Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the pores of Kohn in the alveoli?
What is the primary function of the pores of Kohn in the alveoli?
- To allow movement of immune cells between alveoli (correct)
- To maintain the structure of alveoli
- To secrete mucus for trapping microorganisms
- To facilitate gas exchange between blood and alveoli
Which gas diffuses from the alveoli into the blood during gas exchange?
Which gas diffuses from the alveoli into the blood during gas exchange?
- Nitrogen
- Water vapor
- Carbon monoxide
- Oxygen (correct)
What is the primary role of type I alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs?
What is the primary role of type I alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs?
- Secretion of pulmonary surfactant
- Production of alveolar macrophages
- Maintenance of the gas-blood barrier and gas exchange (correct)
- Defense against pathogens
What percentage of the total alveolar surface do type I alveolar epithelial cells comprise?
What percentage of the total alveolar surface do type I alveolar epithelial cells comprise?
What is the thickness of the alveolar-capillary membrane?
What is the thickness of the alveolar-capillary membrane?
What happens to the Pco2 levels in capillary blood after gas exchange?
What happens to the Pco2 levels in capillary blood after gas exchange?
At which anatomical level is the carina positioned?
At which anatomical level is the carina positioned?
What is the main function of type II alveolar epithelial cells?
What is the main function of type II alveolar epithelial cells?
Where does the pulmonary artery receive blood from?
Where does the pulmonary artery receive blood from?
What prevents the trachea from collapsing during bronchoconstriction?
What prevents the trachea from collapsing during bronchoconstriction?
What happens to the lungs when there is a severe loss of pulmonary surfactant?
What happens to the lungs when there is a severe loss of pulmonary surfactant?
How are alveolar macrophages formed?
How are alveolar macrophages formed?
Which arteries supply the tissues in the left side of the thorax?
Which arteries supply the tissues in the left side of the thorax?
Which bronchus is wider and angles more directly toward the lung?
Which bronchus is wider and angles more directly toward the lung?
What component primarily makes up pulmonary surfactant?
What component primarily makes up pulmonary surfactant?
What type of blood does the left atrium normally contain?
What type of blood does the left atrium normally contain?
What generation of the bronchial tree includes the main stem bronchi?
What generation of the bronchial tree includes the main stem bronchi?
What is the main cause of diffusion stopping in the alveolar-capillary membrane?
What is the main cause of diffusion stopping in the alveolar-capillary membrane?
What effect does pulmonary disease have on surfactant synthesis?
What effect does pulmonary disease have on surfactant synthesis?
Which of these bronchioles have a diameter of less than 1 mm?
Which of these bronchioles have a diameter of less than 1 mm?
Which cell type is most susceptible to injury in the pulmonary system?
Which cell type is most susceptible to injury in the pulmonary system?
In which part of the respiratory system does gas exchange primarily occur?
In which part of the respiratory system does gas exchange primarily occur?
Which generation of bronchi do the segmental bronchi belong to?
Which generation of bronchi do the segmental bronchi belong to?
How many alveoli are approximately contained in each terminal respiratory unit?
How many alveoli are approximately contained in each terminal respiratory unit?
What is the primary factor that determines the direction of diffusion of gases in the lungs?
What is the primary factor that determines the direction of diffusion of gases in the lungs?
How does supplemental oxygen affect the driving pressure of oxygen?
How does supplemental oxygen affect the driving pressure of oxygen?
What is true regarding the diffusion coefficient of gases?
What is true regarding the diffusion coefficient of gases?
Which condition would decrease the rate of gas diffusion across the alveolar-capillary membrane?
Which condition would decrease the rate of gas diffusion across the alveolar-capillary membrane?
At high altitudes, what impact does gravity have on the diffusion of oxygen?
At high altitudes, what impact does gravity have on the diffusion of oxygen?
Which of the following best describes gas transport within the body?
Which of the following best describes gas transport within the body?
What happens to carbon dioxide in the lungs during diffusion?
What happens to carbon dioxide in the lungs during diffusion?
How do conditions like pulmonary edema affect diffusion?
How do conditions like pulmonary edema affect diffusion?
What is one of the primary functions of the lymphatic system in the lungs?
What is one of the primary functions of the lymphatic system in the lungs?
What is the primary reason the lungs have a rich supply of lymphatic tissue?
What is the primary reason the lungs have a rich supply of lymphatic tissue?
