describes how the nervous system allows the body to react to changes in the environment?
Which of the following is a function of the peripheral nervous system?
Which of the following is a function of the peripheral nervous system?
Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart?
Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart?
Which organ converts ammonia into urea?
Which organ converts ammonia into urea?
What is the primary function of the excretory system?
What is the primary function of the excretory system?
Where does the blood go after leaving the lungs?
Where does the blood go after leaving the lungs?
Which of the following is NOT a waste product removed by the excretory system?
Which of the following is NOT a waste product removed by the excretory system?
What is the role of the nephrons in the kidneys?
What is the role of the nephrons in the kidneys?
What is the approximate amount of urine produced by the kidneys each day?
What is the approximate amount of urine produced by the kidneys each day?
Which of the following blood vessels has the thickest muscular wall?
Which of the following blood vessels has the thickest muscular wall?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the central nervous system?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the central nervous system?
Which type of neuron carries messages from the central nervous system to muscles and organs?
Which type of neuron carries messages from the central nervous system to muscles and organs?
What is the function of the cerebellum?
What is the function of the cerebellum?
What is the function of interneurons?
What is the function of interneurons?
Which of the following is NOT involved in a reflex response?
Which of the following is NOT involved in a reflex response?
What is the purpose of the skin receptors?
What is the purpose of the skin receptors?
Why do certain areas of the body have a keener sense of touch than others?
Why do certain areas of the body have a keener sense of touch than others?
Which of the following is an example of a reflex?
Which of the following is an example of a reflex?
Which of the following is NOT a component of gastric juices?
Which of the following is NOT a component of gastric juices?
What is the function of bile in digestion?
What is the function of bile in digestion?
What is the role of villi in the small intestine?
What is the role of villi in the small intestine?
Which of the following is a function of the large intestine?
Which of the following is a function of the large intestine?
Why does the color of the bromothymol blue solution in test tube A change after blowing into it?
Why does the color of the bromothymol blue solution in test tube A change after blowing into it?
What is the primary reason for the danger of mountain climbing at high altitudes?
What is the primary reason for the danger of mountain climbing at high altitudes?
What is the main function of the digestive system?
What is the main function of the digestive system?
Flashcards
Cells
Cells
The basic building blocks of all living organisms that perform essential functions.
Tissues
Tissues
Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Organs
Organs
Structures made of different tissues that perform specific tasks in the body.
Structure and Function
Structure and Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical Digestion
Mechanical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Digestion
Chemical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestive System
Digestive System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Response to Stimuli
Response to Stimuli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing
Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins
Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart
Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristalsis
Peristalsis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric juices
Gastric juices
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucus in the stomach
Mucus in the stomach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small intestine
Small intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreas
Pancreas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver
Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large intestine
Large intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal arteries
Renal arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureters
Ureters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder
Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excretory system function
Excretory system function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurons
Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central nervous system
Central nervous system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensory Neurons
Sensory Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motor Neurons
Motor Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebrum
Cerebrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex
Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interneurons
Interneurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Touch Receptors
Touch Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right side of the heart
Right side of the heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left side of the heart
Left side of the heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow loops
Blood flow loops
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys
Kidneys
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Healthy Human Function
- Human function depends on interacting and reacting systems
- Organ systems work together as a single unit to support survival
- Each organ system reacts to internal and external changes to maintain life
Key Concepts
- Cells
- Organs
- Tissues
- Structure and function
- Responses to stimuli
- Systems
Learning Outcomes
- Describe how various body systems work
- Recognize organ and tissue roles in body systems
- Describe how cells help the body function
- Demonstrate how the body responds to changing conditions
Digestive System
- Living organisms need energy from carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
- The digestive system breaks down food into usable parts
- Mechanical digestion breaks food into smaller pieces, while chemical digestion uses enzymes to further break down large particles.
Digestive System Activity
- Chew crackers and hold in mouth for 5 minutes without swallowing
- Describe taste changes over time
- Compare experiences with classmates
- Identify causes for taste changes
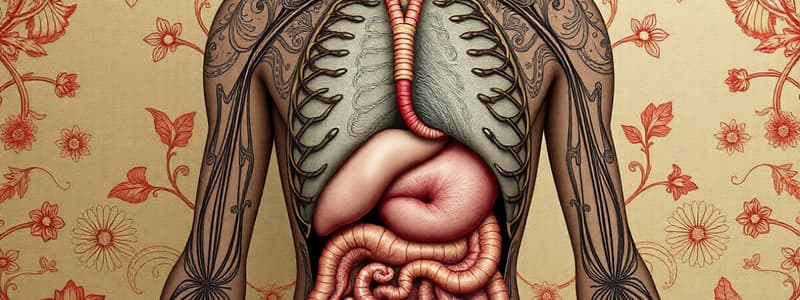
Food's Path Through the Digestive System
-
Digestion begins in the mouth with mechanical breakdown by teeth and saliva, which contains salivary amylase to break down starches into smaller sugars
-
Saliva moistens food for easier swallowing
-
Epiglottis prevents food from entering the windpipe during swallowing
-
Peristalsis moves food through the esophagus
-
Stomach churns food with gastric juice (mucus, hydrochloric acid, water, and enzymes) which breaks down proteins.
-
The stomach slowly releases food into the small intestine
Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, and Gall Bladder
- Mechanical and chemical digestion continues in the small intestine
- Pancreas and liver contribute enzymes and bile for further digestion
- Villi and microvilli in the small intestine increase absorption surface area
- Nutrients are absorbed through blood vessel by the villi.
- Large intestine absorbs water and forms feces.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system supplies the blood with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
- Breathing involves inhaling and exhaling to move air in and out of the lungs
- The process exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the alveoli
Circulatory System
- The circulatory system delivers nutrients, oxygen, and removes waste
- The heart acts as a pump to circulate blood in two loops: to the lungs and throughout the body.
- Blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) are part of the circulatory system
- Blood contains red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma
Heart
- The heart has four chambers (two atria and two ventricles)
- Blood flows through the heart in a specific pattern (oxygen-rich to body; oxygen-poor to lungs)
Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, veins return blood to the heart
- Capillaries are thin-walled vessels found between arteries and veins. This allows for efficient gas exchange between blood and tissues.
Excretory System
- The excretory system removes waste products from the body
- Waste products include carbon dioxide, urea, water and salts
- The liver converts ammonia (toxic) into urea(less harmful)
The Kidney
- Kidneys are the main organs of excretion.
- They filter blood and produce urine.
- Urine is expelled from the body through the ureters and urethra.
- Urea is produced from waste products.
The Skin
- Skin excretes sweat containing salt.
The Formation of Urine
- The kidneys filter waste products from the blood to form urine
- Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery
- Waste products are removed from the blood and sent to the bladder through the ureters
Testing Artificial Urine
- Urine can reveal diseases
- Testing urine can determine the presence of certain diseases e.g., diabetes or kidney failure
- Lab tests for glucose and protein in urine can be done to detect diseases
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.