Which pressure is typically less than atmospheric pressure in a normal lung?
Which pressure is typically less than atmospheric pressure in a normal lung?
What is the term used for the movement of air into the lungs?
What is the term used for the movement of air into the lungs?
What typically measures pressure at sea level?
What typically measures pressure at sea level?
What occurs during external respiration?
What occurs during external respiration?
Which pressure is affected by the size of the thorax?
Which pressure is affected by the size of the thorax?
What type of particles does the lymphatic system in the lungs help to remove?
What type of particles does the lymphatic system in the lungs help to remove?
Which factor does NOT contribute to an increased work of breathing?
Which factor does NOT contribute to an increased work of breathing?
What is the primary function of pulmonary surfactant?
What is the primary function of pulmonary surfactant?
Which muscle is NOT typically involved in accessory breathing?
Which muscle is NOT typically involved in accessory breathing?
What is the approximate tidal volume (VT) during normal breathing?
What is the approximate tidal volume (VT) during normal breathing?
Which pulmonary capacity represents the maximal amount of air that can be inhaled?
Which pulmonary capacity represents the maximal amount of air that can be inhaled?
Which gas exchange is referred to as internal respiration?
Which gas exchange is referred to as internal respiration?
What is the residual volume (RV) typically in the lungs after a forced expiration?
What is the residual volume (RV) typically in the lungs after a forced expiration?
Which volume is included in the calculation of inspiratory capacity (IC)?
Which volume is included in the calculation of inspiratory capacity (IC)?
Which structure separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities?
Which structure separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities?
How many lung segments are located in the right lung?
How many lung segments are located in the right lung?
What type of pleura adheres directly to the lungs?
What type of pleura adheres directly to the lungs?
Which area contains the heart, great vessels, and esophagus?
Which area contains the heart, great vessels, and esophagus?
What is the normal range of intrapleural pressure during inhalation?
What is the normal range of intrapleural pressure during inhalation?
Which muscles are responsible for decreasing the size of the chest during exhalation?
Which muscles are responsible for decreasing the size of the chest during exhalation?
During deep inhalation, what intrapleural pressure can be generated?
During deep inhalation, what intrapleural pressure can be generated?
What is the primary muscle responsible for the majority of the work of breathing during normal, quiet breathing?
What is the primary muscle responsible for the majority of the work of breathing during normal, quiet breathing?
Which nerve is primarily responsible for controlling the diaphragm's actions during breathing?
Which nerve is primarily responsible for controlling the diaphragm's actions during breathing?
What occurs during exhalation in a healthy lung?
What occurs during exhalation in a healthy lung?
Which muscles are considered accessory muscles of ventilation during exercise?
Which muscles are considered accessory muscles of ventilation during exercise?
What is one of the main purposes of the conducting airways?
What is one of the main purposes of the conducting airways?
During inhalation, how does the diaphragm affect the abdomen?
During inhalation, how does the diaphragm affect the abdomen?
Which group of muscles is primarily active during normal inhalation?
Which group of muscles is primarily active during normal inhalation?
What happens to the activity of the accessory muscles during exercise?
What happens to the activity of the accessory muscles during exercise?
What is the composition of the upper airway structures?
What is the composition of the upper airway structures?
What happens during inhalation when intrapulmonary pressure falls?
What happens during inhalation when intrapulmonary pressure falls?
Which factors primarily determine the work of breathing?
Which factors primarily determine the work of breathing?
What happens during expiration when intrapulmonary pressure rises?
What happens during expiration when intrapulmonary pressure rises?
Which pulmonary disease is associated with decreased lung compliance?
Which pulmonary disease is associated with decreased lung compliance?
Which condition is likely to increase airway resistance?
Which condition is likely to increase airway resistance?
At what level is the carina typically positioned?
At what level is the carina typically positioned?
What is the function of the C-shaped cartilaginous rings in the trachea?
What is the function of the C-shaped cartilaginous rings in the trachea?
Which bronchus is narrower and angles toward the left lung?
Which bronchus is narrower and angles toward the left lung?
What is the most common site of aspiration for foreign objects in the lungs?
What is the most common site of aspiration for foreign objects in the lungs?
What do the fourth to ninth generations of the bronchi consist of?
What do the fourth to ninth generations of the bronchi consist of?
What is the diameter of bronchioles?
What is the diameter of bronchioles?
What marks the transition zone of the lungs for gas exchange?
What marks the transition zone of the lungs for gas exchange?
How many alveolar ducts does each respiratory bronchiole give rise to?
How many alveolar ducts does each respiratory bronchiole give rise to?
How many segmental bronchi are included in the bronchial tree?
How many segmental bronchi are included in the bronchial tree?
What is the primary characteristic of the walls of bronchioles?
What is the primary characteristic of the walls of bronchioles?
What process helps keep the alveoli clean and sterile?
What process helps keep the alveoli clean and sterile?
What is the primary role of the pulmonary artery?
What is the primary role of the pulmonary artery?
During gas exchange, why does oxygen diffuse from the alveoli into the blood?
During gas exchange, why does oxygen diffuse from the alveoli into the blood?
How does the capillary blood Pco2 level change after gas exchange?
How does the capillary blood Pco2 level change after gas exchange?
What is the thickness of the alveolar-capillary membrane critical for diffusion?
What is the thickness of the alveolar-capillary membrane critical for diffusion?
What is a typical characteristic of blood entering the pulmonary capillaries?
What is a typical characteristic of blood entering the pulmonary capillaries?
Where does blood go after gas exchange in the alveoli?
Where does blood go after gas exchange in the alveoli?
What role does physiological shunting play in the pulmonary circulation?
What role does physiological shunting play in the pulmonary circulation?
Which of these structures branches off from the aorta to perfuse the left side of the thorax?
Which of these structures branches off from the aorta to perfuse the left side of the thorax?
How does the diffusion of gases across the alveolar-capillary membrane occur?
How does the diffusion of gases across the alveolar-capillary membrane occur?
Flashcards
Carina location
Carina location
The carina (where the trachea branches into the two main bronchi) is roughly at the level of the aortic arch, fifth thoracic vertebra, or slightly below the angle of Louis.
Trachea structure
Trachea structure
The trachea is made of C-shaped cartilaginous rings, which support its structure and prevent collapse, especially during inhalation and exhalation.
Right bronchus angle
Right bronchus angle
The right main stem bronchus angles about 20-30 degrees from the midline.
Left bronchus angle
Left bronchus angle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aspiration risk
Aspiration risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchial generations
Bronchial generations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchioles structure
Bronchioles structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli function
Alveoli function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation: Start
Pulmonary Circulation: Start
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation: Pathway
Pulmonary Circulation: Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation: Return
Pulmonary Circulation: Return
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Capillary Membrane: Structure
Alveolar Capillary Membrane: Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Capillary Membrane: Function
Alveolar Capillary Membrane: Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange: Direction
Gas Exchange: Direction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange: Equilibrium
Gas Exchange: Equilibrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchial Arteries: Supply
Bronchial Arteries: Supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli: The Gas Exchange Hub
Alveoli: The Gas Exchange Hub
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type I Alveolar Cells: Thin Walls
Type I Alveolar Cells: Thin Walls
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II Alveolar Cells: Surfactant Makers
Type II Alveolar Cells: Surfactant Makers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surfactant: Keeping Alveoli Open
Surfactant: Keeping Alveoli Open
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Macrophages: Lung Cleaners
Alveolar Macrophages: Lung Cleaners
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Alveolar Macrophages?
What are Alveolar Macrophages?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Roles in Gas Exchange
Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Roles in Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is Surfactant Important?
Why is Surfactant Important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Circulation
Lymphatic Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Vessel Location
Lymphatic Vessel Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic Drainage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air Movement
Air Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhalation vs. Exhalation
Inhalation vs. Exhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Respiration
External Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Respiration
Internal Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pressure Gradient for Ventilation
Pressure Gradient for Ventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Surfactant - Decreasing Factors
Pulmonary Surfactant - Decreasing Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Work of Breathing - Increase
Work of Breathing - Increase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accessory Muscles - Increased Work
Accessory Muscles - Increased Work
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tidal Volume
Tidal Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expiratory Reserve Volume
Expiratory Reserve Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Residual Volume
Residual Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inspiratory Capacity
Inspiratory Capacity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion
Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Driving pressure
Driving pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Diffusion in Lungs
Oxygen Diffusion in Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide Diffusion in Lungs
Carbon Dioxide Diffusion in Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Factors Affecting Diffusion Rate
Factors Affecting Diffusion Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion Coefficient
Diffusion Coefficient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Transport: Bloodstream
Gas Transport: Bloodstream
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissue Level Gas Exchange
Tissue Level Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oblique Fissure
Oblique Fissure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lung Lobes
Lung Lobes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mediastinum: What's inside?
Mediastinum: What's inside?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pleura: Double-Layered Membrane
Pleura: Double-Layered Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrapleural Pressure
Intrapleural Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles of Ventilation
Muscles of Ventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm: Key Inhalation Muscle
Diaphragm: Key Inhalation Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm's Role in Breathing
Diaphragm's Role in Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phrenic Nerve's Function
Phrenic Nerve's Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens during exhalation?
What happens during exhalation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why do we need accessory muscles for breathing?
Why do we need accessory muscles for breathing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the conducting airways?
What is the purpose of the conducting airways?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do the upper and lower airways differ?
How do the upper and lower airways differ?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the C3-C5 injury impact?
What is the C3-C5 injury impact?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What muscles help with inhalation?
What muscles help with inhalation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between normal and active exhalation?
What is the difference between normal and active exhalation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inspiration (Inhalation)
Inspiration (Inhalation)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expiration (Exhalation)
Expiration (Exhalation)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Work of Breathing
Work of Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Properties of Lungs
Elastic Properties of Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resistive Properties of Lungs
Resistive Properties of Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Main Stem Bronchus
Right Main Stem Bronchus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Main Stem Bronchus
Left Main Stem Bronchus
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Bronchioles?
What are Bronchioles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Alveoli?
What are Alveoli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Airways
Respiratory Airways
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Respiratory Bronchioles?
What are Respiratory Bronchioles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Aspiration?
What is Aspiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiological Shunting
Physiological Shunting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Pulmonary Anatomy and Physiology
- The pulmonary system comprises the thorax, conducting airways, respiratory airways, and pulmonary blood and lymph supply.
- The primary functions of the pulmonary system are ventilation and respiration.
- Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs, involving oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release.
- Respiration is the process of gas exchange, where oxygen is taken into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is expelled.
- A strong understanding of anatomy and physiology is critical for patient care in cases of pulmonary dysfunction.
Thorax
- The thorax houses the major organs of respiration and is a cone-shaped structure with a rigid frame.
- The framework features 12 thoracic vertebrae, ribs, and the sternum.
- Ribs are attached to the vertebrae posteriorly and, in the anterior portion, their attachment varies. The first seven pairs are directly linked to the sternum while the 8th, 9th, and 10th attach to the ribs above by cartilage. The 11th and 12th, also referred to as floating ribs, lack anterior attachment.
- The second rib attaches to the sternum at the angle of Louis, a notable ridge beneath the suprasternal notch.
- The thorax's components form a ventilatory pump, the mechanism for breathing.
Lungs
- Lungs are cone-shaped organs, with an apex (superior portion) and a base (inferior portion).
- The apex of each lung extends a few centimeters above the clavicle.
- The right lung, larger and heavier than the left, is divided into three lobes (upper, middle, and lower).
- The left lung is divided into two lobes (upper and lower).
- Fissures divide the lobes. Lobes are further separated into segments (a total of 18). Each has its own bronchus branching. Ten segments are found in the right lung, and eight in the left.
Mediastinum
- The mediastinum sits between the lungs, encompassing the heart, great vessels, lymphatics, and esophagus.
Pleura
- The pleura is a thin membrane that lines the outside of the lungs and the inside of the chest wall.
- The visceral pleura attaches to the lungs, extending to the hilar bronchi and major fissures.
- The parietal pleura lines the inner chest wall and mediastinum.
- An airtight space exists between these pleural membranes, containing a lubricating fluid.
- The pleural membranes glide over each other without friction during breathing.
Intrapleural Pressure
- Intrapleural pressure is the pressure within the pleural space. It's less than intrapulmonary and atmospheric pressure.
- Under normal conditions, it ranges from 4 to -10 cm H₂O during inhalation and exhalation.
- Deep inhalation can create intrapleural pressure of 12 to -18 cm H₂O.
Muscles of Ventilation
- The central nervous system governs the muscles of ventilation through nerve impulses that cause their contraction and relaxation.
- Muscles that expand the chest are called inhalatory muscles, and those that reduce chest size are called exhalatory muscles.
- The diaphragm is the principal inspiratory muscle; during quiet breathing, it contributes to about 80% of the work involved. This dome-shaped fibromuscular structure separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
- Accessory muscles such as the sternocleidomastoid, scalene, and pectoral muscles aid in breathing, particularly during exercise.
- Exhalation in healthy individuals is usually passive and requires minimal energy.
Conducting Airways
- The conducting airways (upper and lower) warm and moisten inhaled air.
- They also function as a protective barrier against foreign particles entering the gas exchange areas.
- The upper airways comprise structures above the glottis (nose, mouth, pharynx).
- The lower airways are below the glottis (larynx, trachea, bronchi).
Larynx
- The larynx, or voice box, consists of nine cartilages, six of which are paired and three are unpaired.
- The unpaired cartilages—thyroid (Adam's apple), cricoid, and epiglottis—are crucial.
- The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped cartilage that prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing.
- The vocal cords regulate the airflow and are responsible for voice production.
Trachea
- The trachea is the windpipe, roughly 11 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter.
- It's a hollow tube, supported by C-shaped cartilaginous rings, and connects the larynx to the bronchi branching at the carina.
- The trachea divides into two main bronchi.
Bronchial Tree
- The bronchial tree has sequentially branching structures within the lungs.
- Bronchi split into progressively smaller structures such as lobar, segmental, and subsegmental bronchi.
- Finally, they divide into bronchioles, then to alveolar ducts and alveoli.
- The right main bronchus is wider and angles more directly downward compared to the left, placing the right lung as more vulnerable to aspirated foreign bodies.
- The characteristics of increasing branching and decreasing tube diameter throughout the bronchial tree are key to understanding respiratory physiology.
Respiratory Airway
- The respiratory bronchioles connect conducting airways to gas exchange units (alveoli).
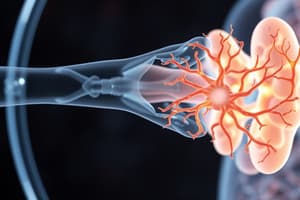
Alveoli
- Alveoli are the primary site of gas exchange in the lungs. Hundreds of millions of clustered alveoli give enormous surface area for gas diffusion.
- Alveolar walls contain specialized cells (type I and type II alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages). Each terminal respiratory unit contains approximately 100 alveolar ducts and 2000 alveoli.
- Type I cells form the majority of the alveolar wall and are pivotal to forming the gas-blood barrier.
Alveolar-Capillary Membrane
- The alveolar-capillary membrane is a very thin structure separating the alveoli from the capillaries, enabling efficient gas exchange. Its thinness facilitates the rapid transfer of both oxygen and carbon dioxide across its membrane.
- Factors like thickness of the membrane and the surface area affect the rate of diffusion.
Pulmonary Circulation
- The pulmonary circulatory system begins at the pulmonary artery and ends at the pulmonary veins.
- Venous blood from the right heart enters the pulmonary artery, which branches into smaller vessels leading to the alveolar capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
- After gas exchange, oxygenated blood returns to the left heart via the pulmonary veins.
Work of Breathing
- The work of breathing is the amount of effort required to overcome the lung's elastic and resistive properties aided by the muscles of inhalation and exhalation to achieve the necessary mechanical actions.
- Lung recoil, chest wall compliance, and surface tension are key elastic determinants of the work of breathing.
- Airway resistance and the presence of pathologies are key in influencing the work of breathing.
- During normal quiet breathing, the work required is relatively low (less than 1% to 2%). However, the work load increases during heavier work or presence of pathologies.
Pulmonary Volumes and Capacities
- Measures of the volume of air that can be exchanged throughout varying respiratory actions and stages.
- Key measurements such as tidal volume (amount of air exchanged during a normal breath), inspiratory reserve volume (maximal inspiration after a normal breath), expiratory reserve volume (maximal expiration after a normal breath), and residual volume (air remaining after a maximal expiration) dictate the lungs' capacity for breathing.
Respiration
- Respiration encompasses external respiration (gas exchange in the lungs) and internal respiration (gas exchange at the tissue level).
- Diffusion is the primary mechanism of gas transport, moving gases across the thin alveolar-capillary membrane down a pressure gradient.
- Factors influencing the diffusion rate include the membrane's thickness and surface area, and the diffusion coefficient of each gas.
Gas Transport
- Gas transport refers to the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues.
- The blood stream moves these gases throughout the body.
- At the tissue level, oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across membranes and move into and out of cells as needed.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.